What marginality is considered good in trading. How the margin is calculated: the difference between mark-up and margin. Examples and formulas
Margin (gross profit, return on sales ) - the difference between the selling price of a commodity unit and the cost of a commodity unit. This difference is usually expressed as profit per unit of production or as a percentage of the selling price (profit margin). In general, margin is a term used in trading, stock exchange, insurance and banking practice to denote the difference between two indicators.
Margin (PE) = OC - CC
Where:
OTs - selling price;
CC - unit cost.
Profitability ratio and profit per unit of production. When marketers and economists talk about margins, it is important to keep in mind the difference between profitability and profit per unit of sales. This difference is easy to reconcile, and managers must be able to switch from one to the other. The margin ratio (profitability ratio) is calculated by the formula:
Margin ratio (KP) = PE / OC
Where:
KP - profitability ratio in%;
PE - profit per unit of production;
OTs - the selling price of a unit of production.
Managers need to know the margin to make almost any marketing decision. Margin is a key factor in pricing, marketing ROI, profit forecasting, and customer profitability analysis.
Gross Margin in Russia. In Russia gross margin is the difference between the company's revenue from product sales and variable costs.
Gross Margin = BP - Zper,
where: ВР - proceeds from product sales;
Zper - variable costs of manufacturing products.
However, this is nothing more than marginal income, margin profit (contribution margin) - the difference between the proceeds from the sale of products and variable costs. Gross margin is a calculated indicator, which in itself does not characterize the financial condition of the company or any of its aspects, but is used in the calculation of a number of financial indicators. The value of the marginal income shows the contribution of the enterprise to covering fixed costs and making a profit.
Gross Margin in Europe... There are discrepancies in the understanding of gross margin that exist in Europe and the concept of margin that exists in Russia. In Europe (more precisely, in the European accounting system) there is a concept Gross margin... Gross margin, (gross margin) is the percentage of total sales revenue that the company leaves after incurred direct costs associated with the production of goods and services sold by the company. The gross margin is calculated as a percentage. These differences are fundamental for the accounting system. For example, the Europeans calculate the gross margin as a percentage, while in Russia the “margin” is understood as profit.
Under average marginal income understand the difference between product price and average variable costs. The average value of the marginal income reflects the contribution of the unit of the product to covering fixed costs and making a profit. The norm of marginal income is the share of the value of the marginal income in the sales proceeds or (for an individual product) the share of the average value of the marginal income in the price of the product. The use of these indicators helps to quickly solve some problems, for example, to determine the amount of profit for different volumes of output. The value of the marginal income shows the contribution of the enterprise to covering fixed costs and making a profit.
Number of impressions: 301,099
Quite often, entrepreneurs start their business on the basis of good margins. She evaluates the profitability of the business. In this article, we will talk in detail about the margin, as well as some of the features associated with it.
It doesn't matter how much income your business generates, it is important that as little money as possible is spent on its production. For example, if you receive $ 100 million a year, but spend $ 100 million and one dollar, then you will not be able to make money on such a business. In order for your business to exist for a long time, it must generate income. No firm will last long if it generates little income. The resulting profit keeps your business afloat.
Every entrepreneur starting his own business must estimate the expected profitability. For your business to be successful, this is a prerequisite. Therefore, before starting your business, you need to calculate the expected marginality. This check will help you save your money and assess the possible risks. You can often observe such a situation when a business starts without miscalculating the risk. We recommend that you do this at the initial fuck of starting your business.
Determination of margin
Margin is an increase in cash equivalent, taking into account costs and the cost of goods. However, such a concept will not give you a complete definition of this monetary instrument. Margins increase if production costs decrease and product prices rise. So, you need to ensure that you maximize your profits by reducing costs. Let's analyze this definition in more detail.
First, you need to supplement the above concept.  Usually, marginality is understood as the increase in money capital per unit of goods.
Usually, marginality is understood as the increase in money capital per unit of goods.
That is, marginality is the difference between all costs that were spent on production and the profit received.
The process of calculating the margin will be carried out both at the start of your business and throughout its entire existence.
The more often you determine the margin, the better your business will be, because you will correctly estimate the expected monetary growth.
Calculation formula
To understand the essence of this procedure, you need to specify the formula for calculating the marginality:
MAR = DOH-ISD
This formula provides us with a visual understanding of the margin calculation process. There is nothing difficult in calculating the margin. Two indicators will be enough for you to determine the profitability of your business.
Let's look at a specific example.
Let's say you need to produce 2,000 units of a product, the market price of which is 20 rubles a piece. Total production costs 25 thousand rubles.
Substituting the data into the above formula:
MAP = 2000 * 20-25000 = 15,000 rubles.
Thus, we have established that the margin of our enterprise will be 15 thousand rubles.
You also need to indicate that the margin can be calculated not in monetary terms, but as a percentage.
Let's look at another example.
Let's say your broker offers you to buy 500 shares at $ 1 each. In addition, he said that their cost next month will be $ 3.
It turns out that you had $ 500, with an investment in the stock market, your amount became equal to $ 1,500.
In formulaic form: MAR = 1500 * 100/500 = 300%
That is, when investing in stocks, your margin will be 300%. Any businessman will tell you that this is a great investment. We will not consider the possibilities of the stock market, but you need to understand that this occupation has its own risks. Therefore, it is up to you whether money matters to you.
Purpose of calculating margin
The purpose of calculating marginality is to assess the profitability of a business.
In order to correctly calculate marginality, you do not need to have a lot of knowledge in the field of economics or investment finance. All you need is to use the above formulas. We recommend that you use a formula to determine the margin as a percentage.
This option will allow you to correctly assess the possibilities of your monetary investment. The margin rate will help determine the expected return over time. Guided by the correct assessment of the situation, you will be able to choose the right solution.
Difference between margin and mark-up
The margin is the difference between the wholesale and retail prices. And we have established earlier that marginality is the difference between profit and cost. So the markup is defined as the difference in relation to the cost price, and the margin will be determined by the difference between the value and the cost price.
Thus, we have established formulas for determining marginality. Which option to choose is up to you. Correctly defined marginality will allow you to settle your money more intelligently.
The economic term "margin" is used not only in trade, exchange transactions, but also in insurance and banking. This term describes the difference between the trade value of a product, which is paid by the buyer, and its cost, which is made up of production costs. For each field of activity, the term will have its own specificity of use: in stock exchange activity, this concept describes the difference in securities prices, interest rates, quotes or other indicators. This is a rather peculiar, non-standard indicator for exchange transactions. In the conditions of brokerage operations on the stock markets, margin acts as a pledge, and trades are called "margin" trades.
In the activities of commercial banks, margin is the difference between the interest on loan products issued and active deposits. One of the most popular concepts in banking is "credit margin". This term helps to describe the difference obtained if the contractual amount is subtracted from the total loan amount handed out to the bank's clients. Another indicator that directly describes the efficiency of banking activities can be considered "net margin" expressed in percent. The calculation is made as finding the difference between capital and net income, measured as a percentage. For any bank, net income is generated through the sale of credit and investment products. When issuing a loan amount secured by property, to determine the profitability of the transaction, a “guarantee margin” is calculated: the amount of the loan amount is deducted from the value of the collateralized property.
The concept of profit is simplified to describe this term. The indicator can be expressed in:
- percent (calculated as the ratio between the difference between the cost and the cost of goods to the cost);
- absolute values - rubles (calculated as a trade margin);
- the ratio of shares (for example, 1: 4, used less often than the first two).
Thanks to this indicator, the costs of delivery, rejection of products, and organization of sales are reimbursed, which are not reflected in the cost of goods. Also, at his expense, the formation of the company's profit occurs.
If the margin does not grow with an increase in trade value, this means that the cost of goods increases faster, and the company risks soon to be unprofitable. To prevent this from happening, the formation of the price of the product must be adjusted.
This indicator is relevant for the calculation, both for large organizations and small ones. Let's summarize why it is needed:
- analysis of the profitability of the organization;
- analysis of the financial condition of the organization, its dynamics;
- when making a responsible decision, in order to justify it;
- forecasting the profitability of potential clients of the organization;
- formation of a price policy for certain groups of goods.
It is used in the analysis of financial activities on a par with net and gross profit both for individual goods or their groups, and for the entire organization as a whole.
Gross margin is the proceeds from the sale of products for a certain period from which the variable costs allocated for the production of these products are deducted. This is an analytical indicator that, when calculating, may include income from other activities of the enterprise: the provision of non-production services, income from the commercial use of housing and communal services and other activities. The indicator of the net profit and the fund allocated for the development of production depend on the indicator of the gross margin. That is, in the economic analysis of the activities of the entire enterprise, it will reflect its profitability, through the share of profit in the total amount of proceeds.
How to calculate the margin
The margin is calculated based on the ratio in which the final result will be expressed: absolute or percentage.
The calculation can be made if the trade margin and the total cost of the goods are accurately indicated. This data allows you to mathematically determine the margin, expressed as a percentage, since the two indicators are interrelated. First, the cost is determined:
Total cost of goods - Trade margin = Cost of goods.
Then we calculate the margin itself:
(Total cost - Cost of goods) / Total cost X 100% = Margin.
Due to different approaches to understanding the margin (as a profit ratio or as a net profit), there are different methods for calculating this indicator. But both methods help in the assessment:
- the possible profitability of the launched project and its development prospects, existence;
- the value of the product life cycle;
- determination of effective volumes of production of goods, products.
Margin formula
If we need to express the indicator in terms of percent, in trading operations, the formula is used to determine the margin:
Margin = (Product cost - Product cost) / Product cost X 100%.
If we express the indicator in absolute terms (foreign or national currency), we use the formula:
Margin = Product cost - Product cost.
What is marginality
Most often, marginality is described as capital gain in monetary terms per unit of output. In general terms, it is the difference between the cost of production and the profit obtained as a result of the sale of products.
Marginality in commerce is called the marginal profit of a product, subject to the minimum cost and the maximum possible margin. In this case, they talk about the high marginality of the enterprise. If the product is sold at a high price, the amount of investment in production is large, but with all this, the profit barely compensates for the costs - we are talking about low marginality, since in this case the profitability (margin) ratio will be quite low. In terms of the "profitability ratio", we take the cost of the goods paid by the consumer as 100%. The profitability of the enterprise is higher, the higher this coefficient.
The marginality of a business, an enterprise is its ability to receive a net income from the invested capital for a certain period, measured in interest.
The procedure for determining the margin is carried out not only at the initial stage of launching the product (or the company as a whole), but also during the entire production period. The constant calculation of the margin allows you to adequately assess the possible inflow of income and the more stable the business development will be.
It should be noted that Russia and Europe have different approaches to understanding marginality. For Russia, the approach is more typical, where net gross income is considered under this concept. Another analogue of this concept is the coverage amount. At the same time, the emphasis is on this amount as part of the revenue that forms the company's profit and is responsible for covering costs. The main principle here is the increase in the profit of the organization in proportion to the reimbursement of production costs.
The European approach tends to reflect the gross margin as a percentage of the total income received after the sale of the product, from which the costs associated with the production of the product have already been deducted.
The main difference in approaches is that the Russian one operates with net profit in monetary units, the European one relies on percentage indicators and is more objective in assessing the financial well-being of an organization.
When calculating marginality, economists pursue the following goals:
- assessment of the prospects of a particular product on the market;
- what is its "lifespan" in the market;
- the ratio of the prospects or risks of bringing the product to the market and the success of the launched enterprise.
It is important to calculate the margin of a product for those firms that are engaged in the production of several types or groups of goods. At the same time, we get indicators of marginality, which can clearly show which of the goods have more chances for the future, and the production of which can, or even need, be abandoned.
Margin and markup their difference
If we express the margin as a percentage, then in this case it is impossible to say that it can be equated to a mark-up. When calculating in this case, the margin will always be higher than the margin. Also, in this case, it can be more than 100% (in contrast to the expression in absolute terms, where it cannot be more than 100%). Example:
Margin = (price of goods (2000 rubles) - cost of goods (1500 rubles)) / cost of goods (1500 rubles) X 100 = 33.3%
Margin = price of goods (2000 rubles) - cost of goods (1500 rubles) = 500 rubles.
Margin = (price of goods (2000 rubles) - cost of goods (1500 rubles)) / price of goods (2000 rubles) X 100 = 25%
If we consider in absolute terms, then 500 p. - this is the margin = mark-up, in the case of calculating as a percentage margin (25%) ≠ mark-up (33.3%).
The resulting markup is the ratio of profit to cost, and margin is the ratio of profit to the trading value of the product.
Another nuance through which you can identify the difference between the concepts of "mark-up" and "margin": the mark-up can be viewed as the difference between the wholesale and retail cost of goods, and the margin - as the difference between cost and cost.
In professional economic analysis, it is important not only to calculate the indicator mathematically correctly, but also to take the initial data necessary for specific circumstances and correctly use the results obtained. Using one or another calculation method, you can get data that is different from each other. But taking into account the conventionality of the considered indicators, for a full and effective description of the economic state of the organization, additional analysis is performed on other indicators.
Many have heard the term "margin", but not everyone understands what it means in reality. In this article, we will take a closer look at what marginality is, how it is calculated and why any entrepreneur or businessman needs to understand this term.
The word marginality is often used today in business, in trade, on the stock exchange and in the banking sector. It denotes the difference between the value of a product (the price at which it is sold) and its actual cost. This term is also used to calculate the profit received from a unit of manufactured goods or services, and to find the profitability ratio, expressed as a percentage of the selling price.
In short, margin is the return on sales. The higher it is, the more the company earns and the higher its profits. If the company has good indicators, then this means that the business is going well, if the margin falls, then it is necessary to revise the policy of work or pricing. That's why the company's management should always know the indicators and compare them for the reporting periods to determine if the correct strategy has been chosen.
So, now you know everything about marginality, what it is and what it is for. Next, we will consider certain nuances of this concept. So, the margin is considered the main factor on the basis of which the calculation of pricing policy, profitability, and enterprise efficiency is based. It is noteworthy that in the Russian Federation most economists and accountants call the marginal profit gross, but this is not entirely correct. Marginality is the difference between the profit received from the sale of services or goods and the costs of the company for their production, excluding value added tax and excise taxes. Sometimes it is even called the amount of coverage, since the margin can also be part of the proceeds used to generate profits, that is, to cover real production costs. It turns out that the growth of the company's profit is directly dependent on the rate of recovery of production costs.
How to count correctly
Next, let's take a look at how the marginality calculation is carried out. It is most correct to tie it exactly to the unit of the released and sold product, and not to the batch or time, since this way you can understand whether the release of the product will increase profits.
Attention: marginality does not show the economic structure or business model of an enterprise. This factor allows you to find unprofitable and profitable products / services and calculate which options are more interesting.
Since profit directly depends on the cost of manufacturing products and the price of goods, in order to achieve its growth, it is necessary to increase sales volumes or raise the margin.
Let's calculate the marginal profit for the product, the cost of which is one thousand rubles. In one cycle, the company produces 100 bearings, while spending 40 thousand rubles on it (this amount includes all variable costs, which include the cost of purchasing raw materials, payments to employees, warehousing, delivery). We consider: MR = 1000 * 100-40,000 = 60,000 rubles. As you can see, there is nothing difficult in counting.
Next, we will analyze how to correctly find additional revenue. To do this, we use the formula MR = TR (V + 1) -TR (V), where TR (V) is the profit that the company makes when selling goods with the available volume of production, and TR (V + 1) is the profit that the company can get it if it starts producing goods in volumes more by 1 piece. It is not difficult to calculate the additional revenue: for example, our conditional workshop receives 60 thousand rubles for 100 bearings. Having released 101 bearings, he will receive 61 thousand, which will be considered additional revenue.
Break even
It should be understood that marginality is considered by separating variable and fixed expense when generating pricing. Fixed costs are those that operate constantly, that is, even if production is not carried out. These include rent, taxes, administrative staff and management salaries, and loan and credit payments.
When the costs of the enterprise are fully paid off by the products sold, the break-even point comes. That is, this is exactly the amount of goods produced and sold that is necessary for the company to fully recoup the costs made, but at the same time not making a profit.
In the picture above, the main indicators are clearly visible. In our case, the break-even point begins after the company produces two dozen units of products (and, accordingly, sells them).
Consider whether there is a difference between marginality and profitability. Profitability is the size of the company's income from its activities. This indicator allows you to determine how efficiently the enterprise is operating. If it is even simpler, then profitability is called between costs and profits, while margin refers to the pricing policy.
How you can increase marginality
A competent leader will always find ways to raise margins. To do this, you need to have a good understanding of the production process, follow market trends, have reliable suppliers and a developed sales network. How to raise this indicator? There are several ways:
- Participate in various tenders in order to increase sales and product value.
- Reducing the level of fixed and variable costs through optimization.
- Increase production in order to spread costs against profit margins.
- Search for new suppliers of raw materials with more interesting prices and offers.
- Capturing new markets, re-profiling production.
A competent approach to marketing will also help increase margins. Often the cost of "promoted" products is higher than that of classic products, which also has a beneficial effect on profits.
Hello dear colleague! Today's article will focus on such a well-known economic term as margin. Many aspiring entrepreneurs, as well as procurement participants, have no idea what it is and how it is calculated. This term, depending on the area in which it is used, has different meanings. Therefore, in this article we will consider the most common types of margin and dwell in detail on the margin in trading. it is she who is of greatest interest to suppliers participating in government and commercial tenders.
1. What is margin in simple terms?
The term "margin" is most commonly found in areas such as trading, stock trading, insurance and banking. Depending on the field of activity in which this term is used, it can have its own specifics.
Margin(from the English. Margin - difference, advantage) - the difference between the prices of goods, stock prices, interest rates and other indicators. Such a difference can be expressed both in absolute terms (for example, ruble, dollar, euro) and as a percentage (%).
In simple words, the margin in trade is the difference between the cost of a product (its manufacturing cost or purchase value) and its final (selling) price. Those. it is a certain indicator of the efficiency of economic activity of a particular company or entrepreneur.
In this case, it is a relative value, which is expressed in% and is determined by the following formula:
M = P / D * 100%,
P - profit, which is determined by the formula:
P = selling price - cost price
D - income (selling price).
In industry, the margin rate is 20% , and in trade - 30% .
However, I would like to note that the margin in our and Western understanding is very different. For European colleagues, it is the ratio of the profit from the sale of a product to its selling price. For us, for the calculation, net profit is used, namely (selling price - cost price).
2. Types of margin
In this section of the article, we will consider the most common types of margin. So let's get started ...
2.1 Gross (gross) margin
Gross margin (English gross margin) is the percentage of the company's total revenue that it retains after incurred direct costs associated with the production of its goods and services.
Gross Margin is calculated using the following formula:
VM = (VP / OP) * 100%,
VP - gross profit, which is defined as:
VP = OP - SS
OP - sales volume (revenue);
CC is the cost of goods sold;
Thus, the higher a company's BM value, the more funds the company saves for each ruble of sales to service its other expenses and obligations.
The ratio of VM to the amount of proceeds from the sale of goods is called the gross margin ratio.
2.2 Profit margin
There is another concept that is similar to gross margin. This concept - profit margin ... This indicator determines the profitability of sales, i.e. share of profit in the total revenue of the company.
2.3 Variation margin
Variation margin - the amount paid / received by the bank or a trading participant on the exchange in connection with a change in the monetary obligation for one position as a result of its market adjustment.
This term is used in exchange activities. In general, there are a lot of calculators for stock traders to calculate the margin. You can easily find them on the Internet for this search query.
2.4 Net Interest Margin (Bank Interest Margin)
Net interest margin - one of the key indicators for assessing the effectiveness of banking. NIM is defined as the ratio of the difference between interest (commission) income and interest (commission) expenses to the assets of a financial institution.
The formula for calculating NIM is as follows:
NPM = (DP - RP) / BP,
DP - interest (commission) income;
RP - interest (commission) expenses;
AD - income-generating assets.
As a rule, the NIM indicators of financial institutions can be found in open sources. This indicator is very important for assessing the stability of a financial institution when opening an account in it.
2.5 Guarantee margin
Guarantee margin - this is the difference between the value of the collateral and the amount of the loan issued.
2.6 Credit margin
Credit margin - the difference between the assessed value of the goods and the size of the credit (loan) issued by the financial institution for the purchase of this product.
2.7 Bank margin
Bank margin (bank margin) is the difference between the rates of loan and deposit interest, loan rates for individual borrowers, or interest rates for active and passive operations.
The BM indicator is influenced by the terms of loans issued, the storage periods of deposits (deposits), as well as the interest on these loans or deposits.
2.8 Front and back margin
These two terms should be considered together because they are related,
Front margin Is the profit from the margin, and back margin Is the profit received by the company from discounts, promotions and bonuses.
3. Margin and Profit: What's the Difference?
Some experts are inclined to believe that margin and profit are equivalent concepts. However, in practice, these concepts differ from each other.
Margin is the difference between indicators, and profit is the final financial result. The formula for calculating profit is shown below:
Profit = V - SP - KI - UZ - PU + PP - VR + VD - PR + PD
B - revenue;
SP is the cost of production;
KI - commercial costs;
UZ - management costs;
PU - interest paid;
PP - interest received;
BP - unrealized expenses;
VD - unrealized income;
ПР - other expenses;
PD - other income.
After that, income tax is charged on the resulting value. And after deducting this tax, it turns out - net profit .
Summing up all of the above, we can say that when calculating the margin, only one type of costs is taken into account - variable costs, which are included in the cost of production. And when calculating profit, all expenses and incomes that the company incurs in the production of its products (or the provision of services) are taken into account.
4. What is the difference between a margin and a mark-up?

Very often, margin is mistakenly confused with a trading margin. Extra charge- the ratio of profit from the sale of goods to its cost. So that you don't have any more confusion, remember one simple rule:
Margin is the ratio of profit to price, and markup is the ratio of profit to cost.
Let's try to determine the difference with a specific example.
Suppose you purchased an item for 1,000 rubles and sold it for 1,500 rubles. Those. the amount of the margin in our case was:
H = (1500-1000) / 1000 * 100% = 50%
Now let's define the size of the margin:
M = (1500-1000) / 1500 * 100% = 33.3%
For clarity, the relationship between margin and margin indicators is shown in the table below:

An important point: The trading margin is very often more than 100% (200, 300, 500 and even 1000%), but the margin cannot exceed 100%.
In order to better understand the difference between these two concepts, I suggest you watch a short video:
5. Conclusion

As you can already understand, margin is an analytical tool for assessing the performance of a company (with the exception of stock trading). And before increasing production, introducing a new product or service to the market, it is necessary to estimate the initial value of the margin. If you increase the selling price of a product, and the size of the margin does not increase, then this only indicates that the amount of costs for its production is also growing. And with such dynamics, there is a risk of being at a loss.
This, perhaps, is all. Hopefully you now have the necessary understanding of what margin is and how it is calculated.
P.S .: If after studying the above material you still have questions, then ask them in the comments to this article. Be sure to like and share links to the article with your friends and colleagues on social networks.

 What is KTU in the composition of wages: concept, calculation formula
What is KTU in the composition of wages: concept, calculation formula Product deficit and surplus: definition and implications
Product deficit and surplus: definition and implications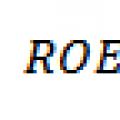 Tutorial: Financial Analysis
Tutorial: Financial Analysis