Economic, organizational, social, legal and technological essence of ur. The system of protection of unemployed citizens is a complex of economic, organizational and legal forms and methods. A complex of legal organizational economic
PREVENTION OF EMERGENCY SITUATION complex of legal, organizational, economic, engineering and technical, environmental protection, sanitation
complex of legal, organizational, economic,
engineering and technical, environmental protection, sanitary-hygienic, sanitary-epidemiological and
special events aimed at
organization of monitoring and control over the condition
environment and potentially dangerous objects,
prediction and prevention of occurrence
sources of emergency, as well as
reducing the scope of possible emergency
situation and preparation for its elimination.
Ways and means of protection against emergency situations
Protection methods- ways to achieve
protection objectives
person from
dangerous (striking
x) factors
emergency
situations.
Remedies -
what is achieved
ways to protect against
emergency
situations. The monitoring system is open
information system, priorities
functioning of which is to protect
vital environmental interests
human and society, preservation of natural
ecosystems; prevention of crisis
changes in ecological status
environment and prevention
environmental emergencies.
The monitoring system is aimed at:
ecological
- increasing the level of study and knowledge about
condition
the environment;
- improving the efficiency and quality of information services
users at all levels;
- improving the quality of justification of environmental protection measures and
the effectiveness of their implementation;
- promoting the development of international cooperation in the field of protection
environment, rational use of natural resources and
environmental safety.
The main tasks of the subjects of the monitoring system are:
- long-term systematic monitoring of the state of the environment
Wednesday;
- analysis of the ecological state of the environment and forecasting its changes; - information and analytical support for the adoption of re
- analysis of the ecological state of the environmentenvironment and forecasting its changes;
- information and analytical support
decision-making in the field of environmental protection
environment, rational use of natural
resources and environmental safety;
- information service of bodies
state authorities, local authorities
self-government, as well as ensuring
environmental information of the population of the country and
international organizations.
.
Emergency Risk Management - Based on Risk Analysispurposeful activity of state
authorities and administration at all levels, local authorities
self-government, organizations, enterprises and citizens on
implementation of the best possible system of interconnected
measures to reduce the risks of emergencies to the level that society
considers it acceptable based on the existing restrictions on
resources and time. Alerting the public about
emergency
The essence of the method:
Communicating to the population
a single signal
alerts "Attention
all "
Informing
population about
emergency
What is used
for achievement
goals:
Sirens,
production and
traffic horns
Mass media
information and communication
Evacuation
Forcedmovement of people to
safe
places (areas)
Municipal
or personal
transport
10. Shelter
Occupation andusage
special or
adapted
protective
structures
Vaults, basements,
basement
premises of buildings,
protozoa
shelters, elements
relief
terrain
11. Use of satellites
Applicationindividual
means of protection
skin, organs
breathing,
medical
funds
Protective clothing and
shoes,
gas masks,
respirators,
cotton-gauze
bandages, first aid kits
individual
12. Search and rescue operations
Performancesearch and
rescuing people in
lesions
Forces and means
search -
rescue
formations
13. Emergency rescue and recovery work
Recoveryobjects
production
and social
infrastructure
Forces and means
emergency
formations
Ministry of Emergency Situations and local
authorities,
organizations
14. Medical assistance
Rendering first,medical and
specialized
oh medical
help
victims in
extraordinary
situations
Forces and means
medical
service
15. Humanitarian assistance
Securityaffected in
Emergency to all
necessary for
normal
life activity
ti
Food,
clothes,
medicines,
cash
funds,
temporary housing ...
16. Maintenance of law and order
Securitypublic
order in zones
Emergencies, on the tracks and in
evacuation zones
Subdivisions of the Ministry of Internal Affairs
Ukraine, local
authorities,
public
organizations
17. Education of the population on protection from emergencies
Study withpopulation
various
ways and
means of protection
from emergencies
Means of education
at the place of work,
study,
residence in
GZ system
18. Prevention of emergencies
Preventivemeasures for
warning or
decline
probabilities
dangerous consequences
Emergency
Forces and means in
depending on the type
Emergency. Held
well in advance in
everyday
activities
Lecture 1.
Topic 1 : ENTERPRISE IN THE SYSTEM MARKET RELATIONS
В1: Improving the organization of production activities of the enterprise
The organizational activity of the enterprise covers a complex of tasks of an organizational, technical and economic nature, provides for the choice and justification of the production structure of the enterprise, organizational forms and economic methods of management production, In progress organizational activity, the necessary production ties are established and conditions are created that ensure the interaction on an economic basis of all elements of the production process and internal divisions. The production activity of employees is organized on the basis of the division of labor, responsibilities within a certain hierarchical structure. The rational organization of the production activity of the enterprise ensures the coordination and optimization in time and space of all production resources, the influence of organizational factors to achieve the goals of the enterprise - to meet the needs of consumers, ensure the superiority and competitiveness of the enterprise and, ultimately, economic growth.
Improving the organization of production activities of enterprises is one of the most important areas of enterprise reform.
When organizing production processes, people, tools and objects of labor are combined to ensure a rational combination in time and space of the main, auxiliary and service processes. The basis is the principles of rational organization of the production process. Parts of the production process are combined in the space and the kind of production structure that needs to be changed. It should be dynamic depending on the changing conditions of production activities. The main factors in the development of production structures are optimization of the number and size of production units of the enterprise; ensuring a rational balance between the main, auxiliary and service units; raising the technical level of production.
To ensure the rational interaction of all elements of the production process and streamline the work performed in time and space, it is necessary to form the production cycle of the product. Reducing the duration of the production cycle is achieved by reducing the time of the working period and interruptions in the production process, which, in turn, is due to the improvement of equipment and technology, an increase in the level of organization of production.
In the context of the transition to market relations, requiring a flexible response to changes in consumer demand for a particular type of product, the role of operational management of production increases, the main disadvantages of which are due to the inconsistency of the equipment throughput in sections and workshops, the emergence of "bottlenecks", unscheduled equipment downtime; shortcomings in the organization of production, labor, planning; interruptions in material and technical supplies; low level of labor and production discipline.
Stage 2
The solution of the problems of operational management of production (PMO) is associated with the implementation of the entire complex of works for each of the elements of the PMO. By operational schedulingproduction - it is differentiation and bringing control tasks to the immediate performers; coordination of the work of workshops, sections of the enterprise and justification of their need for resources (materials, components, equipment, tools); formation of coordinated plans for the activities of sections, teams, individual workers for the production of blanks, parts of products. By operational accounting (control) of the stateproduction - this is the provision of reliable, timely
information; accounting for the movement of parts, assembly units along the technological route (by workshops, sections, workplaces), the movement of materials and components in the warehouses of the enterprise; organization of storage and accounting of finished parts and assembly units; accounting for the sale of products and the fulfillment of the delivery plan under contracts. Analysis of production progress provides for the determination of the deviation of the fulfillment of tasks in terms of the number and timing of the release of blanks, parts, products; identification of shortages of materials, components, causes and culprits of production downtime. Operational regulation and coordination of production involves taking measures to prevent and eliminate deviations from the plan and downtime during production; coordination of the current work of interconnected production units; management of the preparation of the necessary resources to fulfill the production schedules and shift-daily tasks.
Highly efficient enterprises are enterprises capable of innovation and development. The development and mastering of the production of new products involves the implementation of a set of processes of a scientific, technical and organizational-economic nature. In this case, basic goals - creation of new products of a given technical level and quality; reduction of costs and duration of the cycle of creation, production and development of new products. Main problem, requiring a solution - extremely long duration of the preparation cycle and mastering the release of new types of products. Basic measures to reduce the preparation time for production - reducing the time of the working period by taking measures to reduce labor costs; reducing the time of breaks in the process of preparing for production, the introduction of a parallel-combined method of organizing work. The acceleration of the development of new products is facilitated by the participation of developers, manufacturers and consumers in the design and production of new products, the readiness of production for development, the ability to quickly restructure it to release new products with minimal loss of time and money, and coordination of work on the preparation of production.
Development of innovative activities carried out in the following areas:
Organization of examinations, implementation and replication of inventions, know-how, scientific and technical developments, scientific works, discoveries, industrial designs, trademarks, creation of prototypes, conducting pilot tests, creation of new samples of equipment, technology and scientific and technical documentation, preparation of production ;
Carrying out research, design, development, marketing research in order to create samples of new equipment and technologies;
Patent and licensing activity.
The rational organization of innovative activity involves the choice of the optimal organizational form: scientific institutions, design organization, rationalization and invention bureaus, problem commissions, temporary teams, scientific unions and foundations, including investment associations, consortia; small innovative enterprises; technopark structures; program-targeted and technopark organization of innovative activities at small enterprises.
The efficiency of manufacturing and production of competitive products with minimal costs and uninterrupted production and economic activities of the enterprise are ensured not only by a rational organization of technological processes, but also by a high level of maintenance of the main production and all divisions of the production infrastructure.
Enterprise infrastructure is a complex of departments and services, the main task of which is to ensure the normal functioning (without interruptions and stops) of the main production and all areas of the enterprise.
For most enterprises, the subdivisions of auxiliary production and the entire system of maintenance are repair, tool, energy, transport, storage and container facilities.
The enterprise maintenance system must meet the following requirements: provide conditions for the release of competitive products at minimum costs; to carry out technical, economic and organizational regulation of service processes; be of a preventive nature; to provide flexibility, continuity and minimum restructuring during the transition of the main production to the release of new products.
Thus, subsidiary farms require a high organization, adequate to the level of organization of the main production.
Underestimation of the role of maintenance, shortcomings in its organization led to a number of problems. There are large irrational costs of enterprises associated with the implementation of the entire range of works but technical maintenance by the enterprise itself. The costs of manual labor and the cost of products of the production infrastructure units are significant. Low quality products and services. There is a gap in the technical and organizational levels of the main and auxiliary industries, the number of auxiliary workers is high, and their qualification level is insufficient. There are significant shortcomings in the rationing and planning of the activities of the production infrastructure units. The irrational organization of the activities of the auxiliary production is one of the reasons for the lack of spare parts in production, the performance of the work of the main production by auxiliary shops.
Improvement of the activities of the production infrastructure units is associated with the implementation of part of the work by third-party organizations; centralization and concentration of homogeneous service processes and their specialization, which creates conditions for the use of advanced equipment, scientific methods of organizing production and labor, high-performance technology. There is a need for mechanization and automation of technological processes, rationalization of management, improvement of the regulatory framework, reasonable planning of the number of employees, development and implementation of technically sound norms of time and measures for the scientific organization of labor, the use of incentive wage systems, the creation of integrated technology, and centralized production of spare parts.
The rational organization of the work of auxiliary industries is the most important condition for stabilizing the main production, increasing the volume of output. To eliminate the above disadvantages, it is necessary to study and implement the basic theoretical provisions and practical experience of the rational organization of the production activity of the enterprise.
Question 2: Organizational and legal forms of enterprises
There is a great variety of enterprises in the country's economy. They differ from each other, firstly, in size. The number of people employed is usually used as indicators of the size of an enterprise; the number of products manufactured or services rendered; the amount of capital. Second, businesses differ in the variety of products they produce or the services they provide. Third, businesses differ in the way they own property.
However, the most important feature of the classification of an economic entity in a market economy is the division of economic entities on the basis of organizational and legal forms of enterprises.
The ongoing economic reform in the country is impossible without appropriate organizational and legal structures, which are regulated by the state through the Civil Code and special laws.
The civil code introduced concepts such as "commercial organization" and "non-profit organization". A commercial organization pursues making profit as the main goal of its activities. A non-profit organization does not pursue this goal, and if it makes a profit, then the latter is not distributed among the participants in the enterprise.
Entrepreneurial activity, according to Russian legislation (in particular, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), activities are recognized that meet such characteristics as:
independence of the entrepreneur's activities at his own risk;
the focus of activity on the systematic receipt of profit from the use of property, the sale of goods, the performance of work or the provision of services;
compulsory registration of a person carrying out activities as an entrepreneur, in accordance with the procedure established by law.
Entrepreneurial activity, according to Russian legislation, can be carried out:
with the formation of a legal entity - a commercial organization;
without the formation of a legal entity - individual entrepreneurship.
Forms of entrepreneurship varied and typical for both legal entities and individuals. Distinguish between individual, collective and corporate forms of entrepreneurship.
If a citizen is registered as an entrepreneur without forming a legal entity, then he is considered individual entrepreneur from the moment of its state registration in this capacity. Moreover, if entrepreneurial activity is carried out without the involvement of hired labor, then this is considered individual labor activity.
If a citizen hires someone to engage in his chosen type of activity, then this is considered as educationenterprises.
Individual entrepreneurship is associated with sole ownership of property in order to obtain personal income or profit.
Individual entrepreneurs, acting on the market on an equal basis with legal entities, have the right to engage in production, provision of services, trade, trade and procurement, innovation, consulting and other economic activities not prohibited by law.
An entrepreneur can have a bank account, his own trademark, use a bank loan. To achieve the main goal of any entrepreneurship - making a profit, an individual entrepreneur has the right to conclude civil law contracts for the performance of various transactions and to attract employees under labor contracts. This form of entrepreneurial activity is associated with the simplest financial and tax accounting.
An individual entrepreneur is a person who conducts business at his own expense and on his own behalf, is personally involved in business management and bears personal responsibility, independently makes decisions and bears the risk of losses in the event of bankruptcy. An individual entrepreneur who is unable to satisfy the claims of creditors related to his entrepreneurial activities may be declared insolvent (bankrupt) by a court decision.
Advantages individual entrepreneurship are as follows:
Minimum regulation by the state;
Simplified procedure for registration, tax and accounting and reporting;
Customers are personally known to the entrepreneur and, therefore, he can quickly respond to changes in their needs and tastes;
Flexibility and efficiency in decision making;
Having an incentive to work hard (works for oneself). TO disadvantages individual entrepreneurship include:
Full property (subsidiary) responsibility of the entrepreneur;
Limited scope of business within the framework of capital (limited by personal funds and loan opportunities);
Weak competitiveness, strong dependence on the external environment.
The main subjects of entrepreneurial activity are legal entities. Entity - an organization characterized by the following features:
Has separate property (in ownership, in economic management, in operational management);
Responsible for its obligations with property;
Can acquire property and personal non-property rights on its own behalf;
May carry responsibilities;
Can be a plaintiff and a defendant in court;
Has an independent balance sheet or estimate.
Any organization, in order to be recognized as a legal entity, in addition to formal criteria (such as the mandatory registration of constituent documents) must, in the aggregate, have the above characteristics.
The transition from a state to a market organization of the economy means that the main distinguishing feature of a legal entity, instead of organizational unity (a collectively organized team), becomes a separate "personified" property.
It is, of course, not property that manages, but people, but it is the presence of property that allows, firstly, to reduce the entrepreneurial risk of the merchants who created the enterprise, since not they, but a legal entity, is responsible for the debts of the enterprise; secondly, it guarantees the satisfaction of possible claims of creditors.
Property can belong to a legal entity on the basis of ownership or on a limited property right - economic management or operational management. This means that the enterprise can no longer operate solely on the basis of property obtained under a lease agreement, property lease or on the basis of borrowed funds. The contributions of the founders of legal entities to its authorized capital (authorized capital, pooled capital) are required.
An enterprise that owns property is responsible for its obligations.
A legal entity has the right to conclude contracts on its own behalf (purchase and sale, delivery, transportation, loan, lease, contract, etc.).
Branches and representative offices endowed with the property of the legal entities that created them have a balance sheet and a sub-account in the bank, but are not entitled to conclude contracts on their own behalf. The heads of branches and representative offices act exclusively on behalf of and under the power of attorney of the legal entities that created them.
Depending on the goals of their activities, legal entities are divided into commercial and non-commercial. The purpose of the activity commercial enterprises is making a profit, non-profit- the achievement of social results, the implementation of charitable activities, management, cultural, educational functions, etc. Non-profit organizations have the right to engage in entrepreneurial activities in order to achieve their statutory goals.
Entrepreneurial activity is carried out in a certain organizational form. Under organizational and legalform This implies a complex of legal, legal, economic, economic norms that determine the nature, conditions, methods of forming relations between the owners of commercial organizations, as well as between commercial organizations and other business entities external to it and public authorities.
The participation of the Russian state in business entities is one of the ways for the state, represented by the Government of the Russian Federation and regional administrations, as well as local authorities, to implement the powers of the owner of the property in order to replenish the corresponding budget, to solve other economic and social problems common to the country, region, territories.
Currently, we can talk about the main forms of participation in economic entities: the creation unitary enterprise , the property of which belongs to him on the basis of the right of economic management or operational management.
The organizational and legal form of a unitary enterprise owes its origin and formation to the peculiarities of the Soviet economic turnover. The emergence of non-proprietor legal entities in the economic turnover was caused by the fact that the state, as a de facto monopoly owner of property and means of production, could not effectively deal with them directly. Therefore, the state created enterprises, retaining the ownership right to their property and endowing them with special property rights - the right of economic management or the right of operational management.
The difference between the rights of economic management and operational management consists in the content and volume of powers that enterprises receive from the owner for the property assigned to them. The right of economic management is broader than the right of operational management, which is associated with the possibility of additional (subsidiary) liability of the founder-owner.
Unitary enterprise - this is a state or municipal enterprise that is not endowed with the ownership right to the property assigned to it by the owner. Unitary enterprises belong to the founder-owner entirely, without dividing their property (or part of it) into any contributions (shares, shares), including between employees. Property is indivisible, which is directly emphasized by the term "unitary" in translation from Latin - unity.
The owner of a unitary enterprise (represented by the relevant body of the authorized manager of property) for the purpose of economic incentives for members of the labor collective can create various kinds of "profit-sharing funds". In this case, employees acquire ownership of funds or other property received by them from these funds in accordance with the rules for their distribution.
A prerequisite for the creation of a unitary enterprise is that it has a statutory fund. The size and procedure for its formation are reflected in the charter, which is the only constituent document.
Unlike most other commercial organizations, a unitary enterprise has a target legal capacity, not a general one. The scope and nature of this legal capacity must be expressly defined in the articles of association by the founding owner.
For its obligations to third parties (counterparties), a unitary enterprise is responsible for all that belongs to it on the basis of the right of economic management or operational management of property. The Civil Code protects the rights of a unitary enterprise as the owner of limited property rights to the property assigned to it both from the encroachments of third parties and from the founder-owner.
In the process of implementing the state economic policy, due to various reasons, the transfer of a unitary enterprise from one public owner to another is possible, i.e. change of ownership.
A small number of state-owned enterprises, which are federal property and operate under strict state control, have the status state-owned enterprises. The need to create this kind of commercial legal entities is due to the presence of organizations acting as production, on behalf of the state as a whole. Such enterprises include state production associations, communications enterprises, some defense enterprises, etc.
In terms of property, the position of a state enterprise is partly similar to that of a state (state budget) institution. But there are significant differences: the institution is financed by the owner according to the estimate, and the state-owned enterprise has an independent balance sheet and itself receives income from the results of its activities.
Sources formation of property and financial resources of state-owned enterprises are:
Property transferred to him by the decision of the Government of the Russian Federation for the conduct of the main activities;
Cash and other funds received from the sale of products (works, services) produced in accordance with a government order;
Funds allocated from the federal budget and (or) federal extra-budgetary funds;
Part of the income received as a result of conducting independent economic activities (the charter of a particular plant indicates which part of the income is).
Topics of reports:
Production cooperative
Business partnerships
Business companies
Financial and industrial groups, holding companies, non-profit organizations
Coursework >> Botany and Agriculture
Their use ... 21 3. Organization production milk 3.1. The place of the industry in the economy farms ………………………………… ..... 23 3.2 Analysis of gross ... the organization production and management. The crisis state of our the economy accompanied by a decrease ...
The economic mechanism of the enterprise's functioning is a combination of organizational and economic forms and methods of influencing economic and financial activities to achieve the goals set, to ensure sustainable effective development.
The incentive for the activities of people and organizations in a market economy is economic interest, which is expressed in economic benefit, which takes various forms. For the owner, the entrepreneur, the benefit consists in increasing the market value of the enterprise, making a profit, for the employee - in timely and reasonable remuneration for labor, for members of non-profit organizations - in meeting the needs for benefits, the receipt of which is the purpose of creating these organizations. The economic mechanism of the enterprise's functioning should ensure a combination of the interests of all participants in economic activity - owners, managers of enterprises, employees.
The economic mechanism of the enterprise's functioning should be focused on achieving strategic development goals. The main goal of any enterprise is to ensure sustainable development, strengthening the competitive position in the market. Based on this goal, the mechanism of enterprise functioning should contribute to the solution of the following tasks:
- formation of conditions for the fullest satisfaction of customer demand for their products (services) within the selected market segment. To solve this problem, it is necessary to study the market, develop an effective product and price policy;
- ensuring the efficiency of economic and financial activities. This task is solved on the basis of minimizing the costs of labor, material, financial resources for the organization of production processes, for the implementation of commercial operations, the performance of enterprise management functions;
- maximizing the amount of profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise, and ensuring its efficient use. This problem is solved on the basis of increasing the volume of the enterprise through the implementation of an effective pricing and depreciation policy, tax planning, optimization of the ratio of capitalized and consumed parts of profit;
- minimization of the level of economic risks associated with the activities of the enterprise. To solve this problem, it is necessary to effectively manage commercial, financial, investment and other risks. Minimization of risks ensures stability of development and predictability of performance results;
- ensuring a constant increase in the market value of the enterprise. This task is implemented on the basis of high investment activity, the ability of the enterprise to effectively accumulate its own financial resources to ensure the growth of assets in all their forms, to increase the financial stability of the enterprise. The growth of the market value of an enterprise is influenced by the won positions in the market, business reputation, personnel qualifications, technology of business and management.
The essence of the economic mechanism of the functioning of an enterprise is determined by its constituent links, structural elements. As part of the economic mechanism of functioning, the following main links are distinguished, presented in Figure 6.1.
Figure 6.1 - Links of the economic mechanism of functioning
enterprises
The mechanism of market regulation of the enterprise. This mechanism is clearly manifested in the market of goods and services in the context of its individual segments. Supply and demand determine the formation of prices for goods, determine for enterprises the possibility of finding a new market niche or expanding the volume of activities within the existing market segment. Under the influence of market conditions, a system of economic relations with suppliers of raw materials and buyers of finished products is being formed. In addition, the activities of enterprises are associated with the manifestation of a market regulation mechanism in the financial market, the market for factors of production, and the labor market. Thus, supply and demand in the financial market affect the formation of the interest rate, determine the availability of credit resources, and reveal the average rate of return on capital. Supply and demand in the labor market affect the formation of workers' wages.
The market mechanism encourages enterprises to be guided by commercial calculation in making management decisions. Commercial settlement- This is a set of principles for justifying the economic feasibility of individual operations and the entire entrepreneurial business (creating an enterprise, purchasing equipment, completing a transaction). The main principles of commercial calculation are cost recovery, profitability, maintaining its place in the market, ensuring the competitiveness of the enterprise.
The mechanism of state regulation of the enterprise. The tasks of state regulation of the activities of enterprises are:
- ensuring a balance of interests of business entities;
- regulation of the rights and obligations of market participants;
- legal protection of property relations of enterprises;
- formation of a competitive environment, development of antimonopoly policy;
- stimulation of business activity of enterprises;
- effective control of compliance by enterprises with the requirements of laws and regulations.
State regulation of the activities of enterprises is carried out by various methods:
- legal - through the creation of a legislative and regulatory framework that regulates the activities of enterprises;
- financial and economic - through the use of a system of taxes, benefits, subsidies, credit policy, customs policy, development of government programs to stimulate the development of certain industries and activities, etc .;
- social - on the basis of protecting the rights of employees of enterprises, ensuring guarantees in the field of social and labor relations, regulation of employment, remuneration, as well as on the basis of a system of technical regulation, standardization, certification of goods and services in order to protect consumer rights.
The system of laws is based on the Constitution of the Russian Federation, which enshrines the rights of citizens and regulates property relations. A special place in the legislation is occupied by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which are the starting point for the formation of individual laws and regulations in the field of regulation of various aspects of the activities of enterprises. The next level is the laws of the Russian Federation concerning the functioning of enterprises of various organizational and legal forms, regulation of certain types of activities of enterprises, their economic relations (for example, "On joint-stock companies", "On limited liability companies", "On the development of small and medium-sized enterprises in Of the Russian Federation "," On Competition and Restriction of Monopolistic Activity in Commodity Markets "," On Protection of Consumer Rights "," On Investment Activities in the Russian Federation in the Form of Capital Investments "," On Technical Regulation "," On the Basics of State Regulation of Trade activities in the Russian Federation ”, etc.). On the basis of laws, the President of the Russian Federation and the Government of the Russian Federation issue legal acts in the field of financial, banking, foreign economic, customs, investment activities, in the field of tax regulation, pricing, etc.
The practical implementation of state regulation of the activities of enterprises is carried out through federal and territorial executive bodies: the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation, the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation, the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and other government bodies within their competence.
The adoption of management decisions at the enterprise takes place within the framework of the current state laws and other regulatory legal acts, taking into account the regional aspects of the regulation of certain types of activities.
Internal mechanism for managing the activities of the enterprise. This mechanism is formed within the enterprise itself and includes the following main elements:
- the choice of the organizational and legal form of the enterprise;
- building the organizational structure of the enterprise;
- building a system of internal regulation of economic and financial activities;
- planning;
- pricing;
- quality control;
- economic incentives for labor;
- innovative activity;
- investment activity;
- organization of control of management decisions;
- use of forms of external support for economic and financial activities.
Choice of organizational and legal form is of great importance when creating an enterprise. This choice is determined by a number of general and individual factors. Such factors are: the planned volumes of economic activity and the pace of development of the enterprise in the future, the capital intensity of a particular type of activity in a particular market, the possibility of obtaining tax and other benefits by the enterprise, the available start-up capital, the proposed ways of mobilizing additional financial resources, the attitude of the entrepreneur to high economic and financial risks, etc.
Building the organizational structure of the enterprise. Organizational structure is the composition and ratio of structural units that are part of the enterprise, distinguished according to the criteria of production, organizational and management processes. The organizational structure of the enterprise includes the production and organizational structure of management, establishes the relationship between them. Building an organizational management structure should ensure flexibility and speed of decision-making and implementation, effective work of the entire enterprise.
Building a system of internal regulation of the enterprise based on the creation of regulatory documents. So, many aspects of managing the activities of an enterprise are regulated by its charter, regulations on structural divisions. The accounting policy adopted by the enterprise, the approved system of internal standards and requirements for the organization of individual business processes is of a regulatory nature. The presence of an internal mechanism for regulating certain aspects of an enterprise's activities contributes to an increase in management efficiency.
Planning- the main function of enterprise management. In modern conditions, enterprises independently set goals for themselves, determine the types, volumes of economic activity. Planning allows you to develop a strategy and tactics for the behavior of an enterprise in the market, to ensure the effective use of material, labor, financial resources, technologies, land.
Pricing at the enterprise is carried out under the influence of the market, supply and demand. However, there are very few purely competitive markets, in most cases there is monopolistic competition. Therefore, enterprises are developing a pricing policy. The price should drive sales.
High prices slow down the increase in production volumes, make it difficult to sell certain goods, while low prices can lead to losses. Correctly chosen pricing policy ensures the development of economic activities and strengthening the competitiveness of the enterprise.
Quality control presupposes a constant, systematic process of influencing the factors and conditions that ensure the high quality of the enterprise's work - the quality of goods, services, organizational processes, the quality of staff work. Of particular importance in a competitive environment is the quality of products, work performance, and services. Product quality is a combination of product properties that determine its suitability to meet certain needs in accordance with its purpose. Achieving high quality products is based on the quality of the resources used, production technologies and management.
Economic incentives for labor is an important element of performance management. Enterprises independently choose the forms and systems of remuneration, set the size of official salaries, rates of remuneration, indicators and amounts of bonuses. This solves the problem of motivating labor, increasing its productivity, harmonizing the interests of the owners of the enterprise, management personnel and employees.
Innovative activity is an activity aimed at finding and implementing innovations in order to improve the products of the enterprise, the organization and technology of production, management. In the modern economy, innovation is becoming a fundamental factor in economic growth, the best way to strengthen the competitiveness of an enterprise. In this regard, in the mechanism of management at the enterprise, the innovative component has a special role. Innovations can change not only the scientific and technological level of management, the quality of work, but also the organization, enterprise management, and labor motivation.
Investment activities is the process of investing in new projects and a set of actions for their implementation. The investment activity of the enterprise is due to the need to update the material and technical base, increase production volumes, improve product quality, master new types of products, and new business areas. Developing an investment policy, the enterprise solves not only current, but also long-term tasks of increasing the efficiency of activities, increasing competitiveness.
Organization of control of management decisions is of particular importance as part of the internal mechanism for managing the activities of an enterprise, since it is control that largely determines the effectiveness of the entire management system. The control system is based on monitoring the economic and financial activities of the enterprise and is closely related to analysis, management accounting, and current planning. Control allows you to timely detect deviations from planned indicators, identify unused reserves for improving performance, and prevent possible imbalances in the development of the enterprise.
Using forms of external support for economic and financial activities often necessary for the enterprise to achieve strategic and current development goals. External support includes: government and other external forms of financing or providing benefits to an enterprise (for example, within the framework of state and regional programs to support small businesses), lending, leasing, insurance, etc.
All links and elements of the enterprise functioning mechanism are closely related to each other and affect each other. Thus, the internal mechanism for managing the activities of an enterprise is built taking into account market conditions and the current state regulation. The planning of the enterprise is associated with pricing, innovation, the use of external support mechanisms, the organization of control, and labor incentives.
The economic mechanism must constantly improve, change under the influence of changing environmental conditions and changes in the activities of the enterprise itself.
The viability of a modern organization is ensured by exchange processes with the environment, which accelerate with the development of technical and technological means of production, the strengthening of the role of a person in them, require a change in the concept of management, its orientation towards the integrated management of economic and social processes.
The organization's management system forms the basis of any socio-economic system. It consists of the following components (subsystems):
Control subsystem, which contains static (subjects of control) and dynamic (control processes - planning, organization, analysis, control, accounting, etc., which ensure the implementation of general and specific control functions) functional subsystems;
Support subsystems (regulatory, organizational, accounting and analytical, financial, personnel, informational, etc.) should create favorable conditions for the functioning of the main subsystems of the organization's management;
A management mechanism (a set of organizational, economic, socio-psychological and other management methods), which determines, in particular, goals, principles, methods of managing objects and processes.
Mechanism - (from Greek mechodos - machine) a sequence of states, processes that determine a certain phenomenon, action.
In the scientific literature, the term "control mechanism" is widely used, but there are many different points of view regarding its formulation. In general, in economics and management science, "mechanism" means "internal structure, a system of something."
The mechanism contains a certain sequence of economic phenomena: its constituent elements are simultaneously incoming and outgoing phenomena, as well as the entire process that occurs in the intervals between them. The mechanism is a natural system that determines the necessary relationship that occurs between various economic phenomena.
There are also two main approaches to defining the concept of "mechanism":
Structural and organizational;
Structural and functional.
The structural-organizational approach defines a mechanism as a set of certain constituent elements that create an organizational basis for certain phenomena and processes.
The structural-functional approach focuses not only on the organizational basis of its construction, but also on its dynamics, real functioning.
The statics of the control mechanism is determined by the subjects and objects of control, they constitute the organizational and structural basis of the mechanism, and the dynamics are the complex of connections and the interaction between them.
The control mechanism is considered as an integral part of the control system, provides an effective influence on the factors, the state of which determines the result of the control object.
An integrated management mechanism should be built as a relatively independent system, that is, it is necessary to determine its structure, establish the relationship between the elements, analyze their functions and the ability to act purposefully with their own characteristics. This allows us to consider it as an effective way of knowing reality and scientifically grounded influence on the processes that occur in an organization that meets the requirements of a systematic approach.
Besides, control mechanism as a difficult management category includes :
Management objectives (TSU)
A quantitative analogue of goals (NS) - management criteria;
Control factors (WHOO) - control elements and their connections, which are influenced to achieve the set goals;
Interaction Methods for Specified Control Factors (MB)
Management resources (RU) - material and financial resources, social potential, with the help of which and using the appropriate management method, the achievement of the specified goal is ensured.
Accordingly, for a specific object, the control mechanism can be displayed with functionality:
Synchronization of the main functions of individual control mechanisms as part of an integrated mechanism contributes to the creation of such operating conditions that would ensure maximum efficiency and effectiveness of management.
is an interconnected system of elements of organizational, economic, motivational and legal impact on the process of managing an organization.
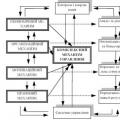
is a complex and systemic formation, organically combines the following constituent elements (mechanisms) (Fig. 3.1):

Rice. 3.1 -
- Economic (methods of planning and forecasting, methods and tools for managing the material and technical, financial, investment and innovation subsystem)
- Motivational (a set of command-administrative and socio-economic incentives that induce personnel to work highly efficiently);
- Organizational (objects, subjects of management, their goals, tasks, functions, management methods, organizational structures and the effectiveness of their functioning);
- Legal (regulatory support of management: the Economic Code, the Labor Code, the Civil Code, the Tax Code, laws and resolutions of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, resolutions and orders of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine, guidelines and instructions).
Let's consider in more detail the elements and tools of the above mechanisms.
Economic Mechanism determines possible ways to maintain the proper state of control objects, reasonable ways of developing the system and methods of attracting resources for this.
The economic mechanism is aimed at balance the overall efficiency of managing the functioning of the organization and forms a system of analytical relationships, on the basis of which a system of effective interrelated indicators is established.
Economic management methods are ways to achieve economic management goals based on the implementation of the requirements of economic laws (financing, pricing, cost accounting, commercial accounting, etc.). Traditionally, economic instruments are considered as management control over decision-making in the current activities of the organization in order to increase profitability, profitability and strengthen the financial condition of the organization.
Motivational mechanism should act as a complex of methods, methods and forms of interest in achieving the best socio-economic results of managing the elements of the system. Interest contributes to the emergence of incentives for the achievement of certain goals by the subjects of management, which determines the initiation of a certain activity of the subjects of management in the dynamic conditions of the external and internal environment.
Among the variety of economic methods of motivation, one can single out, for example, methods of economic incentives. Economic incentive is a management method that relies on the economic interests of workers. It is based on the formation of the income of the enterprise and each employee, depending on the personal contribution.
Economic incentives are based on the following basic principles:
The relationship and consistency of the goals of economic incentives with the development goals of the organization;
Differentiation of economic incentives aimed at implementing the necessary changes in the structure of production;
Combination of economic incentives with other methods of motivation;
A combination of economic incentives, economic sanctions, providing for material liability of employees.
Organizational mechanism enterprise management is a set of specific organizational actions that are different in nature, designed to organize the effective activity of an organization as an open production, economic and social system operating in an unstable environment.
The organizational mechanism is based on such processes as the formation of management bodies of the organization, the distribution of competence between them, the formation of a system of internal and external document flow, the formation and consolidation of regulations for interaction between the managing and controlled subsystems.
The main purpose of the organizational mechanism as part of an integrated management mechanism is the formation and strengthening of the organizational potential of the company as a component of management resources that provide an impact on the factors of production.
Organizational capacity building is achieved by:
Designing the structure of the organization and its formation as a purposeful production and economic socio-technical system;
Organization of the company's activities in accordance with the established objectives of the activity;
Organization of information support for the management of the company's activities;
Restructuring the company and reorganizing its activities in accordance with changes in the needs of society, the goals of the organization and the state of the external environment;
Development of motivation to rationalize organizational structures and management systems.
Legal Mechanism should ensure the regulation of legal relations between the subjects of management. In practice, some legal norms reinforce the influence of one of these mechanisms, while other legal norms lose their potential impact. The main task of the legal mechanism is the elimination of the number of contradictions from the legal relations of the participants in the management process and providing them with optimal content.
The main form of implementation and application of administrative and legal management methods is management and operational intervention in the management process in order to coordinate the efforts of the participants to fulfill the tasks assigned to them. These methods differ from other methods of management by the clear targeting of directives, the obligation to comply with orders and instructions; their failure is considered as a direct violation of the performing discipline and entails certain penalties.
These mechanisms, taken together, are capable of ensuring a balanced and effective functioning of the organization. Each individual of these mechanisms should contribute to the ultimate goal in the process of managing the organization.
 The system of protection of unemployed citizens is a complex of economic, organizational and legal forms and methods. A complex of legal organizational economic
The system of protection of unemployed citizens is a complex of economic, organizational and legal forms and methods. A complex of legal organizational economic Responsibilities of a sales manager: what to demand from an employee
Responsibilities of a sales manager: what to demand from an employee Job description Which department does the procurement agent belong to?
Job description Which department does the procurement agent belong to?