Analysis of the current assets of the enterprise. Profitability - economic value, main profitability factors Methods for determining the need for working capital
The profit of an enterprise is the most important indicator that reflects the result of its activities and indicates how rationally and efficiently production resources were used. In a broad sense, profit is understood as a positive difference between income and costs, negative is a loss. Depending on the calculation method, profit is distinguished:
- From sales - when calculating it, in addition to the cost price, administrative and selling expenses are taken into account.
- Gross - gives an assessment of the results in a broad sense, it is the difference between total sales revenue and the cost of production.
- Before tax - when calculating it, operating income and expenses are additionally taken into account, as well as income and expenses from activities not related to the sale of products.
- Net - calculated after tax, calculated net of tax liabilities.
The enterprise may receive profit or loss based on the results of its operations. These indicators are subject to analysis, which will give an understanding of what factors influenced the result, to what extent and what actions should be taken to change the situation for the better.
Why is the profit analysis carried out?
The analysis of the indicator will allow solving the following tasks:
- assessment of the compliance of the obtained financial result with the planned profit indicators, taking into account the volume of products sold;
- assessment of strategic objectives in terms of making a profit;
- determination of factors and components, as a result of which the actual profit indicator deviated from the planned one;
- determination of methods with which it will be possible to improve the indicator of the volume of profit.
The analysis enables the company's management to determine the main ways of further development of the enterprise, to find hidden reserves to improve the financial result. The results obtained help to identify bottlenecks, adjust plans, increase the efficiency of resource use and the company's activities as a whole.
Sources of information for assessing profit
To conduct a comprehensive analysis of the indicator, the company's management uses information from:
- accounting statements;
- profit accounting register;
- financial plan.
How to increase profits
Increasing profits can be achieved by increasing revenues or reducing costs for the enterprise. Sales revenue can be increased by increasing sales volumes or product value. An increase in value can have the opposite effect - a drop in sales. Therefore, this method is used less frequently, usually during times of rising inflation. Before raising the value, it is necessary to study the market, competitors' offerings and consumer expectations. There are non-price methods to stimulate profit growth. These include a balanced marketing policy, expanding (updating) the range, improving the quality of goods, etc. Cost reduction can be achieved through efficient use of resources. Today, innovative technologies are actively used for this, which allow more efficient use of fuel and raw materials, labor resources, and reduce depreciation charges. You can also reduce costs through competent logistics, the use of staff optimization (outsourcing), and the use of modern cost management methods. It is necessary to assess the profit, as this allows you to identify deviations from the planned indicators and respond in a timely manner to external challenges. Based on the analysis, the management of the enterprise can develop a set of measures that can qualitatively improve the financial result.
Introduction.
In modern economic conditions, the activity of each economic entity is the subject of attention of a wide range of market participants interested in the results of its functioning.
To ensure the survival of an enterprise in modern conditions, management personnel must, first of all, be able to realistically assess the financial condition of both their enterprise and existing potential competitors. The most important in determining the financial condition of an enterprise is the timely and high-quality analysis of financial and economic activities.
The goal of any enterprise is profit, which, accordingly, is the most important object of economic analysis. However, the size of the profit itself cannot characterize the efficiency of the enterprise's use of its resources. One of the main indicators characterizing the efficiency of the enterprise is profitability. Profitability, in a general sense, characterizes the expediency of expended resources in relation to newly acquired (profit) resources.
Profitability and profit are indicators that clearly reflect the efficiency of the enterprise, the rationality of the enterprise's use of its resources, the profitability of activities (production, entrepreneurial, investment, etc.).
The enterprise sells its products to consumers, receiving cash receipts for it. But this does not mean making a profit yet. To identify the financial result, it is necessary to compare the proceeds with the costs of the production of products and their sale, i.e. with the cost of production.
The enterprise makes a profit if the revenue exceeds the cost price; if the revenue is equal to the cost price, then it is only possible to reimburse the costs of production and sale of products, and there is no profit; if costs exceed revenues, then the company receives a loss, i.e. negative financial result, which puts him in a difficult financial position, not excluding bankruptcy. To maximize profit and avoid bankruptcy, it is necessary to study profit indicators, the factors affecting it, and the profitability indicator, which reflects the efficiency of current costs and is a kind of synthesis of various qualitative and quantitative indicators.
Concept and economic content of profitability
One of the most important indicators of the company's activity is profitability.
Profitability is a generalizing indicator characterizing the quality of work of an industrial enterprise, since for all the value of the mass of the profit received, the most complete qualitative assessment of the production and economic activity of the enterprise is given by the value of profitability and its change. It represents the ratio of profit to production assets or to the cost of production. The profitability indicator assesses the efficiency of production and its costs.
The main factors that have a direct impact on increasing the level of profitability in enterprises include:
1. Growth in the volume of production;
2. Reducing its cost;
3. Reducing the turnover time of fixed assets and working capital;
4. Growth in the mass of profits;
5. Better use of funds;
6. Pricing system for equipment, buildings and structures and other carriers of fixed assets;
7. Establishment and observance of the norms of stocks of material resources, work in progress and finished goods.
To achieve a high level of profitability, it is necessary to systematically and systematically introduce the advanced achievements of science and technology, effectively use labor resources and production assets.
According to the method of calculation in the national economy, there is a profitability of enterprises P pr. And a profitability of products P prod. The first indicator is defined as the ratio of the balance sheet profit P to the average annual cost of fixed assets F op and working capital F about:
P pr = (P / (F op + F about)) x 100% (6)
The second indicator of profitability is expressed by the ratio of the balance sheet profit P to the cost of the finished product C:
P pr = (P / S) x 100% (7)
Methods for determining profitability clearly show that the level of profitability and its change are directly related to prices for industrial products. Consequently, an objective pricing system is an important prerequisite for determining a reasonable level of profitability, which at the same time can influence the change in the level of prices for products. Thus, sound methods of establishing and planning profitability are closely related to the pricing system. The amount of profit, and, consequently, the level of profitability, first of all, depend on changes in prices for products and their cost.
In the concept of profitability of production, the accumulations created in the process of manufacturing products are compared with the production assets initially allocated to a given enterprise. The profitability of production serves as a measure of the effectiveness of the use of funds at the disposal of the enterprise.
The economic sense of the profitability of production is not limited to reducing the cost of living and materialized labor for the production of a unit of output. The mass of funds involved in the production process differs significantly from their amount, which is included in the amount of costs associated with the manufacture of products. A huge amount of fixed assets materialized in buildings, structures, equipment and inventory takes part in the production process. The costs of production include their depreciation, that is, the share of their value transferred at one time or another to the cost of production. The cost of working capital is included in production costs only in the amount spent in the manufacture of products.
Various means are used to increase the profitability of production. One of the main sources of growth in production profitability is an increase in the mass of profits received by the enterprise. This growth is achieved as a result of a decrease in production costs, a change in the structure of manufactured products and such an increase in the scale of production, when, while maintaining the amount of profit received from the sale of a unit of each type of product, the total amount of profit received grows.
The main factor of profit growth is the reduction of production costs. However, the value of the balance sheet profit is influenced by a number of other factors - changes in product prices, the amount of the remainder of unsold products, sales volume, production structure, etc. prices (their increase in connection with an increase in the quality of products or a decrease due to the aging of certain types of products, saturation of the consumer market with some products, or in connection with the transition to new equipment and production technology). An increase in the profitability of production means an increase in the return on each hryvnia of the advanced funds and, thus, their more efficient use.
Profitability indicators are important characteristics of the financial results and efficiency of the enterprise. They measure the profitability of an enterprise from various positions and are grouped in accordance with the interests of participants in the economic process, market exchange.
Profitability indicators are important characteristics of the factor environment for the formation of profit (and income) of enterprises. For this reason, they are indispensable elements of comparative analysis and assessment of the financial condition of the enterprise. When analyzing production, profitability indicators are used as a tool for investment policy and pricing.
The system of indicators of profitability.
Profitability indicators are the main characteristics of the efficiency of an enterprise's economic activity. They are calculated as a relative indicator of the financial results obtained by the company for the reporting period. The economic content of profitability indicators is reduced to the profitability of the enterprise. In the process of analyzing profitability, the level of indicators, their dynamics are investigated, a system of factors influencing their change, and their quantitative assessment are determined.
The main indicators of profitability can be grouped into three groups:
return on equity (assets) indicators;
indicators of profitability of sales of products;
indicators calculated on the basis of cash flows.
First group profitability indicators is formed as the ratio of profit to various indicators of advanced funds, of which the most important are: all assets of the enterprise; investment capital (equity + long-term liabilities); share (own) capital.
For example,
The specification of these indicators is that they meet the interests of all participants in the business of the enterprise. For example, the administration of an enterprise is interested in the return (profitability) of all assets (total capital); potential investors and lenders - return on invested capital; owners and founders - stock returns, etc.
Return on assets indicators are calculated as the ratio of profit indicators to indicators of the average assets of the enterprise for the reporting period. Return on assets is the most important indicator of the efficiency of a commercial organization, the basic standard (i.e., the average value in a market economy), with which the individual indicators of enterprises are correlated to substantiate their competitiveness. Such a rate of return (or rate of return), as the ratio of accounting profit (profit before tax) to the total value of assets, is the main indicator of cross-industry competition, the main indicator for determining the effectiveness of investment projects. The rate of return (or rate of return) is on a downward trend at the present time. According to foreign institutions of economic analysis, it is about 18-20%. Hence, in the global market economy, a coefficient of 0.20 is often used to determine effective projects.
Each of the listed indicators can be easily modeled according to factor dependencies. Consider the following dependency:
![]()
Where is the net profit;
K - all assets;
N - sales.
This formula shows the relationship between return on all assets, return on sales and asset turnover. The formula directly indicates the ways to increase profitability: when the profitability of sales is low, it is necessary to strive to accelerate the turnover of assets.
Let's consider another factorial model of profitability:
Where is equity (capital).
As you can see, the return on equity (equity) capital depends on changes in the level of profitability of products, the rate of turnover of total capital and the ratio of equity and debt capital. The study of such dependencies is of great importance for assessing the influence of various factors on profitability indicators. From the above dependence it follows that, other things being equal, the return on equity capital increases with an increase in the share of borrowed funds in the total capital.
Second group indicators are formed on the basis of calculating the levels of profitability according to the indicators of profit, reflected in the reporting of the enterprise. For example,

Note that the arrow indicates the logic of the formation of profit indicators.
The increment in profit can be associated with both intensive and extensive use of production resources. Therefore, the indicator of true efficiency can only be the profitability of sales, i.e. the ratio of profit to sales revenue.
Depending on the numerator that reflects certain aspects of economic activity, there are:
![]() ,
,
Where is the profit from sales;
N - proceeds from sales in net selling prices (p. 010 f. No. 2 of the profit and loss statement);
2.the profitability of probation on accounting (pre-tax) profit
Where - accounting profit (p. 140 No. 2);
3. profitability of sales by net profit ():
![]()
Where  - net (undistributed) profit (p. 190 f. No. 2).
- net (undistributed) profit (p. 190 f. No. 2).
In management accounting and analysis, the indicator of profitability of sales is used as the ratio of profit from sales to the cost price (full or production) of sales of products ( 
 ):
):
 ,
,
Where  - cost of goods sold.
- cost of goods sold.
(continued page 199)
Third group profitability indicators are formed similarly to the first and second groups, however, instead of profit, the net cash inflow is taken into account.
These indicators give an idea of the degree of the enterprise's ability to pay off creditors, borrowers and shareholders with cash in connection with the use of cash inflow. The concept of profitability, calculated on the basis of cash, is widely used in countries with developed market economies. It is a priority, because operations with cash flows that ensure solvency are an essential sign of the "health" of the financial condition of an enterprise.
The variety of indicators of profitability determines the alternative search for ways to increase it. Each of the initial indicators is decomposed into a factor system with varying degrees of detail, which sets the boundaries for identifying and assessing production reserves.
"legitimacy ... Economic content tax mechanism and tax administration in Kazakhstan Abstract >> Financial Sciences
Economic content tax mechanism 1. TAXES AND ... the impact on characteristics such as profitability the project, its payback period, etc. ... if we talk about the range of covered the notion"finance" economic institutions, then there are several ...
Profitability metrics are used to assess the current profitability of an enterprise. It is a relative measure of efficiency (effect / cost).
There are the following profitability indicators:
The specified list can be supplemented at the request of individual project participants or financial structures, as well as in connection with the introduction by state bodies of new or change, existing criteria for starting an enterprise bankruptcy procedure.
It is advisable to analyze the values of the corresponding indicators in dynamics and compare them with the indicators of similar enterprises. Each project participant, as well as lending banks and lessors, may have their own idea of the limit values of these indicators, indicating the unfavorable financial position of the company. However, in any case, these limit values significantly depend on the production technology and the structure of prices for manufactured products and consumed resources. Therefore, it is not always advisable to use the ideas about the maximum levels of financial indicators that have developed at the time of calculation to assess the financial position of an enterprise over a long period of implementation of an investment project.
Determine the factors affecting profitability
 asset turnover
asset turnover

Рп * - asset turnover *
- As the asset turnover grows, the return on sales and the return on assets grow.
- All types of ROI are expressed through ROI
In 1919, DuPont specialists proposed a factor analysis scheme. In the Du Pont factor model, for the first time, several indicators are linked together and presented in the form of a triangular structure, at the top of which is the return on equity ratio (ROA) as the main indicator characterizing the efficiency of funds invested in the company's activities, and at the base of two factor indicators - the profitability of sales NPM and resource efficiency TAT.
In the future, this model was expanded into a modified factor model, presented in the form of a tree structure, at the top of which is the return on equity (ROE) indicator, and at the base - the features characterizing the factors of the production and financial activities of the enterprise. The main difference between these models lies in a more fractional allocation of factors and a change in priorities relative to the effective indicator. A fairly effective way of assessing is the use of rigidly deterministic factor models; one of the variants of such an analysis is just performed using a modified factor model. The factorial model of DuPont is used for factor analysis of the return on equity, it establishes the relationship between the return on equity and the main financial indicators of the company: return on sales, asset turnover and financial leverage. The modified DuPont model is: ROE = Net Income / Revenue * Revenue / Assets * Assets / Equity.
For each specific case, the model allows you to determine the factors that have the greatest effect on the return on equity. From the presented model, it can be seen that the return on equity depends on three factors: return on sales, asset turnover and the structure of advanced capital. The significance of the selected factors is explained by the fact that in a certain sense they generalize all aspects of the financial and economic activity of the enterprise, its statics and dynamics.
The modified factor model clearly shows that the return on equity of an enterprise and its financial stability are inversely related. With an increase in equity capital, its profitability decreases, but the financial stability and solvency of the enterprise as a whole increase.
Profitability indicators are relative characteristics of the financial results and efficiency of the enterprise. They measure the profitability of an enterprise from various positions and are grouped in accordance with the interests of participants in the economic process, market exchange. Profitability indicators are important characteristics of the factorial environment for the formation of profit and income of the enterprise. For this reason, they are indispensable elements of comparative analysis and assessment of the financial condition of the enterprise. When analyzing production, profitability indicators are used as a tool for investment policy and pricing.
The main indicators of profitability can be grouped into the following groups:
Indicators calculated on the basis of profit (income);
Indicators calculated on the basis of production assets;
Indicators calculated on the basis of cash flows.
The first group of indicators is formed on the basis of calculating the levels of profitability (profitability) according to the indicators of profit, which are defined in the reporting of the enterprise. For example:
These indicators characterize the profitability (profitability) of sales. Using the methods of factor analysis, the influence of price changes is determined
for products and their cost (material costs) to change the profitability of products.
Let us denote the profitability of the products of the baseline and the reporting period through and, respectively. There is by definition:
![]()
where is the profit from the sale of the reporting and base periods, respectively;
Sales of products (works, services), in accordance with the reporting and base period;
Cost of products (works, services), in accordance with the reporting and base period;
Δ R- change in profitability for the analyzed period.
The influence of the factor of change in the price of products is determined by calculation (using the method of chain substitutions):
![]()
Accordingly, the influence of the factor of cost price change on the change in profitability will be:
![]()
The sum of the factorial deviations will give the total change in profitability for the period:
The second group of indicators is formed on the basis of calculating the levels of profitability, depending on changes in the size and nature of the advanced funds: all production assets of the enterprise; invested capital (equity, long-term liabilities); share (own) capital. For example:
The discrepancy between the levels of profitability for these indicators characterizes the degree to which the company uses financial leverage to increase profitability: long-term loans and other borrowed funds.
These indicators are very practical. They serve the interests of the various participants. For example; the administration of the enterprise is interested in the return (profitability) of all production assets; potential investors and lenders are interested in the return on invested capital; owners and founders are interested in stock returns and so on.
Each of the listed indicators is easily modeled by the method of identical transformations based on factor dependence. For example, consider this obvious dependency:
This formula reveals the relationship between the profitability of sales and return on assets (an indicator of the turnover of production assets). The economic meaning of the relationship lies in the fact that the formula directly indicates the ways to increase profitability: with a low profitability of sales, it is necessary to strive to accelerate the turnover of industrial assets.
Let's consider another factorial model of profitability.

As you can see, the return on equity (equity) capital depends on changes in the levels of return on sales, the rate of circulation of total capital and the ratio of equity and debt capital. The study of such dependencies has great probative power for assessing the financial condition of an enterprise, assessing the degree of skill in using financial leverage to improve the results of its activities. From this dependence it follows that, other things being equal, the return on equity capital increases with an increase in the share of the company's borrowed funds in the total capital.
Let's consider an example (tab. 5.3).
Table 5 .3
Analysis of the level of profitability of production
|
indicators |
For the last swarm |
For the reporting year |
|
1. Balance sheet profit, thousand UAH |
||
|
2. Chip product sales, thousand UAH |
||
|
3. Average annual cost of fixed assets, thousand UAH |
||
|
4. Average annual balances of material circulating assets, thousand UAH |
||
|
5. Average annual cost of production assets, thousand UAH |
||
|
6. Ratio of production capital intensity, color. (Page 3 / Page 2) |
||
|
7. Coefficient of fixing current assets, kopecks. (Page 4 / Page 2) |
||
|
8. Profit per ruble of products sold, kopecks. (Page 1 / Page 2) |
||
|
9. The level of profitability of the enterprise,%, (p. 1 / p. 5) × 100 |
The level of profitability for the reporting year was 91.6%, and for the last year - 135.8%, then the profitability decreased by 44.2 points.
The influence of the factors that influenced the change in the level of profitability is determined based on the following calculations (by the method of chain substitutions):
1) an increase in the share of profit per hryvnia of products sold led to an increase in the level of profitability by 56.1 points (191.9 - 135.8), where
2) an increase in the capital intensity of production, that is, a decrease in capital productivity of fixed assets led to a decrease in profitability by 89.6 points (102.3 - 191.9), where
3) an increase in the coefficient of fixing material working capital, that is, a slowdown in their turnover, led to a decrease in the profitability of production by 10.7 points (91.6 - 102.3).
So, the overall decrease in profitability by factors is 44.256.1 - 89.5 - 10.7), which corresponds to the overall change in the profitability of production in comparison with the data for the last year.
The third group of profitability indicators is calculated on the basis of net cash inflows. For example

The latest indicators give an idea of the company's ability to fulfill its obligations to creditors, borrowers and shareholders in cash. Profitability, calculated on the basis of cash inflows, is widely used in countries with developed market economies. It is overwhelming because cash flow operations are an essential sign of an intensive type of production, a sign of the "health" of the economy and the financial condition of an enterprise.
Factor models of profitability reveal the most important causal relationships between indicators of the company's financial condition and financial results. Therefore, they are an indispensable tool for "explaining" (assessing) the current situation.
Factor models of profitability are also models for predicting the financial stability of an enterprise, driven. The need to foresee the near and distant development prospects is an urgent task for enterprises. Production growth rates depend not only on demand, sales markets, enterprise capacities, but also on the state of financial resources, capital structure and other factors.
The most important limitation of the planned growth rate of an enterprise is the rate of increase in its equity capital, which depends on many factors, but primarily on the profitability of sales (factor X1), the turnover of all capital (balance sheet currency - factor X2) of the financial activity of the enterprise in attracting borrowed funds (factor X3) rates of distribution of profits for development and consumption (factor X4).
Thus, the growth rate of equity capital, which characterizes the potential of an enterprise to expand production, can be represented by a multiplicative model of the relationship of the listed factors:
where Y- the growth rate of equity capital (equal to the ratio of profit directed to accumulation to the average annual cost of equity capital);

The model reflects the action of tactical (factors X1, X2) and strategic (factors X3, X4) financial decisions. Correctly produced pricing policy, expansion of sales markets lead to an increase in sales and profits of the enterprise, increase the rate of circulation of its capital. At the same time, an irrational investment policy and a decrease in the share of borrowed capital can reduce the positive result of the first two factors.
This model is remarkable in that it can easily be expanded to include new factors. Moreover, such important indicators of the financial condition as liquidity, the turnover of current (mobile) assets, the ratio of fixed-term liabilities and capital, fall into the manager's field of vision.
The extended model for calculating the sustainable growth rate is as follows:
where y - equity capital growth ratio;
a - capital structure (the ratio of the balance sheet currency to the average cost of equity capital);
b- the share of urgent liabilities in the capital of the enterprise (the ratio of the amount of urgent liabilities (current liabilities) to the balance sheet currency);
with- current liquidity ratio (the ratio of current assets to current liabilities);
d- the turnover of current assets (the ratio of net sales to current assets);
e- the financial result from the sale of products per unit of sale (profitability of sales) (the ratio of net profit to net sales);
f- the rate of distribution of profit for accumulation (the ratio of profit directed to investments to the amount of net profit).
The practical application of sustainable growth models is recommended in planning the development of an enterprise, taking into account the risk of bankruptcy.
It is known that one of the criteria for bankruptcy is an unsatisfactory balance sheet structure, which is determined by the current liquidity ratio, the ratio of current assets with own funds and the amount of debt in equity. If we take all these coefficients at the standard level, and the rate of distribution of profit for accumulation is equal to 1.0, then the optimal value of the sustainable growth rate will be 0.5 of the return on current assets, or 0.05 of the return on equity working capital.
These are very important conclusions from the analysis of formulas. But it is not the numerical characteristics that are important. The important thing here is that the rate of sustainable growth depends on very unstable parameters or factors. After all, the amount of current assets, i.e. working capital and own working capital are very mobile and depend on many factors: the size of the business; industry affiliation of the enterprise, that is, the type of activity; the growth rate of product sales; structure of working capital; the fate of value added in the price of a product; inflation; the accounting policy of the enterprise; settlement systems and so on. So, the stability of development becomes a derivative, and it can be said without exaggeration, a direct consequence of the stability of the current economic activity of the enterprise.
When assessing the levels of profitability, the following indicators are used:
the total profitability of production, calculated as the ratio of the balance sheet profit to the average annual cost of fixed assets, stocks and costs;
profitability of products sold, calculated as the ratio of profit from products sold in the wholesale prices of the enterprise.
The analysis of the level of profitability is carried out by the elements included in the formula, i.e. the influence of changes in the value of profit from the sale of the cost of OPF and IOS on the level of profitability is revealed. Such an analysis often distorts the economic sense, since by themselves the values of fixed assets and normalized working capital do not show the effectiveness of their use. Any increase in the value of the production facility reduces the level of profitability.
The study of the factors affecting the indicator of profitability of production is carried out in dynamics (in comparison with the data for previous years).
The profitability of products must be analyzed in dynamics over a number of years, identifying the influence of relevant factors.
The factors that mainly affect the profitability of production include:
profitability of products sold;
production capital ratio;
the coefficient of fixing current assets.
Let us now consider these factors in more detail.
Among the factors affecting the profitability of production include the profitability of products sold, the capital intensity of products (return on assets), the coefficient of fixing the working capital (the turnover of working capital). To identify the influence of these factors, we transform the formula for calculating the profitability of production:
We divide both the numerator and the denominator by the amount of proceeds from product sales:

We get R - the profitability of products sold, or a share of profit per 1 ruble. products sold; Fe - capital intensity, which can be obtained as 1 / H; H - the level of return on assets; Кз - the coefficient of fixing, which can be found as 1 / К; K is the turnover ratio.
The study of the factors affecting the indicator of the profitability of production is carried out in dynamics (in comparison with the data for previous years). Assessing the influence of these factors, the following calculations should be performed. Total change in profitability of production (DRpr):

Including:
1) due to a change in the profitability of products -

2) due to changes in the capital intensity of products (return on assets):

3) due to a change in the coefficient of consolidation (turnover) of current assets:

The total value of the influence of three factors will give an overall change in the profitability of production:
Consider the stated analysis methodology using a specific example (Table 1.1).
The level of profitability of production for the reporting year increased by 0.84 points: DRpr = 12.93-12.09 = 0.84. The influence of individual factors was as follows.
1. The increase in the profitability of sold products (works, services) led to an increase in the level of profitability of production by 0.31 kopecks. for each ruble of resources used:
2. Decrease in capital intensity, i.e. an increase in capital productivity of fixed assets, led to an increase in the profitability of production by 0.47 kopecks. for each ruble:
Table 1.1. The profitability of production and its determining factors for the enterprise for the year

3. Decrease in the coefficient of consolidation of material circulating assets, i.e. the acceleration of their turnover, led to an increase in the profitability of production by 0.06 kopecks:
Thus, the overall increase in profitability for all analyzed factors
for every ruble of resources used.
This is the overall change in the profitability of production compared to the data for the previous year (12.93-12.09 = 0.84 kopecks)
The profitability of individual products depends on their market prices and costs.
Let us consider the influence of these factors in the following example (Table 1.2).
Table 1.2. The influence of the market price and cost of the product on its profitability

The profitability of the product increased by 2%, this change was influenced by the increase in price and the rise in the cost of production. To determine the influence of each factor, we will make the following calculations.
where DR (P) is the change in the profitability of the product as a result of price changes; economic financial profitability competitive
Conditional profitability of the product at the base cost and the price of the reporting year;
Consequently, the increase in the market price led to an increase in the profitability of the product by 10.6%.
The increase in the cost of the product reduced its profitability by 8.6%.
The total change in profitability for both factors was (%): 10.6 + (- 8.6) = 2, which corresponds to the data in Table. 1.2. (Note that an alternative analysis gives)
Thus, conducting a deep financial analysis of the company's activities will determine the potential of the company, their compliance with the prevailing market conditions.
 What is KTU in the composition of wages: concept, calculation formula
What is KTU in the composition of wages: concept, calculation formula Product deficit and surplus: definition and implications
Product deficit and surplus: definition and implications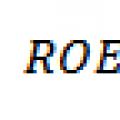 Tutorial: Financial Analysis
Tutorial: Financial Analysis