The concept of enterprise profitability
Profitability(German rentabel - profitable, profitable), a relative indicator of economic efficiency. Profitability comprehensively reflects the degree of efficiency in the use of material, labor and monetary resources, as well as natural resources. The profitability ratio is calculated as the ratio of profit to assets, resources or flows that form it. It can be expressed both in profit per unit of invested funds, and in the profit that each received monetary unit carries.
Among the indicators of the profitability of the enterprise, 5 main ones are distinguished:
1. The total return on investment, showing what part of the balance sheet profit falls on 1 RUB. property of the enterprise, that is, how effectively it is used.
2. Return on investment in terms of net profit.
3. Profitability of own funds, which allows to establish the relationship between the amount of invested own resources and the amount of profit received from their use.
4. The profitability of long-term financial investments, showing the effectiveness of the company's investments in the activities of other organizations.
5. Return on permanent capital. Shows the effectiveness of the use of capital invested in the activities of this enterprise for a long time.
· Overall profitability- the ratio of the balance sheet profit to the average annual value of fixed and current assets. Determined by the formula:
Ro = Pb / F * 100%,
where Ro is the total profitability,
PB - the total amount of balance sheet profit,
Ф - the average annual cost of fixed assets, intangible assets and tangible working capital.
· Return on sales- profit from sales to revenue.
ROS = Profit from sales / Revenue * 100%
· Product profitability- the ratio of (net) profit to total cost.
ROM = PP / Cost * 100%
· Return on equity(ROE) - the ratio of net profit to the average amount of equity capital for the period.
ROE = Net Income / Equity * 100%
· Return on financial investments
It is defined as the ratio of the amount of income from financial investments to the amount of financial investments.
Where Pfv is the profit of the enterprise from financial investments for the period of FV - the amount of financial investments
· Production profitability(cost recovery) (R3) is calculated by the ratio of the balance (PB) or net profit (PP) to the amount of costs for the products sold or manufactured (З):
· Profitability of fixed assets- the ratio of (net) profit to the amount of fixed assets.
ROFA = PE / Fixed assets * 100%
· Return on assets(ROA) - the ratio of operating profit to the average for the period size of total assets.
ROA = Operating Income / Assets * 100%
· profitability of current assets
It is defined as the ratio of net profit (profit after tax) to the company's current assets. This indicator reflects the ability of the company to ensure a sufficient amount of profit in relation to the used working capital of the company. The higher the value of this coefficient, the more efficiently the circulating assets are used.
Where NP is the net profit of OA - the average annual value of current assets
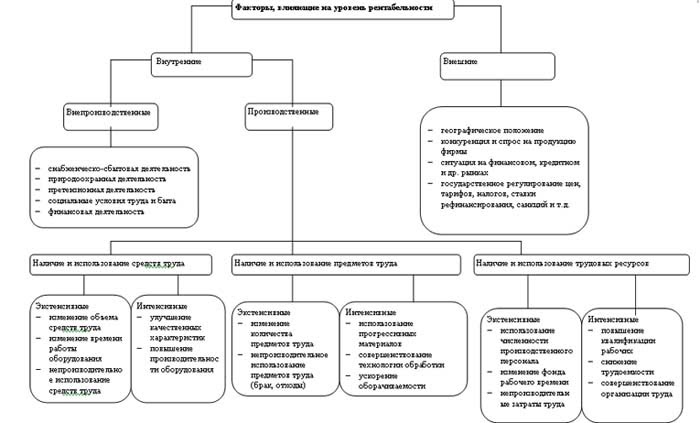
49. The break-even operation of the enterprise depends on many factors, including the choice of the optimal volume of production and the expedient pace of development of the enterprise; for the analysis of break-even, it is necessary to be able to determine the break-even point (self-sufficiency) of the enterprise.
Break even(critical volume of production (sales)) is the volume of sales at which the revenues received ensure the reimbursement of all costs and expenses, but do not make it possible to make a profit, in other words, this is the lower limit of the volume of output at which the profit is zero.
The break-even point is characterized by the following indicators:
1. Critical (threshold) sales volume, pcs. =
Fixed costs for the volume of sales:
: Price - Average variable cost per unit of output.
2. Threshold of profitability, rub. = Critical volume of sales, pcs. x Price.
3. The margin of financial strength, rub. = Sales revenue, rub. - Threshold of profitability, rub.
4. Security margin, pcs. = Sales volume, pcs. - Critical volume of sales, pcs.
The last two indicators assess how far the enterprise is from the breakeven point. This influences the priority of management decisions. If the enterprise approaches the break-even point, then the management problem increases fixed costs, as their share in the value increases. Conditional fixed costs - these are depreciation charges, management and repair costs, rent, interest on a loan, taxes attributed to the cost of production, etc. Profitability threshold - it is such a proceeds from sales in which the enterprise no longer has losses, but does not yet receive profits. Financial safety margin- This is the amount by which the company can afford to reduce revenue without leaving the profit zone.
50. Evaluation of the effectiveness of investment projects produced by calculating a number of indicators:
Net present value (NPV), i.e. E int is defined as the sum of current effects for the entire calculation period, reduced to the initial step, or as the excess of the integral results over the integral costs and is calculated by the formula
where r t - the results achieved at the t-th calculation step;
З t - costs incurred at the t-th step;
T is the time period for the calculation;
E is the discount rate.
The time period for the calculation is taken based on the timing of the project, including the time of the establishment of the enterprise (production), its operation and liquidation.
If NPV value investment project positive, then it is recognized as effective, i.e. providing the level of investment investments not less than the accepted discount rate.
51. To assess the financial stability of the enterprise the autonomy ratio and the financial stability ratio are used.
The autonomy coefficient characterizes the independence of the enterprise from borrowed sources of raising funds and reflects the ratio of equity capital to the balance sheet total:
K auto = SS / B,
where K av is the coefficient of autonomy;
SS - own funds (rubles);
B - balance sheet total (rubles).
The financial stability ratio is the ratio of the company's own funds:
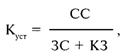
where K mouth is the coefficient of financial stability;
ЗС - borrowed funds (rubles);
KZ - accounts payable (rubles).
The ratio of equity and borrowed capital is largely determined by the condition of the interest rate on borrowed funds and the efficiency of the enterprise's use of equity capital. The excess of own funds over borrowed funds indicates a sufficient margin of financial stability of the enterprise and its relative independence from external sources of financing.
The financial stability of an enterprise is determined not only by the compliance with the "standard" of the autonomy coefficient (the minimum value of this indicator is taken at the level of 0.6), but also by the correctness of investments in its assets of equity capital. Practice determines that at least 1/3 of equity capital should be included in the working capital.
The amount of own circulating assets is determined as the difference between the amount of own funds and fixed assets and investments:
SOBS = SS - OS,
where SOBS - own circulating assets (rubles);
OS - fixed assets and investments (rubles).
The ratio of own working capital to the total amount of equity capital reflects the coefficient of maneuverability K man
![]()
When analyzing the financial condition of an enterprise, it is advisable to pay attention to the correct use of its own circulating assets and to identify their immobilization, i.e. their use for other purposes (in fixed assets, intangible assets and long-term financial investments).
52. Payback period – this is the expected number of years required to fully recover the investment costs.
The payback period calculation scheme includes the following stages:
1) calculation of the discounted cash flow of income for the project based on the discount rate and the period of income;
2) the calculation of the accumulated discounted cash flow as an algebraic sum of costs and income flow for the project is performed until the first positive value is obtained;
3) determination of the payback period T ok by formula (3.3). The payback period is calculated as follows:
where No. o- the number of years preceding the payback year; C n- unreimbursed cost at the beginning of the payback year; DDP g.o- discounted cash flow in the payback year.
53. The financial plan of the enterprise: concept, composition.
Financial plan is a comprehensive plan for the functioning and development of an enterprise in value (monetary) terms. In financial terms, the efficiency and financial results of the production, investment and financial activities of the firm are forecasted.
The financial plan reflects the final results of production and economic activities. It covers inventory items, financial flows of all structural units, their relationship and interdependence.
Financial plan is the final synthesizing and reflecting in value terms the results of the firm's activities. The information base for drawing up a financial plan is mainly accounting documentation. First of all, these are the balance sheet and balance sheet supplements.
In the financial plan of the company, the enterprises are reflected:
§ income and receipts of funds;
§ expenses and deductions of funds;
§ credit relationships;
§ relationship with the budget.
The results of calculations of the specified income and expenses are summarized in the form "Balance of income and expenses". The financial planning documents also include the company's balance sheet.
Financial plan composition
The financial plan includes three documents:
Report about incomes and material losses. With its help, the size of the profit received for a specific period of time is determined. The purpose of compiling profit reports is to summarize the results of the enterprise in terms of profitability.
This part usually consists of the following sections:
In many cases, the plan shows what comes after taxes. The profit statement is the most common indicator of a company's financial reserves.
Balance plan shows the financial condition of the company at the end of the calculated period of time. From his analysis, one can draw conclusions about the growth of assets and the stability of the financial position of the company in a specific period of time.
Cash flow statement characterizes the formation and outflow of cash, as well as cash balances of the company in dynamics. Cash flow projection is the most important financial forecast in a business plan. The cash flow statement reflects the actual cash inflows and their transfer. The final figure of the cash flow statement reflects balance of the company's cash turnover rather than its profit. Unlike the statement of income, the statement of cash flows reflects the actual receipt of all money from all sources, including revenue from sales of products, from the sale of shares or received on debt, as well as funds from the sale or liquidation of certain assets. For costs, the actual payment of all costs is included in the cash flow statement. Some costs can be covered immediately, while others can be covered over time.
Not included in the statement of funds depreciation... Although it is an expense, it does not constitute a monetary obligation. At the same time, the repayment of the principal amount of the debt, although not an expense, is included in the statement of cash flows, as it is a cash liability. Other spending of money aimed at purchasing equipment or paying dividends is not a cost. Therefore, they affect cash flows.
The final part of the financial plan usually contains break-even analysis, demonstrating what the sales volume should be in order for the company to be able to fulfill its timely monetary obligations without assistance. Such an analysis allows one to obtain estimate of the amount of sales, which is necessary for the company to have no losses.
54. Marketing research(eng. marketing research) is a form of business research and an area of applied sociology that focuses on understanding the behavior, desires and preferences of consumers, competitors and markets in a market-driven economy. Marketing research – This, first of all, the study of the market and its conjuncture, the assessment of the capabilities of the enterprise. Marketing research provide a comprehensive assessment and analysis of markets, allow you to study consumer behavior.
Marketing Research Objectives:
- Search goals - collection of information for a preliminary assessment of the problem and its structuring;
- Descriptive goals - a description of the selected phenomena, objects of study and factors affecting their condition;
- Causal goals - testing the hypothesis about the presence of some causal relationship;
- Test goals - selection of promising options or assessment of the correctness of decisions made;
- Predictive goals - predicting the state of an object in the future.
 Discounted payback period
Discounted payback period Methodological aspects of project management
Methodological aspects of project management Scrum development methodology
Scrum development methodology