Central place of finance in business planning
When there is significant experience in business planning, there is a strong feeling of a special professional orientation of the document - the business plan of the project. Marketing and technical and technological innovation play a guiding role in this process, but, undoubtedly, the financial section of the business plan is of key, central, end-to-end importance. And this aspect literally permeates the entire process of planning a new project or a whole line of activity. In this material, we will talk about the financial plan as a large block of the business plan.
Approaches of different methods
Immediately I want to "stake out" the universal context of business planning from the position that the direction of the project plan does not matter much. Indeed, whether an entrepreneur forms a business from scratch or the company is organized as a continuous series of large projects with a product or regional focus. The approach is similar in both cases. But the existing business has more chances to create a successful model due to the more likely presence of The Best Practice. But, again, it's how you look.
Nordström's funky business is already here, Nassim Taleb's "black swans" are "sailing" more and more often. The life cycle of products and business ideas is getting shorter. You don’t have to go far, take, for example, the restaurant business or the gadget manufacturing business. Everything is very short lived. Does the role of business plans increase in such conditions? Yes and no. Trust in market and technology forecasts in projects is increasingly devalued. And the need for dynamic multivariate financial modeling is growing.
It should be clearly understood that the business plan of the project is a means of persuading an investor or a lender with financial and analytical arguments, no matter what form he takes. An interested person may be the owner of a design company, a strategic investor, a state representative managing budget funds. Sometimes the counterparty acts as a collective body, for example, the credit committee of a credit institution. The purpose of the financial part of the plan is to have an effective persuasive impact on the object of communications according to two theses:
- financial calculation and investment analysis performed professionally;
- calculation options take into account the main risks of the project.
Professionalism usually manifests itself in taking into account all industry, corporate, accounting, fiscal and other nuances of the project, as well as in following the standards of the applied methodology. The business planning methodology is usually imposed by the person with the strongest negotiating position, to whom the project manager has approached in the hope of obtaining support or approval for the project. The options for the composition of the main document used in different methods are discussed by us in an article on the topic. All of them focus on the financial part of the plan.
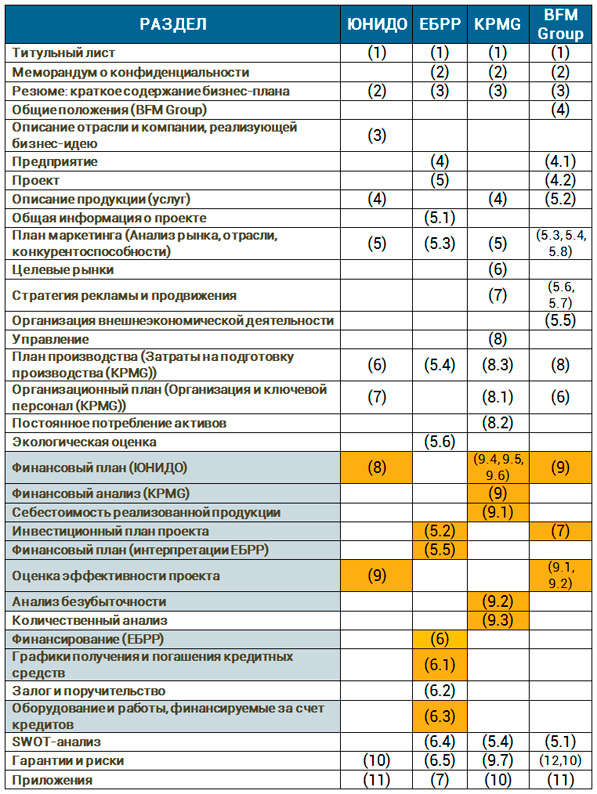
Comparison of the composition of the financial block in the four main methods of business planning
Using the comparison table above, it can be concluded that the EBRD business plan methodological model provides the most detailed financial planning. This is quite natural, since a significant part of the rationale is occupied by the issue of security of the credit resources planned in the project. The numbers in brackets indicate the serial numbers of the sequence of sections and subsections of the document. It is worth noting that in almost all recommendations, the calculation of the financial plan of the project is supplemented by an analysis of the effectiveness of investments, which is called differently, but the essence is the same. The financial part has three blocking vectors.
- From the standpoint of the financial management functions performed, the section is divided into a factual set of financial reports, a planning part, an analytical block, and the calculation of a project simulation.
- From the point of view of financial information localization, the section can be divided into the financial plan of a separate project and a plan integrated into the corporate financial model of the company's activities for the entire project period.
- In terms of the type of financial plan of the project or report on its execution.
The last section division vector means that we subtract from it:
- profit and loss plan, cash flow plan and balance sheet forecast, which are sometimes called budgets, but the essence of this does not change;
- reports of the same name: profit and loss, movement of DS and balance sheet.
Income and expense planning
As already noted, the planning part of the financial section of the business plan consists of three documents that arise in connection with the implementation of the project, the first of which is the profit and loss plan. The form of this document completely coincides with the form according to OKUD 0710002, approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation (profit and loss statement is presented below). The purpose of this plan is to provide an opportunity for the investor to be convinced of the profitability of the project developer.
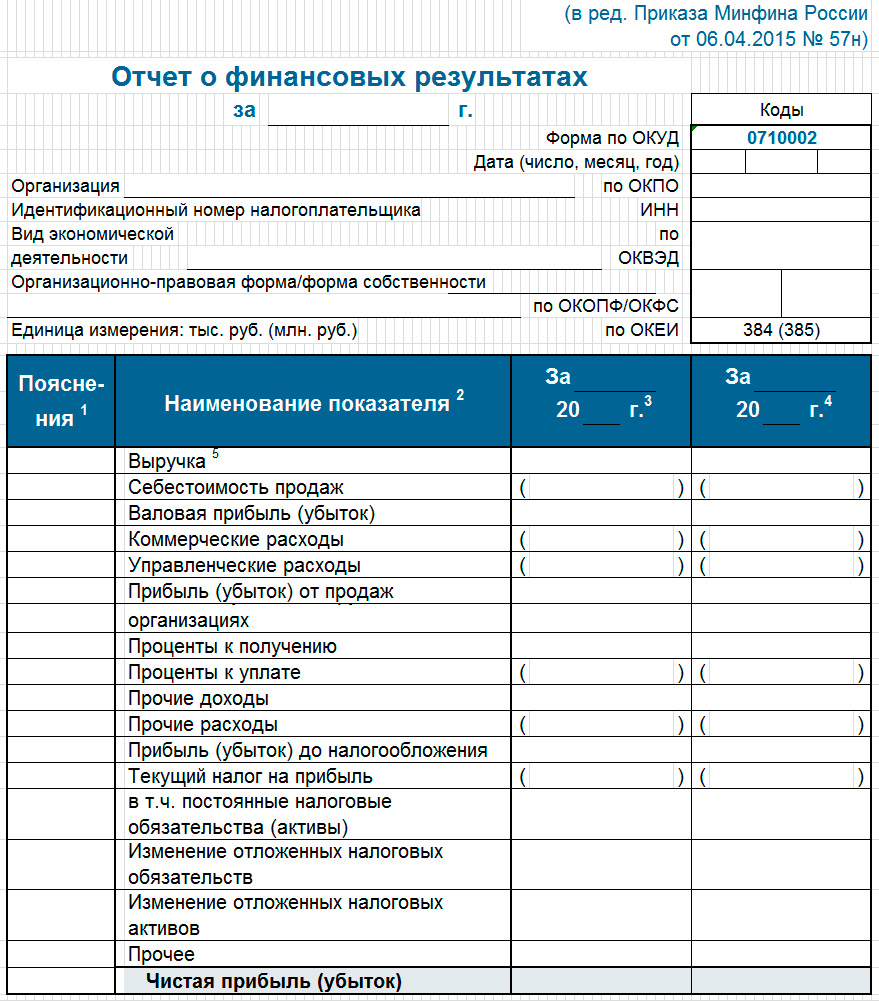
(click to enlarge)
The calculation of the main values for filling out the document is carried out both as a result of transferring data from other plans, and by special calculations, which will be discussed below. When planning, the accrual method is used, taking into account not only the possibilities of market profitability, prices for the main expenditure items, but also the features of the company's accounting policy. To build a profit and loss plan, you will need to involve the following information.
- Planned gross revenue and sales loss plan by month for the first two years of the project. In subsequent periods (years) of the project, the financial model allows you to switch to longer planning periods (quarter, year). The revenue is taken from the sales plan data, which is of a contractual nature. The credit policy is not taken into account, and if the contracts do not provide for a different procedure, the revenue is formed in the planned values of the full shipment (closing of the acceptance certificates) by calculation periods.
- Part of the costs as part of variable costs for the production and release of project products (rendering services) is imported from the cost plan. This type of expenditure is directly dependent on the production plan for the billing periods (year, quarter, month).
- Part of the costs as part of semi-fixed costs for production and management: operating costs (main and auxiliary production), administrative (general) expenses, distribution costs (sales expenses). At the same time, we must not forget that depreciation, interest on a loan payable and taxes accrued also belong to semi-fixed expenses.
In my opinion, the third block of information is formed very laboriously. On the one hand, the accrual method allows you to ignore the terms of a likely commercial loan from suppliers and contractors. And we can assume that as soon as materials, raw materials not related to production volumes, electricity, services of a regular nature are received, the costs are entered into the model. On the other hand, there are a lot of factors that must be taken into account. Among them:
- the above depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets (amortization), the amounts of which depend on the accrual policy (in a linear or non-linear way);
- accounting for deferred expenses (expenses for licensed software, product certification, VHI, etc.);
- the need to form reserves for future expenses and payments (accumulation of funds for repairs, seasonal work, vacation pay, etc.);
- the applicable tax and legal model of activity, the choice of which greatly affects not only the size of fixed, but also variable costs).
Balance Sheet Forecast
The balance sheet or statement, which is officially referred to as the balance sheet, is a planning and reporting document of a completely different nature than the profit and loss plan (report). If the latter reflects information on the accrual of income and expenses, the formation of the financial result within the billing period, that is, the dynamics of the corresponding values \u200b\u200bis shown, then the balance sheet is a document reflecting statics, a state. It is not for nothing that they say about the asset of the balance sheet that it demonstrates the state of funds and their placement, but about the liability - as the state of the company's sources of funds.
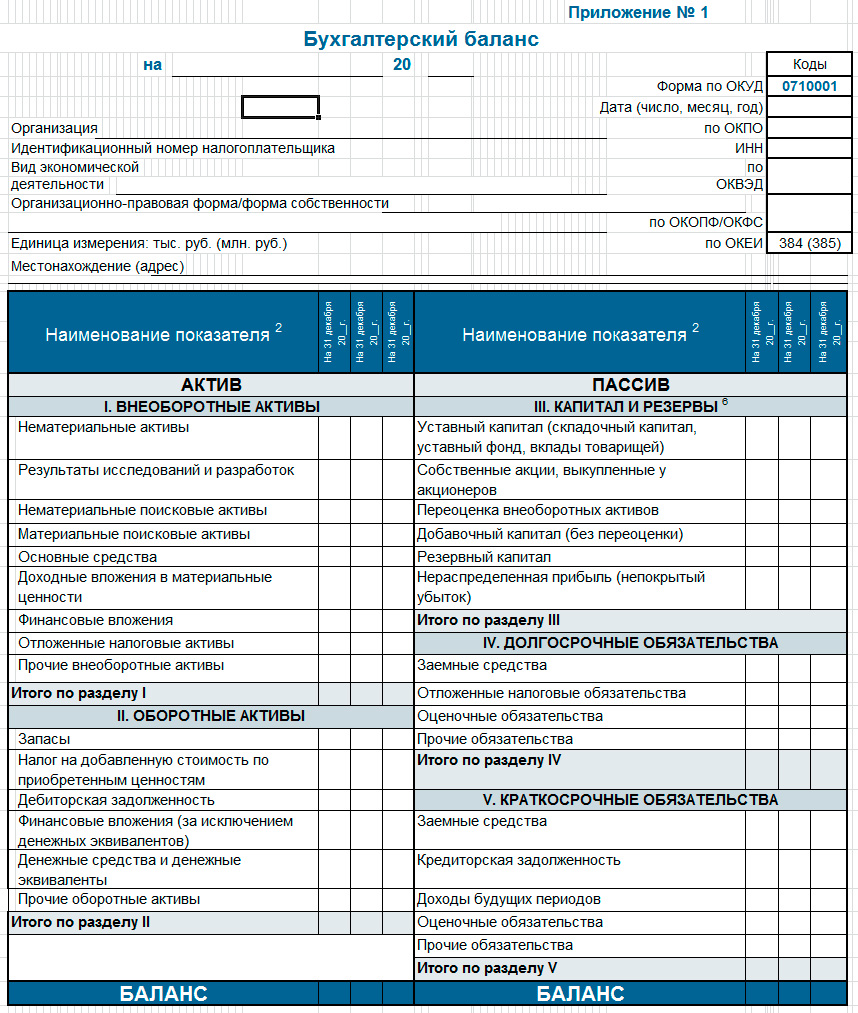
(click to enlarge)
Above is an adapted form of the balance sheet for forecasting purposes as part of the preparation of the business plan of the project. The purpose of the balance sheet is to show stakeholders whether or not the financial condition of the company (liquidity, independence, solvency) is stable or not, which intends to implement the project in a certain period of time. The company's balance sheet planning is usually performed on December 31 of each accounting year, during the entire period of the project. This does not at all cancel the withdrawal of balances of assets and liabilities on intermediate dates. In addition, to work on the forecast, you need a starting balance if the project does not imply a business from scratch.
For lenders and investors who are evaluating the possibilities of their participation, the forecast balance is no less, and sometimes even more important, than the profit and loss plan. If the enterprise is operating, I recommend planning the balance sheet, and then the DS movement plan according to a certain algorithm.
Step 1 . To study the statistics of balances of short-term liabilities (short-term obligations) and establish standard values of non-reducing balances for the articles of the section, taking into account the planned growth in turnover. I recommend starting with the wage arrears standard, then moving on to debt to suppliers and contractors, to short-term debt obligations, etc. This is the first iteration of working with Section V.
Step 2. Perform planning of balances of current (current) assets. It is better to start with the normalization of the level of stocks, for a guideline, you should use the statistics of the dynamics of the turnover of working capital for different groups of goods and materials. Extrapolating the obtained values to the growth of production volumes, develop the residue standards for all estimated dates of the project implementation. The next step is to determine the amount of capital investment in stocks.
Step 3 Continue planning for Section II of the balance sheet. Perform normalization of balances of receivables. Calculate the value of the coefficient of diversion of current assets into accounts receivable for the last 3 years. Refine the company's credit policy and build a forecast for the remote control for the entire period of the project.
Step 4 Based on liquidity indicators, refine the parameters of sections V and II of the balance sheet in several iterations, maneuvering through the most mobile articles of these sections in order to prevent the failure of current and absolute liquidity.
Step 5 Using , perform the first iteration of forecasting long-term liabilities, including additional equity from investors and debt capital. When building a new financial capital structure, rely on a functional financial strategy for the business.
Step 6 Having calculated the effect of financial leverage, plan the optimal amount of borrowed capital. Return to the Profit and Loss Plan, adjust the values of the interest for the loan payable. Further steps of the algorithm are transferred to the motion planning of the DS and the block of dynamic simulation.
Cash Flow Forecast and Dynamic Modeling
It would be most correct if the cash flow plan is drawn up at the end after the profit and loss plan and the balance sheet. It is recommended to consider it by two methods: indirect and then direct. This is where the two previous planning documents help. The purpose of Cash Flow is to demonstrate the ability of the company to implement the project without cash gaps in the logic that allows to obtain satisfactory results of the investment analysis. Unlike the balance sheet, which shows the balance of assets, liabilities and their structure, the cash flow plan must convince of the sufficiency of cash flows and their balances. Below is a typical form of the corresponding report (form 0710004).
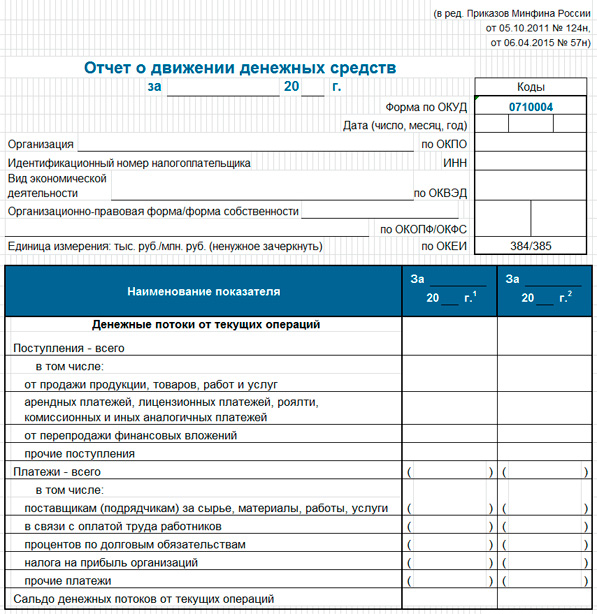
(click to enlarge)
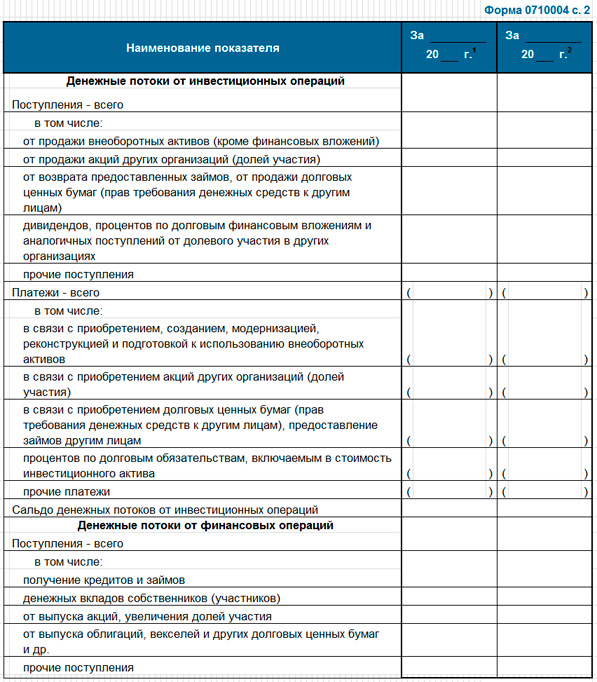
Page 2
(click to enlarge)
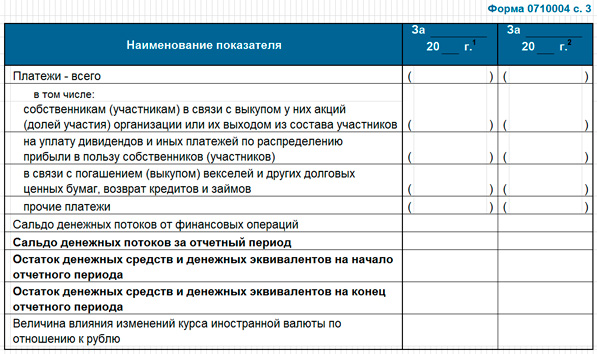
Page 3
(click to enlarge)
The composition, logic and example of constructing a cash flow statement is given in an article on the topic, so I don’t see the point in a methodological review. I would like to continue the algorithm that was started in the previous section, since it is of some value.
Step 7. Using an indirect method, form an enlarged Cash Flow of the company, and then isolate a plan of cash flows from it in relation to the turnover generated by the project.
Step 8 Break down the DS movement plan obtained at the previous step to item-by-item detailing, starting with the operational CF. Pay attention to the differences between receipts and accruals of revenue. Display the values of disposals of DS in the order of settlements with suppliers and contractors, in contrast to the accrual of production and distribution costs.
Step 9 Using the investment plan and the sale of fixed assets, at the end of operation, detail the investment CF.
Step 10 Using the first draft of the borrowing plan, perform financial CF planning, assuming that the capital structure will be consistent with the optimal results in terms of the effect of financial leverage. Check NCF.
Step 11 Based on the detailed Cash Flow and capital structure, complete the refinement of the balance sheet items (Sections I, III and IV) and the profit and loss plan. Calculate indicators of profitability, business activity, financial independence and sustainability. If the parameters deviate from the normative values, make corrections according to the capital structure.
Step 12. Repeat the cycle of Steps 1 through 11 for each billing period. Calculate the economic efficiency of the project and evaluate it based on traditional investment analysis parameters (NPV, PI, DPP, IRR, MIRR, ARR).
Step 13 Carry out simulation modeling for at least three scenarios: optimistic, pessimistic, balanced. Take sales volumes, key cost items, inflation rate and other risky positions as factors of scenario dynamics.
Conclusion
They say that business planning is a technology. Probably yes, technology. But for me, if we consider true business planning, it is in many ways an art, not without the pangs of creativity. I am convinced that the planning of new directions and products should be carried out by highly qualified economists at the level of the CFO or just one step below. The work is very labor intensive. Keeping the whole model in mind and taking into account many factors can be incredibly difficult.
It is clear that it is unbelievable to manually execute a business plan at a good level even for an average operating enterprise without automation tools. This is where packages such as Project Expert, or at least a well-programmed MS Excel, should help. At the same time, I strongly recommend that financiers consciously go to the trouble and at least once do all the calculations themselves with paper, pencil, calculator and a standard spreadsheet editor. Let there be mistakes, let there be inaccuracies. I am sure that such experience will give a powerful impetus to the development of a professional and the level of persuasiveness of calculated arguments.
 Discounted payback period
Discounted payback period Methodological aspects of project management
Methodological aspects of project management Scrum Development Methodology
Scrum Development Methodology