Project management systems overview
Basic concepts of project management
The project is called a set of events or works distributed over time, aimed at achieving a goal. Examples of projects are the construction of buildings, complexes, enterprises, mastering the release of a new type of product, modernizing production, developing a software product, etc.
The project has certain properties.
- The project always has a clearly defined goal, which is expressed in obtaining some result. Achieving this result means the successful completion and completion of the project. For example, for a building project, the result is the building itself, taken into use.
- The project has a well-defined beginning, which coincides with the beginning of the first work aimed at achieving the set goal. The beginning can be specified directively, or calculated as a result of drawing up a work plan for the project.
- The project has a well-defined end, which coincides with the end of the last work aimed at achieving the desired result. Like the beginning, the end of the project can be specified directively, or calculated when drawing up a work plan. For example, for a building construction project, the end of the project coincides with the date of its delivery / acceptance certificate.
- The project is executed by a team, which includes the project manager, managers, executors. In addition to the main team, it may involve third-party performers, teams and organizations that are involved on a temporary basis to perform certain work.
- Material resources are used in the implementation of the project. Their nomenclature and quantity are determined by the nature of the project and the work included in it. So when building a house, sand, crushed stone, cement, brick, etc. are used.
- The project has a budget. The cost of the project consists of the cost of the material resources expended, the cost of remuneration of the team that implements it, and other costs associated with the specifics of specific types of work.
- The project has three types of limitations.
- Budget constraints set the marginal cost of the entire project or specific types of work.
- Time constraints set deadlines for the completion of either the entire project or some work. For example, test trials should be carried out in the presence of a customer representative who will be present for a specified period of time.
- Resource constraints are determined by limited team composition or material resource flow schedules.
Project life cycle- this is the period of time between the moments of its beginning and end. It is divided into four phases.
- Conceptual phase. Includes formulation of goals, analysis of investment opportunities, feasibility studies (feasibility studies) and project planning.
- Project development phase. Includes determination of the structure of work and performers, construction of work schedules, project budget, development of design and estimate documentation, negotiations and conclusion of contracts with contractors and suppliers.
- Project execution phase. Includes project implementation work, including construction, marketing, staff training, etc.
- Project completion phase. In general, it includes acceptance tests, trial operation and commissioning of the project.
Project result- this is some product or useful effect created during the implementation of the project. As a result, depending on the purpose of the project, there may be: scientific development, a new technological process, a software tool, a construction object, an implemented training program, a restructured company, a certified quality system, etc. The success of a project is judged by how much its result corresponds to the planned level in terms of its costly, profitable, innovative, quality, time, social, environmental and other characteristics.
Controlled parameters project are:
- volumes and types of work;
- cost, costs, costs of the project;
- time parameters, including the timing, duration and reserves of work and project stages, as well as the relationship between works;
- the resources required to implement the project, including human or labor, financial, logistical, and resource constraints;
- the quality of design solutions, resources used, project components, etc.
Tasks project management are:
- defining the purpose of the project and conducting its justification;
- creation of the project structure (sub-goals, main stages of work to be performed);
- determination of the required volumes and sources of financing;
- selection of a team of performers, preparation and conclusion of contracts with third-party performers;
- determination of the project deadline:
- scheduling its implementation:
- calculation of material resources required for the project, conclusion of contracts with suppliers;
- calculation of the estimate and budget of the project:
- planning and risk accounting;
- ensuring control over the progress of the project.
Project management Is a process of planning, organizing and managing work and resources aimed at achieving a set goal, as a rule, under conditions of time constraints, available resources or the cost of work.
Project management consists of three main stages:
- formation of a project plan,
- control over the implementation of the plan and its prompt correction,
- completion of the project.
At the first stage, the project is justified, a list of works and available resources is drawn up, resources are allocated by work and the plan is optimized according to the criteria of the project completion time, the total project cost, even distribution of resources, and risk minimization. Here, all the necessary contracts are concluded with third-party performers, contractors and suppliers. The second stage involves monitoring the implementation of the project in order to timely identify and eliminate emerging deviations from the original plan. In case of significant deviations, the original plan is revised and a new one is drawn up. Completion of a project means the implementation of certain regulated actions necessary to complete and terminate work on the project. For example, the signing of the acceptance / delivery certificate of the work performed.
Currently, a network planning and management methodology is used for automated project management. This methodology was developed in 1956 by specialists from DuPont and Remington Red, M. Walker and D. Kelly, for a project to modernize the factories of DuPont. An impressive result of its use is the design by Lockheed Corporation of the Polaris missile system to equip US Navy submarines. As a result of the application of network planning methods, the work was completed two years ahead of schedule! One of the examples of the successful application of this method in Russia is the restoration of the Cathedral of Christ the Savior in Moscow.
Network planning and management consists of structural and scheduling planning and operational management.
Structural planning consists in dividing the project into stages and works, assessing their duration, determining the sequence of their implementation. The result of structural planning is a network work schedule that is used to optimize the project in terms of duration.
Scheduling consists in drawing up a time chart of work and the distribution of labor resources (performers) between the works. The result of scheduling is a Gantt chart that graphically displays work execution periods on a time axis. At this stage, the optimization of the resources and the budget of the project can be carried out.
Operational management consists in regularly comparing the actual work schedule with the planned one. Major deviations result in decisions to change the original structural or timetable.
Project management systems overview
Project management systems form a separate software sector, which is widely represented on the Russian market. The emergence of such systems has helped transform the art of project management into a science with clear standards, methods and technologies.
- The standard developed by the Project Management Institute is accepted as the national standard in the United States (ANSI standard).
- ISO 10006 Project Management Quality Standard.
The use of these technologies contributes to the timely implementation of projects within the allocated budgets and with the required quality.
Project management systems are used to solve the following main tasks.
- Structuring and describing the composition and characteristics of work, resources, costs and revenues of the project.
- Calculation of the schedule for the execution of project work, taking into account all existing restrictions.
- Determination of critical operations and time reserves for the execution of other project operations.
- Calculation of the project budget and distribution of planned costs over time.
- Calculation of the time distribution of the project's need for basic materials and equipment.
- Determination of the optimal composition of project resources and the distribution in time of their planned load.
- Analysis of risks and determination of the necessary reserves for the reliable implementation of the project.
- Determination of the likelihood of successful implementation of prescriptive indicators.
- Record keeping and analysis of project execution.
- Modeling the consequences of managerial influences in order to make optimal decisions.
- Maintaining project archives.
- Obtaining the required reporting.
Several project management systems are currently the most popular on the Russian market.
Microsoft Office Project 2007 Is a comprehensive solution of Microsoft Corporation for corporate project management, which allows you to manage projects of any complexity and includes a family of the following software products:
- MS Office Project Standart- entry-level package for managing simple projects;
- MS Office Project Professional- a package for professional project management of any complexity at any management level;
- MS Office Project Server- a server product that is used for interaction of project managers in managing distributed projects;
- MS Office Project Web Access- MS Project web interface, which allows project participants to access project information via Internet Explorer.
Spider Project Professional(there are also Desktop and Lite versions, developed by "Spider Management Technologies") - a project management package designed and developed taking into account practical experience, needs, features and priorities of the Russian market. This package is the only domestic development among the project management systems popular in Russia.
This package, unlike Western counterparts, has the following features:
- built-in system for risk analysis and management of reserves by time and cost of work;
- the ability to create, store and include typical project fragments in projects;
- organization of group work and multi-project management optimized for Russian conditions.
Company software products Primavera Inc:
- Primavera Project Planner Professional- professional version designed to automate project management processes in accordance with the requirements of PMI (Project Management Institute) and ISO standards. First of all, this package is intended for use as part of a corporate information system, although it can also work autonomously, helping to solve the problems of scheduling and network planning, determining the critical path, leveling resources, and other tasks of modeling projects, groups of projects, portfolios and programs.
- SureTrack Project Manager focused on monitoring the implementation of small projects or fragments of large projects. It can work both independently and together with Project Planner in the corporate project management system.
Open Plan(a developer of Welcom Software Technology, now Deltek) provides full-scale multi-project management, critical path planning and resource optimization across the enterprise. It can be effectively used at all levels of project control and management - from top management and project managers to heads of functional departments and ordinary executors.
Open Plan allows leaders of all levels to perform the following functions:
- create operational project plans taking into account various constraints;
- determine the level of priority of projects;
- set the relative importance of projects for resource allocation;
- minimize risks;
- analyze the progress of work.
Welcom offers to use the professional and "light" version of the product in combination (OpenPlan Professional + OpenPlan Desktop), as they are fully integrated.
For creating computer model project using one of the systems mentioned, you need to do the following steps.
- An enlarged description of the project - to create a hierarchical structure of work.
- Specify which cost components will be used for financial analysis and project management.
- Make a list of operations (work, tasks) of the project and set their characteristics.
- Make a list of project resources and set their characteristics,
- Set relationships (restrictions on the order of execution) of project operations.
- Assign resources to execute project operations.
- Assign costs to activities, resources, and project assignments.
- Set limits on financing, supplies, deadlines for the execution of operations.
- Draw up a schedule for the execution of the project's work, taking into account all the restrictions.
- Optimize the composition of the resources used.
- Determine the budget and distribution over time of the planned costs of the project.
- Identify and model risks and uncertainties.
- Determine the necessary reserves, costs and requirements for materials to fulfill the planned indicators with a given reliability.
- Provide planned information to management and executors.
In the course of project execution, these systems allow.
- Keep records.
- Analyze deviations from planned execution.
- Predict the future parameters of the project.
- Simulate management impacts.
- Maintain project archives.
1.3. Control questions
- What is a project?
- What properties does the project have?
- What is the project life cycle and what are its phases?
- What is the result of the project?
- Which project parameters are managed?
- What tasks are solved in project management?
- What is meant by project management and what are its main stages?
- What are the components of network planning and management?
- For what tasks are project management systems used?
- What project management systems are common in the Russian software market?
- What steps should be taken to create a computer model of the project?
- What project controls do project management systems have?
Theoretical course
2.1.1. Structural planning
Structural planning includes several stages:
- splitting the project into a set of individual works, the performance of which is necessary for the implementation of the project;
- building a network diagram describing the sequence of work;
- assessment of the timing of the work and analysis of the network schedule.
The main role at the stage of structural planning is played by the network schedule.
Network schedule Is a directed graph, in which the vertices indicate the work of the project, and the arcs are the temporary relationships of the work.
The network schedule must satisfy the following properties.
- Each job corresponds to one and only one vertex. No work can be shown twice on the network. However, any job can be split into several separate jobs, each of which will correspond to a separate top of the graph.
- No work can be started before all the work immediately preceding it has finished. That is, if arcs enter a vertex, then work can begin only after the end of all work from which these arcs exit.
- No work that immediately follows some work can begin until the moment it is finished. In other words, if several arcs leave the job, then none of the jobs that include these arcs can start before the end of this job.
- The beginning and the end of the project are indicated by works with zero duration. Such works are called milestones and indicate the beginning or end of the most important stages of the project.
Example... As an example, consider the project "Development of a software package". Suppose that the project consists of activities, the characteristics of which are shown in Table 2.1.
The network diagram for this project is shown in Figure 2.1. On it, the vertices corresponding to normal jobs are outlined with a thin line, and a thick line outlined the milestones of the project.
Rice. 2.1. Project Network Schedule
The network schedule allows you to find the critical work of the project and its critical path by the specified values of the duration of the work.
Critical is a job for which a delay in its start will result in a delay in the completion date of the project as a whole. Such works have no time reserve. Non-critical jobs have a certain margin of time, and within this margin, their start may be delayed.
Critical path Is the path from the start to the end top of the network, passing only through critical jobs. The total duration of the work on the critical path determines the minimum project implementation time.
Finding the critical path is reduced to finding critical jobs and is done in two stages.
- Calculation early start time each work of the project. This value shows the time before which work cannot be started.
- Calculation late start time each work of the project. This value shows the time after which work cannot be started without increasing the duration of the entire project.
Critical works have the same meaning of early and late start times.
Let's designate - the time of work execution, - the early start time of work, - the late start time of work. Then
![]()
where is the set of works immediately preceding the work. The early time of the initial work of the project is taken to be zero.
Since the last work of the project is a zero-duration milestone, its early start time coincides with the duration of the entire project. Let's designate this value. Now it is taken as the late start time of the last job, and for other jobs, the late start time is calculated by the formula:
![]()
There are many works here, immediately following the work.
Schematically, the calculations of the early and late start times are shown, respectively, in Fig. 2.2 and Figure 2.3.
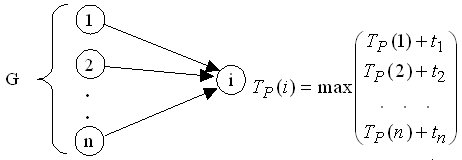
Rice. 2.2. Scheme for calculating early start time
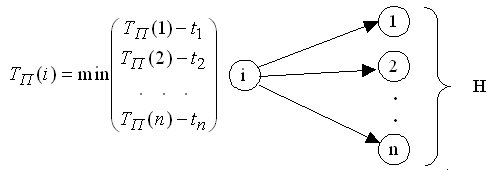
Rice. 2.3. Scheme for calculating late start time
Example... Let's find the critical work and the critical path for the project "Development of a software package", the network diagram of which is shown in Fig.2.1, and the duration of the work is calculated in days and is set in Table 2.1.
First, we calculate the early start time of each job. Calculations start from the initial and end with the final work of the project. The process and results of calculations are shown in Figure 2.4.
The result of the first stage, in addition to the early start time, is the overall duration of the project.
At the next stage, we calculate the late start time of work. Calculations start at the last and end at the first work in the project. The process and results of calculations are shown in Figure 2.5.
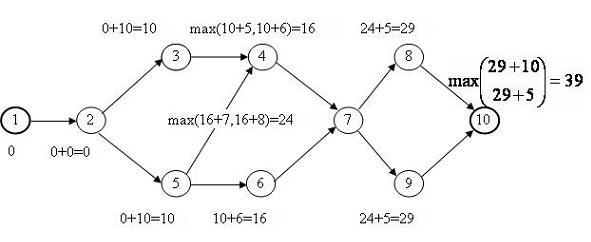
Rice. 2.4. Calculating early start times
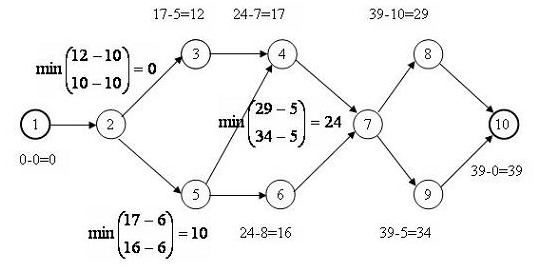
Rice. 2.5. Calculating late start times
The summary calculation results are shown in Table 2.2. Critical works are highlighted in it. The critical path is obtained by connecting the critical jobs on the network. It is shown with dashed arrows in Figure 2.6.
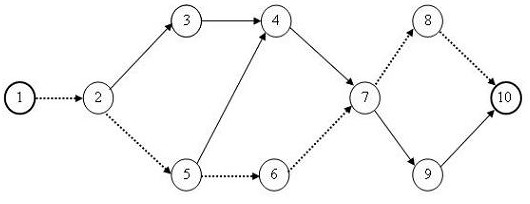
Rice. 2.6. Critical project path
After calculating the values and for each job, the reserve time :
This value shows how much you can delay the start of work without increasing the duration of the entire project.
For critical work, the time reserve is zero. Therefore, the efforts of the project manager should be focused primarily on ensuring the timely completion of these works.
For non-critical work, the reserve time is greater than zero, which gives the manager the opportunity to maneuver the time of their beginning and the resources they use. Such options are possible.
- Delay in the start of work by an amount not exceeding the reserve time, and the resources required for work are directed to perform work on the critical path. This can reduce the duration of critical work and the project as a whole;
- Underload of non-critical work with resources. As a result, its duration increases within the time reserve, and the released resource is used to perform critical work, which will also lead to a decrease in the duration of it and the entire project.
In the given example of the project, works 3, 4 and 9 have a reserve of time according to table 2.2.
2.1.2. Scheduling
At the scheduling stage, a calendar schedule is developed, which is called Gantt chart... The Gantt chart displays the following project parameters:
- structure of work, obtained on the basis of the network schedule;
- the composition of the resources used and their distribution between works;
- calendar dates, to which the moments of the beginning and completion of work are tied.
Let us consider the construction of a calendar using the example of the project "Development of a software package". First of all, you need to decide on the resources that will be used by this project. Suppose that only performers act as resources, and they are distributed between jobs according to table. 2.3.
| Table 2.3. | ||
| Job No. | Job title | Executor |
| Start of project implementation | - | |
| Formulation of the problem | Stage director | |
| Interface development | Programmer1 | |
| Development of data processing modules | Programmer1 | |
| Database structure design | Programmer2 | |
| Populating the database | Programmer2 | |
| Debugging a software package | Programmer1 Programmer2 | |
| Testing and bug fixing | Programmer1 Programmer2 Director | |
| Preparation of software documentation | Stage director | |
| Completion of the project | - |
Let's choose the start date of the project - September 7, 2009. (Monday). Only working days are taken into account when drawing up the calendar. All Saturdays and Sundays, as well as public holidays, are considered non-working days, the nearest of which is November 4th.
The calendar schedule (Gantt chart) is shown in Figure 2.7, where rhombuses indicate milestones, solid lines - duration of work, solid lines with arrows - reserve time for work, dashed lines - connection between the end of previous and the beginning of subsequent work.
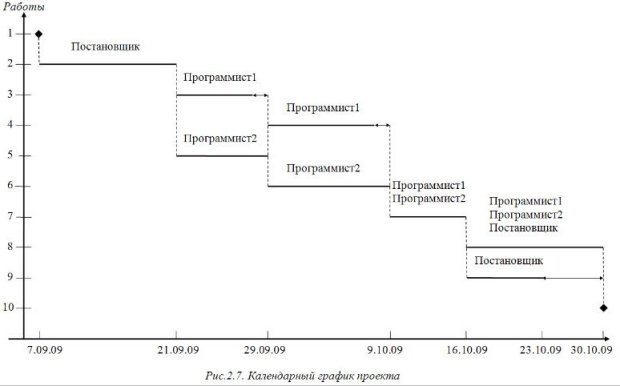
Enlarge image
Rice. 2.7.
Enlarge image
Rice. 2.8.
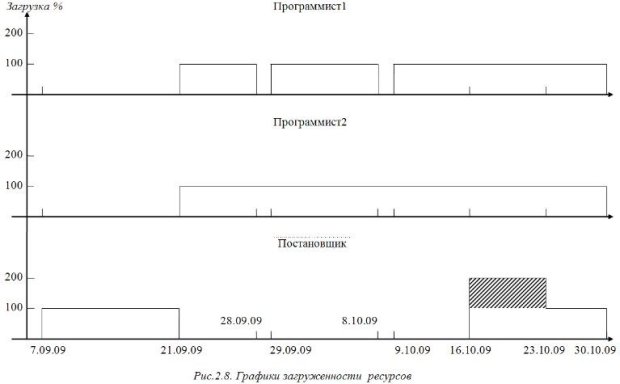
Based on the Gantt chart, resource utilization graph... This graph shows the percentage of utilization of a specific work resource during the course of a project. The abscissa shows the time interval of the project, and the ordinate shows the total percentage of the executor's workload for all the tasks of the project that he is performing at the current time.
Usually, the performer is completely busy with solving some task and upon its completion moves on to the next one. This corresponds to 100% loading. However, in some cases, he can be simultaneously involved in 2 or more tasks, allocating part of the working time to solve them. For example, two tasks of 50% each, that is, half a working day per task. The resource utilization schedule allows in this case to control the total employment of the contractor and to identify possible periods of overload when more work is planned for him than he can perform during the working day. This is evidenced by the total workload of more than 100%.
An example of graphs of resource utilization of the "Development of a software package" project is shown in Fig.2.8. It is built on the assumption that each employee is 100% busy with the task planned for him. It can be seen from the graphs that the Director was overloaded from October 16 to October 23, since he was assigned two parallel jobs during this period. The area of its congestion is highlighted on the corresponding graph by hatching.
Operational management
At the stage operational management the work on the project is being carried out and continuous monitoring of the progress of its implementation. No matter how good the initial plan is, life will certainly make its own adjustments to it. Therefore, the tasks of the manager are:
- tracking the actual work schedule;
- comparison of the actual schedule with the planned;
- making decisions to eliminate emerging deviations from the plan;
- re-planning of the project in case of significant deviations.
The first two tasks are solved using the Gantt chart. On it, parallel to the lines of the duration of the work, lines are drawn, denoting the percentage of the actual completion of these works. This makes it easy to detect any deviations that have occurred.
The method of eliminating the deviation depends on the resources available to the manager. To complete the lagging work, you can either attract additional workers (additional resources), or use the same set of workers overtime. In both cases, the elimination of the deviation will have to pay an increase in the cost of the project (unplanned earlier payment of additional workers, resources and overtime).
If the deviation is such that it cannot be corrected by attracting additional and overtime resources, or an increase in the cost of the project is unacceptable, it is necessary to re reschedule project and do the following:
- completed works are assigned zero duration values;
- for partially completed work, duration values are set corresponding to the remaining amount of work;
- structural changes are being made to the network schedule in order to eliminate unnecessary work and add others that were previously unplanned;
- recalculate the critical path and recalibrate the project.
After the creation of the adjusted project, it is approved by the management and its implementation and operational management begins. This adjustment can be performed several times.
2.1.4. Control questions
- What are the steps involved in a structural planning methodology?
- What is a Network Schedule?
- What are the properties of a network diagram?
- What is critical work?
- What is the critical path?
- What are the steps in finding the critical path?
- How is early start time calculated?
- How is late start time calculated?
- How to find critical jobs based on early and late start times?
- What is working time slack?
- How can the runtime slack be used?
- What is a Gantt chart?
- Give an example of a Gantt chart.
- What is the resource utilization graph for?
- How can resource overload be found from the resource utilization schedule?
- Give an example of a resource utilization schedule.
- What is the essence of the operational management process?
- What actions should be taken when replanning a project in the process of operational management?
© 2015-2019 site
All rights belong to their authors. This site does not claim authorship, but provides free use.
Date the page was created: 2016-02-16
 Discounted payback period
Discounted payback period Methodological aspects of project management
Methodological aspects of project management Scrum development methodology
Scrum development methodology