Start of a business plan for an investment project
In this article, we begin to consider the issues directly. There are three known reasons when it is required to prepare a business plan for an investment project: opening a new business, a new direction of an existing company and creating a new market product. Almost every businessman is faced with business planning, and a reasonable question often arises: where to start, how to act competently and accurately from the first steps?
Initial requirements for a business plan
Suppose an entrepreneur or company leader intends to prepare a business plan on his own, without the involvement of consultants. Even if a company has economists on its staff, it is best to pilot it under the auspices of a decision maker. This significantly improves the overall quality of work and further seriously helps to put business planning (BPL) on stream. In addition, if a business person himself participates in planning, research and analysis, at least in a supervising aspect, the process of negotiations with potential investors is facilitated. The reasoning in the mouth of a competent leader is strengthened and the rationale becomes more powerful.
The goal of the business plan is to convince the main stakeholders of the competence of the developer, the reliability of the data included in the business plan, the literacy of calculations and the effectiveness of participation in the project. Therefore, the development of a business plan for an investment project is based on the strength of its idea, the realism of market forecasts, the consistency of financial plans and the accuracy of economic calculations. By a business plan, we mean a document that logically consistently presents a comprehensive justification for the success of an investment project.
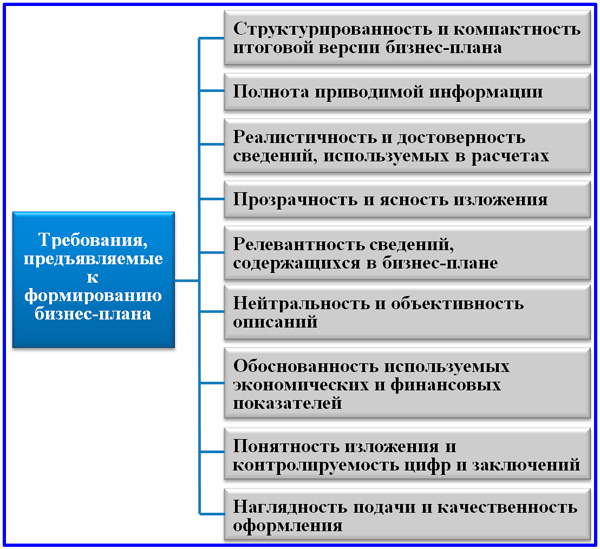
The composition of the requirements for the document of the business plan of the investment project
The plan uses investment marketing, planning, financial performance assessment and simulation tools. It works as a detailed providing factor in the process of persuading the investor, lender, decision maker on the part of the customer. The basic principles of the LTP are set out in the material devoted to. When starting to develop a business plan, in addition to the principles, it is also important to take into account the requirements that apply to the business plan as a presentation document (the diagram presented above). Let's consider some of these requirements.
- Structuredness and compactness of the document. In business, there have been unified requirements for the form, composition and sequence of the main sections of the plan that have been developed for decades. This document should not be excessively large, its maximum length is no more than 50-70 pages.
- Realism and reliability of information. The information that is accepted for calculations must be confirmed by real statistics and data from comparative studies (benchmarking). Information on the external investment environment, sales and internal resource costs must be adequate, reliable and verifiable. Getting some reliable data is very laborious. It is important not to allow adventurous connivance in specifying numbers, which, when checking them, can discredit the entire business plan.
- The relevance of the information used in the calculations. Non-specific, overly generalized conclusions, forecasts for planning actions are unacceptable. Little specific and insignificant facts should also not be accepted for application.
Compliance with the structure of the business plan
The structure of a business plan for an investment project in ordinary activities is not something rigidly formalized. It depends on the field of activity, the size of the project and the type of participants to whom this document is focused. For example, some banks offer borrowers forms for consideration by credit committees. The same practice is used by regional business incubators and republican, regional ministries of economic development for the purpose of making decisions on the allocation of grants.
The article devoted to the comparative analysis of the composition of the sections of the business plan for the main international methods used in Russia (UNIDO, EBRD, KPMG, BFM Group). The most widespread is the implementation of the UNIDO methodology and the corresponding LTP structure. Below are the typical sections of the document that are included in the most detailed version of the business plan.
- Title page.
- Confidentiality Memorandum.
- Summary.
- Introduction.
- Description of the industry, company and its current activities.
- Description of the project and its product (sometimes included in the marketing plan).
- Marketing plan.
- Production and sales plan.
- Investment plan.
- Organizational plan.
- Financial plan.
- Organizational and legal aspects.
- Financial and economic analysis and assessment of the effectiveness of the project.
- Guarantees and risks.
- Applications.
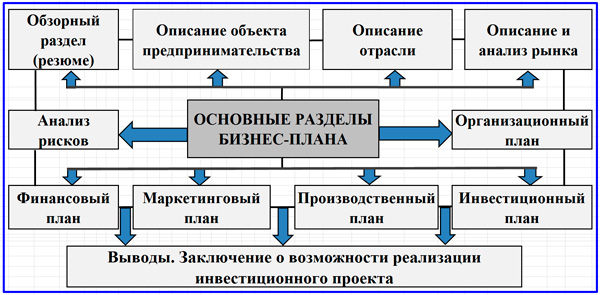
Project business plan structure
The presented sections in their entirety are drawn up for medium and large projects, the implementation of which is carried out with the attraction of significant financial resources from external sources. In such cases, a standardized full justification is required that the profitability and efficiency of the project will not only generate sufficient profit, but also repay the loan on time. The main points, carefully analyzed by banking experts, relate to marketing, financial plans, sustainability, efficiency, break-even analysis and risk assessment.
If the project does not require the attraction of significant investments or significant borrowings, the BPL can be carried out for internal purposes, then in a number of sections there is no need for it. So, for example, you do not need a confidentiality memorandum, part of the introduction, a description of the industry and the company, organizational and legal aspects. The investment plan can be combined with the financial plan, other main sections remain unchanged or somewhat reduced according to the requests of the management. The development and execution of a business plan must comply with the principle of economic feasibility. In some cases, the document is "compressed" to fit the size of a business case in a small Excel file.
Introductory sections of the business plan
The executive summary, confidentiality memorandum and title page of the document are finalized last. The most difficult thing here is the preparation of a resume, which is formed as an advertising brochure of the project as a kind of "business plan in miniature". It is customary to deal with it after the main sections have already been completed, and this is quite reasonable. This is due to the fact that an important component of the overview section is the conclusions on the economic results and project efficiency that arise at the end of the calculations.
The first section is the Introduction, no more than half a page in length. It briefly reveals the main essence of the presented investment project. The reader of this section should understand where the main idea of the project task came from. The introduction usually includes:
- basic prerequisites for the project;
- ideas and goals of the project;
- initiators;
- regulatory documents - the basis for planning.
In the second section of the introductory-descriptive part of the document, the characteristics of the industry are presented, the reader is introduced to the current activities of the enterprise. The industry description provides an analytical overview of the state and problems of the industry in which the company operates. Among the key aspects of the description are reflected:
- products of the industry economy;
- structure of production and capacity;
- the dynamics of the development of the raw material base of the industry;
- the level of depreciation and renewal of the OPF;
- the state of the material and technical base of the industry;
- description of the investment climate;
- implementation of industry development programs;
- the structure of the market segment in which the company operates;
- the size of the industry market and its prospects;
- consumer structure of the industry.
Describing the company and its current activities, it should be remembered that an investment project is conceived as a task of developing an enterprise - a consumer of a project product, which is often the initiator of investments in its fixed assets. Information material, digital data of this part of the section should be as relevant as possible. The following items are included in the enterprise description subsection.
- Historical reference.
- Legal status and environment of the company (details, licenses, certificates, etc.).
- Company management.
- Personnel and organization structure.
- Activities.
- Market position and main customers.
- Industrial complex.
- Analysis of production and economic activities.
- Analysis of the financial situation.
In this article, we examined the initial points of business planning for a new activity: an entire business, a strategic business unit, or the introduction of a new product. The business plan of an investment project should inspire not only investors, credit experts-economists, but also direct developers and executors to participate in its implementation. Therefore, it is of particular importance how the business plan will be structured and presented to the reader, how its introductory and descriptive part will look. It is she and the resume that create the first impression, a sense of a professional approach and competence.
 Discounted payback period
Discounted payback period Methodological aspects of project management
Methodological aspects of project management Scrum development methodology
Scrum development methodology