The main type of activity under okved 96.02. Explanations and clarifications
96.02 Provision of services by hairdressers and beauty salons
96.04 Physical culture and recreation activities
96.09 Provision of other personal services not included in other groups
Codes correspond to the new edition of OKVED 2
Files
Explanations and clarifications
Business on beauty is one of the most popular types of entrepreneurial activity. These services are always in demand among the population, but their organization has several significant nuances.
If in other types of business planning should start with a concept, then when opening a beauty salon first item there must be a question about the premises. The success of such a business directly depends on its location and material base, that is, on the compliance of all this with the target audience. Better to avoid subletting.
Second point a business project to open such a business is a matter for the masters. The client base will depend on their level, and hence the future profit. The entrepreneur himself is also obliged to understand the main issues related to the work of masters of a particular profile.
Third determining factor- selection of consumables. What is important is their quality, compliance with customer expectations, benefits in purchasing, control during use.
Then you need to solve administrative issues: will the entrepreneur himself do this or need to look for a reliable manager.
And finally, before opening, you need to attend to the problems that will become important with the start of work - ensuring cleanliness, washing, repair and maintenance of equipment.
Within the framework of the action of spa salons, beauty salons and hairdressing salons, it is possible to provide clients with such services:
- any manipulations with hair (cutting, washing, dyeing, styling, curling, straightening, building, trimming, etc.), including eyebrows, eyelashes and beards;
- cosmetic massage of the face, hands, feet, body with the application of various products;
- anti-cellulite wraps;
- manicure;
- pedicure, etc.;
If an appropriate additional OKVED is selected, it is possible to sell perfume and beauty products in the beauty elephant room.
When organizing a salon for the provision of cosmetology and hairdressing services, one must remember that since 2015 this type of activity has included massage services, as well as applying makeup and tattoos.
Making wigs is not part of this type of business.
An entrepreneurial activity based on the provision of personal services simply must be successful, since it is for this type of service that there is the greatest consumer demand. Moreover, personal services are especially popular, since it is very important for every person to feel comfortable in this world. Such a business is influenced by geographical location, but it is usually quite profitable. It is for personal services that OKVED 96.02 is used, and for which ones, we will consider in this article.
What is included in this type of service
The services of a personal type, despite their variety, have one thing in common: they are performed specifically for the consumer and are able to satisfy his personal needs. Everyone strives to be beautiful: both women and men, and age does not really matter.
That is why many entrepreneurs want to occupy such a market niche, since the demand for these services usually does not decrease, but only increases, and the correct location of an entrepreneurial point in the territorial plan can provide an entrepreneur with stable profits for a long time.
It is worth noting that the code we are considering includes the services of hairdressing, as well as beauty salons, they are based on washing hair, all types of hairdressing, including creating hairstyles, as well as aesthetic beard correction. In addition, some types of cosmetic services, including beauty massage, can be considered under this code.
Decoding based on the classifier
This code can be deciphered step by step using the new edition of the classifier. This is OKVED-2, recognized as valid in 2017. It is worth noting that this type of activity according to the old classifier had a different code, but we are interested in decoding OKVED 96.02 at the moment:
- The code under discussion refers to the section of the S classifier, which combined other types of services provided to the population.
- 0 is a code used in relation to other personal services.
- 02 is a code that designates the provision of various personal services by hairdressers and beauty salons.
The code in the form in which it is indicated in the last paragraph is prescribed in the registration documents, as well as when it is confirmed. In addition, OKVED can be used to designate the activities of an entrepreneurial object in its charter. In this case, when changing the code, you must make changes to it.

So, the code discussed in this article is used in the work of hairdressers and beauty salons, when they are engaged in the provision of personal services, which cannot include making wigs, even if they are made to order in a salon. Cosmetic services can also be included in the list of services provided by this business entity.
In this article, we will tell you what types of activities you need to obtain a license for in 2020, and what the risks of working without such a permit, if it is required by law.
A license is a permit from authorized state bodies to carry out certain types of activities.
Features of activities requiring a license
Business areas subject to licensing were not chosen by chance. All of them require special technical conditions, qualified personnel, or may adversely affect the life and health of people, the environment, and cultural heritage. Among the licensed areas of business, there are those that are associated with large financial flows (banks, credit institutions, the securities market).
Not all licensed types of activity are available to individual entrepreneurs. The laws do not explain why this is so, but it is known that the state treats individual entrepreneurs as business kids. For entrepreneurs, the fines are several times lower, and there are more tax incentives. But, for example, a license for the production and sale of strong alcohol will not be given to individual entrepreneurs. The maximum that will be allowed to sell from alcohol is.
What activities do you need a license for
![]()
![]() The largest list of licensed species is contained in Law No. 99-FZ dated 04/05/2011, but besides it, there are several other laws, each of which regulates a separate area.
The largest list of licensed species is contained in Law No. 99-FZ dated 04/05/2011, but besides it, there are several other laws, each of which regulates a separate area.
For example, the issuance of a license for the production and circulation of alcohol is controlled by Law No. 171 of November 22, 1995, for the activities of credit institutions - No. 395-1 of December 2, 1990, for holding tenders - No. 325 of November 21, 2011.
List of licensed activities in 2020:
- Freight and passenger transportation by road (except for taxis), rail, water, sea, air
- Loading and unloading operations and transport towing
- Security and detective (detective) activities
- Education of children and adults
- Manufacturing of medicines and medical equipment
- Activities in the field of medicine and pharmaceuticals
- Production and sale of alcohol
- Clearing and insurance activities
- Activities of credit institutions and NPFs
- Trading and professional activities in the securities market
- Activities in the field of space and nuclear energy
- Activities for the protection of state secrets
- Activities related to encryption and special technical means for secretly obtaining information, protection of confidential information
- Activities in the field of information and telecommunication systems
- Communication services, TV broadcasting, radio broadcasting
- Production and sale of special printed products, protected from counterfeiting
- Production, testing, repair of aircraft
- Activities related to weapons, ammunition, military equipment
- Legal circulation of drugs and psychotropic substances
- Carrying out gambling through bookmakers and sweepstakes
- Procurement, storage, processing, sale of scrap metal
- Apartment building management
- Industrial safety expertise
- Operation of industrial facilities of increased danger (explosion, fire and chemically hazardous)
- Neutralization, collection, transportation of waste related to I - IV hazard classes
- Industrial explosives activities
- Activities for the use of sources of ionizing radiation
- Fire extinguishing, installation, repair and maintenance of fire safety equipment
- Use of pathogens of infectious diseases and GMOs
- Employment of Russian citizens abroad
- Production of copies of audiovisual works, computer programs, databases, phonograms on any media
- Geodetic and cartographic activities, hydrometeorology and geophysics, mine surveying
- Preservation of objects of cultural heritage.
Most often, individual entrepreneurs from this list choose cargo transportation, passenger transportation, medical and educational activities, and private investigation. The rest of the licensed activities in 2020 require either the organizational and legal form of a legal entity, or large financial investments.
▼ Try our bank rate calculator: ▼
Move the "sliders", open and select "Additional conditions" so that the Calculator will select the best offer for you to open a current account. Leave a request and the bank manager will call you back: he will advise on the tariff and reserve a current account.
Responsibility for the lack of a license
Failure to comply with the legislation in the field of licensing is an administrative offense, which is punished for an individual entrepreneur in accordance with the articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation /
Penalties for work without a license
- 14.1 (2) - from 4 to 5 thousand rubles with the possible confiscation of manufactured products, tools of production and raw materials (activities without a license);
- 14.1 (3) - from 3 to 3 thousand rubles (non-compliance with the necessary license requirements);
- 14.1 (4) - from 4 to 8 thousand rubles (gross violation of the license terms).
Special fines for a license in the field of transport under article 14.1.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation are much higher:
- lack of a license - 100 thousand rubles with the confiscation of the vehicle;
- violation of the terms of the issued license - 20 thousand rubles;
- gross violation of the terms of the issued license - 75 thousand rubles.
Although the size of penalties for individual entrepreneurs is several times lower than for LLCs, criminal liability does not differ depending on the organizational and legal form. It occurs when you receive income or damage the state or citizens in the amount of 2.25 million rubles (article 171 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
OKVED codes and license
The applicant informs about what kind of business the individual entrepreneur will be engaged in when registering with the tax office. To designate specific types of activity, digital codes are used according to OKVED (All-Russian Classifier of Economic Activities).
It is impossible to compare the list by OKVED codes to the types of activities subject to licensing in Russia. The fact is that licensing directions are broader than a specific OKVED code.
How to determine if OKVED is subject to licensing
For example, if you choose educational activity, then the following codes from OKVED-2 will correspond to it:
- 85.11: Preschool education
- 85.12: Primary general education
- 85.13: Basic general education
- 85.14: General secondary education
- 85.21: Vocational secondary education
- 85.22: Higher education
- 85.23: Training of highly qualified personnel
- 85.30: Professional training
- 85.41: Additional education for children and adults
- 85.42: Additional vocational education
Moreover, these are only four-digit codes, and if we take into account the five-digit and six-digit codes, there will be even more of them. And if we take pharmaceutical activity, then this concept includes the sale of drugs, and their storage, and the manufacture of drugs according to prescriptions.
By itself, the indication in the form P21001 of OKVED codes corresponding to the licensed area does not oblige to obtain a license. Only if an entrepreneur starts a real activity, it is necessary to contact the licensing authority in advance.
However, some inspectors, and sometimes banks, are interested in whether you have a license, if the corresponding OKVED codes are indicated in the extract from the USRIP. If you are not going to work under a license yet, then for your own peace of mind it is not at all necessary to enter these codes in advance even when registering an individual entrepreneur. Later you can always serve them.
How to get an individual entrepreneur license
Licensing of certain types of activities has been entrusted to authorized state bodies. You can find out about which agency you need to apply for a license from the Government Decree of November 21, 2011 No. 957.
Information on the most popular licensing directions among individual entrepreneurs is given in the table.
Each authorized body has its own official website, where you can find contacts of regional divisions and all the necessary information to obtain a license.
If as an individual entrepreneur you plan to engage only in licensed activities, then first study the licensing requirements. For example, in order to obtain a permit for the carriage of passengers by road, you must have:
- Transport equipped with GLONASS equipment;
- Premises and equipment for vehicle maintenance and repair;
- Drivers with the necessary qualifications, work experience, passed a medical examination;
- A specialist for a pre-trip medical examination of drivers or an agreement concluded with a medical organization for its conduct, etc.
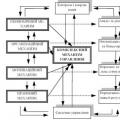 The system of protection of unemployed citizens is a complex of economic, organizational and legal forms and methods. A complex of legal organizational economic
The system of protection of unemployed citizens is a complex of economic, organizational and legal forms and methods. A complex of legal organizational economic Responsibilities of a sales manager: what to demand from an employee
Responsibilities of a sales manager: what to demand from an employee Job description Which department does the procurement agent belong to?
Job description Which department does the procurement agent belong to?