Methods and sources of financing investment activities
Investment financing is the process of accumulating and efficiently spending money for the acquisition of elements of fixed and working capital, including new construction, expansion, reconstruction and technical renovation of existing enterprises, the acquisition of machinery and equipment, the creation of inventories, etc. When financing investments, the following times are decided.
The system of financial support for the investment process is based on determining the sources of its financing. Sources of investment financing are understood as funds and cash flows that allow the investment process to be carried out. The sources of the formation of investment resources can be classified according to various criteria.
Types of investment financing sources:
- 1. In relation to the subject of investment:
- - external;
- - internal.
Internal and external sources of financing form the so-called financing potential, showing the real possibilities of economic entities to invest in certain projects that provide cash receipts over a certain period of time.
- 2. By nationality of the investor:
- - domestic;
- - foreign.
- 3. By title of ownership:
- - own - funds of the enterprise, providing investment activities, belonging to him on the basis of property rights;
- - borrowed - monetary resources received for a certain period, subject to return, as a rule, with the payment of interest.
There are three main economic entities - the consumer of investment resources:
- - the state represented by government bodies;
- - enterprises and entrepreneurs;
- - population as a set of households.
Determining and finding sources of investment financing is the main issue of all investment projects. The need for differentiation and accounting for sources is determined by the different cost of attracting them. The systemic classification of investment sources presupposes, first of all, the division of funding levels. The macrolevel (national economy) and microlevel (enterprise) of investment financing are distinguished.
At the macroeconomic level, domestic sources of investment financing include savings made by commercial and non-profit organizations and citizens, as well as centralized allocations, while external sources are funds received from abroad, including the funds of residents transferred from abroad (repatriated capital) and foreign sources.
The state needs investments to invest in the social and cultural sphere, science, education, defense, state infrastructure facilities, environmental protection, ensuring internal security, financing federal and regional investment programs, etc. The main sources of public investment are shown in Fig. 2.2.
Rice. 2.2.
At the microeconomic level, internal sources of investment are the own funds of enterprises, and external sources are attracted and borrowed funds. Enterprises of various forms of ownership, companies, firms, entrepreneurs are the central agent for attracting and using industrial investments.
All sources of formation of investment resources of the enterprise can be divided into the following groups (Fig. 2.3): external and internal; own, borrowed and borrowed.
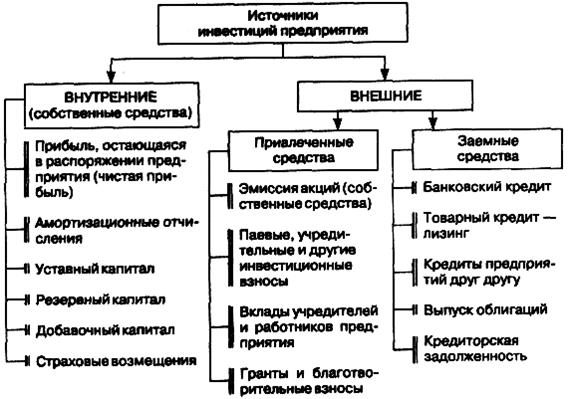
Rice. 2.3.
Own investments are understood as funds of legal entities and individuals allocated for financing on a profit-sharing basis. Own sources of investment include: the reinvested part of net profit, depreciation charges, insurance compensation for losses, etc. Consider the main sources of own financing of investment resources.
Borrowed funds are funds of legal entities and individuals that are directed to finance investments on the terms of a loan for a certain period and are subject to return with payment of interest. Borrowed funds include funds received from the issue of bonds, other debt obligations, as well as loans from banks, other financial and credit institutions, enterprises, and the state.
The attracted funds include funds provided on a permanent basis, on which income can be paid to the owners of these funds (in the form of interest, dividends). These include funds from the issue of shares, additional contributions (shares) to the authorized capital, targeted government funding, etc.
The ratio of own and borrowed sources forms the structure of investment financing and depends on such factors as the development of the financial market, the technical complexity and duration of the project, the established practice of project implementation at the enterprise, the level of financial stability of the enterprise, etc.
The choice of investment financing sources should be focused on optimizing their structure. In this case, one should take into account the advantages and disadvantages of each group of funding sources (Table 2.1).
Table 2.1
Advantages and Disadvantages of Internal and External Funding Sources
|
Dignity |
disadvantages |
|
Internal sources |
|
|
Simplicity and speed of attraction No obvious costs Reducing the risk of insolvency and bankruptcy Retention of ownership and management of the enterprise |
Limited volume of attraction Diversion of own funds from economic turnover Limitations of independent control over the efficiency of the use of investment resources |
|
External sources |
|
|
Significant volume Potential increase in efficiency due to the effect of financial leverage Availability of independent control over the efficiency of the use of investment resources |
Complexity and duration of attraction and registration Costs (interest, dividends) Increased risk of insolvency and bankruptcy of the company Possibility of loss of ownership and management of the enterprise |
The choice of sources for the formation of investment resources is carried out taking into account the following factors:
- 1. Sectoral features of the production activity of the enterprise, which determine the structure of assets and liquidity of the enterprise. Thus, enterprises with a high share of non-current assets, as a rule, have a low credit rating and are forced to rely on their own sources.
- 2. The size of the enterprise. The smaller the size of the enterprise, the more it should be guided by its own sources, and vice versa.
- 3. The cost of capital raised from various sources. In general, the cost of borrowed capital is usually lower than the cost of equity. However, for individual sources of borrowed investment resources, the cost may fluctuate significantly depending on the creditworthiness of the enterprise, the form of loan security, etc.
- 4. Freedom of choice of funding sources. Not all sources are equally available to businesses. For example, budget investments, targeted and preferential government loans can be obtained only by a few of the most significant enterprises.
- 5. The conjuncture of the capital market affects the change in the cost of borrowed capital. With a significant increase in this cost, the attraction of bank loans becomes unprofitable for enterprises.
- 6. The level of taxation of profits. In conditions of low income tax rates, it is more preferable to form the investment resources of an enterprise from its own sources, with a high taxation rate of profit, the efficiency of raising capital from borrowed sources increases.
- 7. The measure of the accepted risk in the formation of investment resources. Aversion to high levels of risk forms a conservative approach to investment financing, in which they are based on their own funds, and vice versa.
- 8. The specified level of concentration of equity capital to ensure the required level of financial control. This factor is important for joint stock companies. It characterizes the proportions in the volume of subscriptions to shares purchased by founders and other investors (shareholders).
In general, the system of financial support for investment activities consists of the unity of two subsystems:
- - - methods of financing investments - this is a mechanism for attracting investment resources in order to finance the investment process.
- - sources of financing for investment activities - funds that can be used as investment resources.
Methods of financing real investments:
- - self-financing (internal sources of financing),
- - financing through capital market mechanisms,
- - raising capital through the credit market,
- - budget financing,
- - Combined investment financing schemes.
Each of the methods of financing investments provides for the availability of certain sources of financing.
 Discounted payback period
Discounted payback period Methodological aspects of project management
Methodological aspects of project management Scrum development methodology
Scrum development methodology