Writing a business plan: production plan
Continuing to learn how to independently draw up a business plan, we move on to the next stage of the project description. The production plan in business planning is an integral part of any document. If almost all the previous sections were essentially more a description of theoretical information, then this whole one is devoted to practical "calculations" - production capacities and resources, which include: raw materials, personnel, premises, equipment used, equipment, inventory, and even intangible assets - information and production technology.
What is a production plan for in a business project description? And is it needed in a business plan, which is not drawn up for production, but, say, for the provision of any services? Of course you do! The production plan of an enterprise, regardless of its type of activity, shows which specific processes are required for the release of the proposed product or the provision of a service.
The description of the technological process should show a potential investor, or prove to you personally, that the company is able to provide an output to the planned production volumes of products (services) of proper quality in a timely manner, provided that certain production capacities are available.
The production plan, when drawing up, should be based on the data of the sales plan for the products manufactured, it should reflect all stages of the production of goods or the provision of the proposed service. For greater clarity and better perception, the content of the production plan should include a calendar containing a listing of the activities necessary for the implementation of the document, the conditions and deadlines for their implementation, as well as the financing of each stage separately.
All production processes should be presented step by step, with maximum detail, starting from the moment of finding a suitable premises and purchasing consumables until the purchaser makes a purchase. It is better if all stages of the production system are accompanied by schemes and work algorithms. On the diagram, it looks something like this:
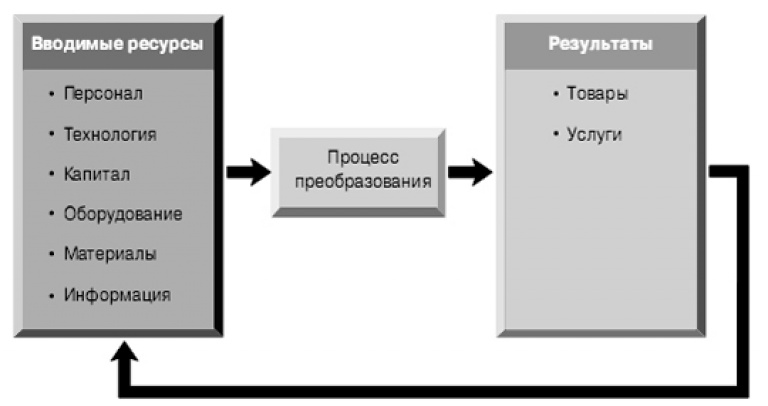
However, you can save the investor from reading the list of everything necessary (for example: 34 spoons, 35 forks, or 3 packs of printing paper and 15 pens - ridiculous, isn't it?), And touch on this topic only superficially. If such data are really of particular importance for the implementation of the project, then they can be taken out in the Appendices to the business plan. I will tell you about them in one of the following topics.
But identifying and listing the required resources is not enough. You also need to convincingly argue why you chose them, and not other similar ones. Quite often, specialists from industry companies involved in project development are involved in the work on drawing up a production plan. Only professionals will be able to explain in an accessible way all the advantages of the facilities planned for use, and show the effectiveness of their work.
Classification of production plans
When describing a project to an investor, do not forget about yourself - after all, your main goal, along with obtaining funds, is to personally understand the whole process "from the inside" in order to make it easier for yourself to work on its implementation.
Having determined for yourself the type of production planning, you must enter the following tactical information in this section of the document:
- Aggregate (general) plan. This is a general description of the production of all goods or services offered by an enterprise.
- The main schedule of the work performed, in which you must show the calculations of the production of the number of units of goods or the number of services provided for a certain period of time.
- Needs plan. Here you must show what consumables, in what quantity and in what time frame you will need to in order to comply with the main schedule of the work performed.

Manufacturing resources
Let's look at an example straight away:
Let the company N decide to start manufacturing cabinet furniture. First of all, in the course of a comprehensive marketing analysis and consumer market research, the company's specialists find out that their target audience is representatives with an average income level and some office companies who are interested in furniture in the middle price range. The next step of the company is to determine the amount of production of goods for the estimated period of time in order to properly plan the creation and loading of production resources.
Logically, the analysis of the future use of the necessary resources directly depends on the calculations of the level of potential demand for future products. That is, if a company plans to produce only living room wardrobes, sell them for 10 thousand rubles, and reach 5 million rubles on sales for the first year of operation, then in order to reach the level of the planned profit, it needs to produce 500 wardrobes per year. A smaller quantity will lead to a failure to fulfill the plan, a larger quantity will lead to an oversupply of production. If the company also starts producing bedroom wardrobes and dressers, then the calculations for creating the necessary resources will be somewhat more complicated.
If the company has been successfully operating for a long time, and it needs a business plan in order to reach a qualitatively new level, then the planned volume of product sales after expansion must first be compared with the existing resources in order to find out what additional capacities it needs. for that. To take it to the next level. An example is educational institutions, the administration of which annually calculates the number of educational places in order to ensure the full load of the educational process.
When working on the planning of production resources, it is necessary to understand that these parameters can increase or decrease depending on the duration of the enterprise's life cycle.
For reference: the life cycle of an enterprise is the stages of its formation: organization, development, reaching the highest peak. In some cases, extinction and elimination can be added. You can draw an analogy with living organisms - birth, growing up, maturity, death. However, not every artificial creation should die, so we will proceed from optimistic forecasts.
Placement of production resources
In any case, if a company is already working and is going to expand, or it is just being created, it needs production facilities to accommodate all the necessary resources. That is, in the production plan of a business project, it is necessary to indicate which buildings, structures, and other areas it will need to ensure a normal working process. This calculation is influenced by factors such as:
- availability of qualified specialists in the area in question
- the level of wages in the region as a whole
- availability of production resources (electricity, water supply, etc.), and their cost
- proximity to consumables suppliers
- proximity to target audience
For our company N it will be obvious that it needs a workshop for the production of furniture, several administrative premises in a city with a fairly large population (from 200 thousand people) with nearby wholesalers (or directly producing) chipboard, MDF, and other materials, from which cabinet furniture is usually assembled.
In the same part of the production plan, you can include a description of the location of the equipment. Organization of workplaces, planning the placement of tools is part of optimizing production, achieving greater efficiency at the lowest cost.
Manufacturing process
The time has come to determine exactly how, in what way the products will be produced, or the service will be provided. Ideally, the interested investor should visualize the complete picture of the creation of the product, and, most importantly, the use of various technologies. It is necessary to show how automated the entire production (service) process will be, what technologies existing in similar industries are going to be borrowed by the company in order to increase work efficiency. To do this, you need to again analyze the use of such technologies by competitors.
In conclusion, it should be noted that without your personal understanding of the entire production process, it will hardly be possible to create a production plan without outside participation and the involvement of specialists. For big business, of course, in principle, this is impossible. But for small and medium-sized - almost mandatory. That's all for today. See you in the next topic - Business Project Organizational Plan. I wish you success!
 Discounted payback period
Discounted payback period Methodological aspects of project management
Methodological aspects of project management Scrum development methodology
Scrum development methodology