Financial threshold of profitability: what is the use of this indicator. Profitability threshold. Financial safety margin. Operating lever The profitability threshold is
One of critical milestones planning the organization's activities is to consider options for possible changes in the market situation and the capabilities of the organization in these conditions.
One of the most accessible methods of business and financial performance management is operational analysis, carried out according to the scheme: costs - sales - profit. This method allows you to identify the dependence financial result from changes in costs, prices, production and sales of products.
With operational analysis, you can:
1.evaluate profitability economic activity;
2. predict the profitability of the organization;
3. assess the entrepreneurial risk;
4. choose the best ways to get out of the crisis;
5. evaluate the profitability of investments;
6. to develop the most profitable assortment policy for the organization in the field of production and sale.
The key elements of operational analysis are the following indicators:
Critical volume of production and sales of products;
Profitability threshold;
financial safety margin.
Business break-even analysis is one of the main tools for a large class solution management tasks... Through such an analysis, it is possible to determine the break-even point and the margin of financial strength (safety zone), plan the target volume of production, set prices for products, select the most efficient production technologies, and adopt optimal production plans.
Break-even point (profitability threshold)- This is the minimum permissible sales volume that covers all the costs of manufacturing products, while not bringing any profit or loss.
If the company produces only one type of product, the break-even point is calculated by the formula:
TB = PZ / (C-Per.Z.ud.),
TB - break-even point, units.
ПЗ - fixed costs, rubles;
P - unit price, rubles / unit;
Per.Zud. - variable costs per unit of production, rubles / unit;
(C -. Per.Z.ud) - marginal income per unit of production, rubles / unit.
In value terms, the profitability threshold is determined as follows:
TB = PZ / Kmd,
TB is the critical value of revenue, rubles.
Кмд - coefficient of marginal income;
Kmd = MD / N
N - sales proceeds, rub.
MD = N - Per.Z.
If there is more than one type of product, the break-even point can be determined for the business as a whole or for individual types of products.
The difference between the actual or planned revenue from the sale (Nfact, - Nplan) and the critical value of revenue (TB) characterizes financial strength margin (FFP):
ZFP = Nfact - TB
or ZFP = Nplan - TB
An organization without risk of loss can reduce the volume of sales proceeds by the amount of FFP. The margin of financial strength can be determined not only in absolute terms, but also in relative terms:
КЗФП = FFP / Nfact * 100%
or KZFP = FFP / Nplan * 100%
Financial safety margin reflects the percentage of acceptable decrease in sales revenue without risk of loss.
Safety metric is often used to assess operational risk: the higher the indicator, the safer the situation, since the risk of lowering the equilibrium point is less.
test questions on this topic
1. What is the role economic analysis in planning the activities of the organization?
2. What's the point budget planning In the organisation?
3. What are the main methods used in developing a business plan?
4. How is the sales budget developed?
5. What is the production budget?
6. How is the estimate of direct material costs compiled?
7. How is the estimate of labor costs and general production costs compiled?
8. How is the estimated calculation of the cost of production carried out?
9. What costs are fixed and variable?
10. Using what method can the total costs be divided into fixed and variable costs?
11. How is the profit margin calculated?
12. How is the profitability threshold calculated?
Tests
1. The total need for working capital is determined:
a) structure equity capital
b) the profitability of the production of this type of product
c) the scale of production and the turnover time of current assets
2. With a decrease in variable costs, the threshold for profitability of the organization:
a) remains the same
b) rises
c) decreases
3. How the increase in fixed costs will affect the financial strength of the organization:
a) will increase
b) decrease
c) will remain unchanged
4. How will the growth of fixed costs affect the critical sales volume?
a) the critical volume will decrease
b) the critical volume will not change
c) the critical volume will increase
5. Part operating budget organization includes:
a) the budget for direct labor costs;
b) stream budget Money;
c) investment budget.
6. A forecast cash flow statement is developed on the basis of:
A) long-term forecast of sales volume
B) the budget of general overhead costs
C) capital investment budget
d) forecast profit and loss statement
7. Financial performance business plans must be balanced:
a) with indicators of capital intensity
b) with indicators of the volume of production and sales of products
c) with indicators of profitability
8. The threshold of product profitability (point of critical volume of production) is determined by the ratio:
a) fixed costs to revenue from product sales
b) fixed costs to variables
c) fixed costs to marginal income per unit of production
9. The company's operating budget includes:
a) budget for direct labor costs
b) cash flow budget
c) investment budget
10. Top-down budgeting process:
a) carried out by workers directly involved in the production process
b) requires general budget directives
c) characterized by a positive attitude of managers at lower levels of management
d) better reflects organizational goals
11. The area of safe or stable work of an organization is characterized by:
a) the difference between marginal income and fixed costs
b) the difference between marginal income and profit from product sales
c) the difference between the actual and critical volume of implementation
12... The elements of costs for the production and sale of products (works, services) are:
a) raw materials, materials, fuel, energy, wages, depreciation
b) depreciation, material costs, wages, general business expenses.
13. One of the methods of compiling financial plan is an:
a) method of percentage of sales
b) the method of chain substitutions
14. The organization's budget is:
a) forecast balance
b) a quantitative plan in monetary terms, showing the planned amount of income and expenses
Practical tasks
1. Determine the threshold of return on sales new products(ETC)... Estimated unit price (C) - 500 rubles. Variable costs per unit of production (PeruZ.unit.) - 60%. The annual amount of fixed costs (PS) is 200 thousand rubles.
2. Determine the size of the margin of financial strength, if:
sales proceeds (N) are 600 thousand rubles, variable costs (Per.Z) - 300 thousand rubles, fixed costs (PS) - 150 thousand rubles.
3.. The share of marginal income in sales proceeds is 30%; sales volume at the break-even point - 600 thousand rubles. What is the amount of fixed costs?
4. Determine the critical sales volume (TB) if:
Fixed costs (PS) - 200t. rubles
Variable costs per unit of production (Per.Z. unit) - 800 rubles
Unit price - 1800 rubles.
5. What is the value of margin income, if:
Sales proceeds - 120,000 rubles.
Fixed costs- 30,000 rubles.
Variable costs - 70,000 rubles.
6. Determine the point of critical sales volume (TB), if:
Sales proceeds (N) - 6000t.rub.
Fixed costs (PS) - 1000 thousand rubles.
Variable costs (Per.Z) - 2000 thousand rubles.
7. Determine the amount of profit (P), if:
Marginal income (MD) - 3000t.r.
Fixed costs (PZ) - 1500t.r.
Sales proceeds (N) –8200t.r.
8. As of the reporting date, the organization has the following indicators:
At the beginning of the period At the end of the period
Material stocks: 2 750 3 250
Work in progress costs 4,800 4,000
Finished products 2 500 1 250
During the reporting year, the following costs were incurred:
For materials - 20,000 rubles.
For wages - 11,000 rubles.
General production costs - 16,500 rubles.
The profitability threshold is an important indicator that characterizes financial condition enterprises. We calculate it in Excel, graphically and using formulas.
How to understand where the border lies, beyond which the enterprise will move from a loss-making zone to a profitable one? The profitability threshold will help you figure this out. Next, you will learn what it means, how it is calculated and what is the relationship between it, as well as financial strength and operating leverage. Download the Excel model and make calculations based on your data.
This is an indicator that gives an idea of how much product, work or service needs to be produced in order to pay off the company's expenses for ordinary activities. In other words, in this case, the sales profit is zero, as are the losses. Otherwise, it is also called profitability. entrepreneurial activity or a break-even point.
The indicator characterizes the company from various angles. On the one hand, it reflects the state of the organization in which the enterprise does not receive profit, but also has no losses. This is a satisfactory financial condition. On the other hand, it allows you to determine the volume of sales or the price level at which production activities will start to make a profit.
Profitability threshold: formula
It is calculated using one of the following formulas:
Profitability Threshold = Fixed Cost ÷ (Price - Variable Cost Per Unit)
According to the above formula, the indicator is calculated in kind, that is, it shows how many units of products or services need to be produced in order for the enterprise to stay afloat.
Profitability Threshold = Revenue × Fixed Cost ÷ (Revenue - Cumulative Variable Cost)
Since the calculation is based on the company's revenue received for the reporting period, as a result, we will receive the value of the profitability threshold in monetary terms. You can use any of these formulas, as well as a graphical method.
Get a set of formulas for profitability: investments, assets, capital, sales, costs, products, core business. Choose which indicators to count: sales efficiency, expended resources, assets or capital. Download guides and sample reports to track profitability certain types property and business processes.
Calculation of the threshold of profitability graphically
The graphical method is the most visual method that allows you to determine and analyze the threshold of profitability. To build a graph, you need to calculate the revenue and variable costs for two values of sales volumes. The results obtained are plotted on a graph, where the X-axis reflects the volume products sold, and the y-axis is the monetary value of revenue and costs. The graph allows you to see the position of the company, as well as understand at what level of implementation the company begins to make a profit and when it works at a loss.
Graphically, it looks as shown in the diagram.
Figure 1. Threshold of profitability: graphical method
How to determine the break-even point: an example
Table 1. Initial data for the example
|
Value for the I quarter of 2019 |
|
|
Sales volume, pcs. |
|
|
Fixed costs per unit of production |
|
|
Cumulative fixed costs |
|
|
Variable unit costs |
|
|
Cumulative variable costs |
Let's calculate the threshold of profitability in kind:
RUB 78,364 ÷ (2,999 rubles - 1,364.55 rubles) = 47.95 pcs. ≈ 48 pcs.
To reach the break-even point, the company needs to produce and sell 48 pieces of the Krokha developmental music center.
Let's define the ruble value of the same indicator. To do this, we will use the second calculation formula:
(401,866 rubles × 78,364 rubles) ÷ (401,866 rubles - 182,850 rubles) = 143,787.79 rubles.
It turns out that in order to reach the break-even point, the company needs to produce and sell products worth 143,787.79 rubles.
If sales growth does not bring additional profits or increases it insignificantly, you need to find out what conditions sales policy this is hindered. To do this, it is necessary to determine the profitability of sales channels, the rationality of the system of bonuses and discounts and the effectiveness of commercial expenses.
Calculating the threshold of profitability in Excel
- we determine fixed and variable costs per unit of goods, as well as sales;
- we calculate the values of revenue, costs and profit from sales;
- we find the zero value of the financial result. Revenue and natural volume of sales at this point will show the threshold of profitability.
The considered indicator is closely related to two more: the margin of financial strength and operating leverage. In fact, they are all united by the same analysis method that underlies - CVP (Cost-Volume-Profit). Let us analyze by what formulas they are calculated and what they mean.
Profitability threshold and financial strength: how are they related?
The financial safety margin is the difference between the actual or planned revenue of the enterprise and the income at the break-even point. Otherwise - the reserve that allows the organization to make a profit. The bigger it is, the better. For example, the break-even point for product A in your company is 1,000 units, but you sold 1,500 units last month. This means that the result of the activity will increase by the marginal income from the sale of those 500 additional units.
________________
Note.
________________
This metric is also called margin or safety margin. It is calculated either in absolute terms - in rubles, or in relative terms - in percent. The relative value also has another name - the safety margin ratio.
Table 2. Financial safety margin: calculation formulas
Why is the revenue shown in the formulas variably: both actual and planned? This moment depends on the calculation period this indicator... If you determine it by the already achieved income values for the last month, quarter or year, then take the actual value. If, however, you are estimating future revenue values from the newly created budget of income and expenses, then use the planned value.
Let's continue with the toy manufacturer example. Let's say:
- proceeds from the sale of the Krokha music center in the budget for the first quarter of 2020 is 497,542 rubles;
- for this, the price is planned to be raised by 5%;
- variable costs per unit will increase by 3%;
- the constant expenses that fall on this product will increase by 20 thousand rubles.
Let's calculate the new value of the break-even point, and at the same time the margin of financial strength.
Table 3. Calculation of the margin of financial strength
|
Indicator (in rubles, unless otherwise indicated) |
Quantity for the 1st quarter of 2020 |
|
Initial data |
|
|
3 149 ≈ 2999 × 1.05 |
|
|
Variable unit costs |
1,405.49 = 1,364.55 × 1.03 |
|
Cumulative fixed costs |
98 364 = 78 364 + 20 000 |
|
Calculated values |
|
|
Profitability threshold |
179 493 ≈ 98 364 ÷ (3 149 - 1 405.49) × 3 149 ≈ 57 units. × 3 149 |
|
Financial safety margin |
318 049 = 497 542 – 179 493 |
|
Financial strength margin,% |
63.9 = 318,049 ÷ 497,542 × 100 |
How to interpret the obtained values of the safety margin? Here are two options:
- even if in the first quarter of 2020 the sales of the Krokha music center turn out to be less than planned by 318 thousand rubles, then there will still be no loss from this product;
- the planned sales volume is almost 64% higher than the break-even one. It turns out that the organization has a significant reserve. It can be used, for example, during a marketing campaign for a product in the form of a price reduction. In addition, thanks to this reserve, the company will not drive into losses unforeseen increases in fixed or variable costs. For example, fixed costs may increase by 177 thousand rubles. (by 80%), and still the organization will remain in the profit zone. This can be clearly seen on the graph.
Figure 3. Margin of financial strength on the break-even chart

Return on investment is an indicator that allows you to assess the effectiveness of financial investments and their return on investment. ROI (returnment of investment) is translated from English as "return on investment". This indicator should be determined both for projects that have already been opened and for those in which the company is only planning to invest.
Download ROI Formula
Operating lever: formula
Operating lever in simple words- This is the ratio between the change in income and profit from sales. Why is it needed? For example, to quickly calculate the value of operating profit or loss, when it is known by what percentage the price or sales in kind will increase.
For the operating leverage, two formulas are derived: one for price, the other for natural. Both are based on the ratio of income to financial results. Only in the first case, the total income from ordinary activities (revenue) is taken, and in the second - the marginal one.
Table 4. Operating Leverage: Calculation Formulas
Obviously, the value for price leverage will always be higher than for natural due to the larger numerator. This has its own logic: an increase in price does not entail costs, but an increase in the volume of sales leads to this. The reason is the variable component in costs: the higher the natural volume of sales, the greater its value.
If you know what the operating leverage is, then calculating the percentage of change in profit from sales will not be difficult. It is based on the formulas from table 5.
Table 5. Impact of operating leverage on profit
Of course, it is possible to calculate the profit for a known changed price or quantity value without this indicator. But the fact is that it can significantly speed up the process. Here's an example.
Suppose that the management of Kolobok and Teremok decided in the second quarter of 2020 to increase the price of the Krokha music center by another 3%. Sales, according to their expectations, in the same period will decline by 1%. How will such changes individually affect sales profit? Let's calculate the result using the formulas from Table 5. To do this, we will additionally calculate the financial result and the total marginal income.
Table 6. Calculation of operating leverage
|
Index |
Value for the II quarter of 2020 |
|
Initial data (Q1 2020) |
|
|
Revenue, rub. |
|
|
Total marginal income, RUB [(Price - Variable Unit Cost) × Quantity] |
275 474.58 = (3 149 - 1 405.49) × 158 * |
|
Profit from sales, rub. (Cumulative Margin Income - Cumulative Fixed Costs) |
177 110,58 = 275 474,58 – 98 364 |
|
Calculated values |
|
|
Price operating lever, units |
2.81 = 497 542 ÷ 177 110.58 |
|
Natural operating lever, unit |
1.55 = 275 474.58 ÷ 177 110.58 |
|
Impact on sales profit through product price,% |
8.43 = 3% × 2.81 |
|
Impact on profit from sales through the product price, rub. |
192,041 = 177 110.58 × 108.43 ÷ 100 |
|
Impact on sales profit through the amount of product sold,% |
1.55 = (-1)% × 1.55 |
|
Impact on sales profit through the amount of product sold, rub. |
174 365.37 = 177 110.58 × 98.45 ** ÷ 100 |
|
Note: * 158 = Revenue ÷ Unit Price = 497,542 ÷ 3,149. ** 98,45 = 100 – 1,55 |
|
We summarized all the indicators and their formulas from the article in the diagram.
Figure 4. Profitability threshold, financial safety margin and operating leverage: calculation formulas
Consider the threshold of the enterprise's profitability, the calculation formula and its relationship with the break-even point and the margin of financial strength.
Profitability threshold(analogue.BEP,breakevenpoint, break-even point, critical point, profitability threshold) Is the sales volume of the enterprise at which the minimum level of profit (equal to zero) is achieved. In other words, the enterprise operates on the self-sufficiency of its costs. The profitability threshold of an enterprise is sometimes called in practice.
The purpose of assessing the threshold of profitability in determining the minimum permissible level of production and sales, on the basis of which the financial strength margin necessary to maintain the sustainable functioning of the enterprise is calculated. The profitability threshold is assessed by the owners of the enterprise when planning future production and sales volumes, as well as by lenders and investors when assessing the financial condition.
When calculating the profitability threshold, two types of costs (costs) are used:
- Fixed costs (eng.VA,VariableCosts)- the type of costs of the enterprise, the size of which does not depend on changes in the volume of production and sales of products.
- Variable costs (eng.FC,FixedCosts)- the type of costs of the enterprise, the size of which directly depends on the volume of production and sales of products.
Fixed costs will include expenses for personnel salaries, rent of production and other premises, deductions for the unified social tax and property tax, marketing costs, etc.
Variable costs consist of the cost of raw materials, materials, components, fuel, electricity, premium wages staff, etc.
The sum of all fixed costs forms the total fixed and variable costs of the enterprise (TVC, TFC).
To calculate the profitability threshold of an enterprise, the following two formulas are used analytically:
BEP 1 (Breakeven point) - the threshold of profitability in monetary terms;
TR (Total Revenue) - proceeds from product sales;
TFC (Total Fixed Costs) - total fixed costs;
TVC (Total Variable Costs) - cumulative variable costs.
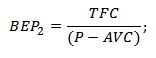
BEP 2 (Breakeven point) - the threshold of profitability expressed in physical terms (production volume);
P (Price) - unit price of goods sold;
AVC ( Average Variable Costs) - the average variable costs per unit of goods.
 |
★ |
Calculating the threshold of profitability in Excel
To calculate the profitability threshold, it is necessary to calculate the fixed, variable costs of the enterprise and the volume of sales (sales) of the goods. The figure below shows an example of the main parameters for calculating the profitability threshold.

Basic parameters for assessing the threshold of enterprise profitability
At the next stage, it is necessary to calculate how the profit and costs will change from the volume of sales of the goods. Fixed costs, presented in column "B", they will not change with the volume of production. Variable unit costs will increase in proportion to production (column "C"). The formulas for calculating income and costs will be as follows:
Enterprise variable costs= $ C $ 5 * A10
Total enterprise costs= C9 + B9
Income= A9 * $ C $ 6
Net profit= E9-C9-B9
The figure below shows this calculation. Profitability threshold in this example achieved with a production volume of 5 pcs.

Assessment of the threshold of enterprise profitability in Excel
Suppose another situation, when the sales volumes, variable and fixed costs are known and it is required to determine the profitability threshold. To do this, you can use the above analytical calculation formulas.
Profitability threshold in monetary terms= E26 * B26 / (E26-C26)
Profitability threshold in kind= B26 / (C6-C5)

Calculating the level of profitability using formulas in Excel
The result is similar to " manual way»Determining the threshold of profitability. It should be noted that in practice there are no absolutely fixed or completely variable costs. All costs are in addition to "nominally fixed" and "nominally variable" costs. The fact is that with an increase in output, a "scale effect" arises, which consists in a decrease in the cost (variable costs) of producing a unit of goods. Also with fixed costs, which can also change over time, for example, the rental rate for the premises. As a result, with the transition of an enterprise from serial to mass production, an additional rate of profit and an additional margin of financial strength arise.
Determination of the threshold of profitability graphically
The second way to determine the threshold of profitability is with the help of a graph. For this, we will use the data obtained above. As you can see, the threshold of profitability corresponds to the point of intersection of income and total costs of the enterprise, or the equality of net profit to zero. The critical level of profitability is achieved with a production volume of 5 units.

Graphical analysis of the income and expenses of the enterprise
The threshold of profitability and the margin of financial strength of the enterprise
Determining the minimum acceptable level of sales allows you to plan and create a margin of financial strength - this is excess sales or net profit, which allows the company to function and develop steadily. For example, if the current volume of production (sales) corresponds to 17 pieces, then the margin of financial strength will be equal to 240 rubles. The graph below shows the area of the company's financial safety margin with a sales volume of 17 pieces.

The financial strength of the enterprise
The margin of financial strength shows the remoteness of the enterprise from the break-even point, the greater the margin of safety, the more financially stable the enterprise is.
 |
★ (calculation of Sharpe, Sortino, Trainor, Kalmar, Modilyanka beta, VaR ratios) + predicting course movement |
Summary
The threshold of profitability allows you to assess the critical level of production of the enterprise, at which its profitability is equal to zero. This analytical assessment is important for strategic management and developing strategies for increasing sales and planning production volumes. Currently, sales are influenced by many different factors: seasonality of demand, sharp changes in the cost of raw materials, fuel, energy, production technologies of competitors, etc. all this makes the company constantly look for new opportunities for development. One of the modern promising directions for increasing the volume of production is the development of innovations, as this creates additional competitive advantages in the sales market.
Profitability Is an indicator of efficiency in the use of labor, economic, material and natural resources.
Profitability threshold- is a set of products sold, thanks to which the company covers its production costs without making a profit from sales, that is, goes to zero.
If we talk about trading companies, the profitability is expressed by specific numerical characteristics, that is, by the correlation of profits and capital investments. A business is profitable if the company is in positive territory at the end of the year.
Dear reader! Our articles tell about typical solutions legal issues but each case is unique.
If you want to know how to solve exactly your problem - contact the online consultant form on the right or call by phone.

It's fast and free!
The profitability ratio is the ratio of profit to resources (tangible assets, flows, etc.) that form a given profit.
Most often, profitability is determined as a percentage. But in some cases, it can be presented in the form of profit per unit of assets invested, or in profit from each earned financial unit.
Depending on the type of business, profitability is classified as follows:
- Overall return on tangible assets. It is formed by the ratio of profit (before taxes) to the aggregate of tangible assets attracted to the company for a fixed period of time.
- Product profitability. It is determined as a total from dividing the profit from the sale of a product by the costs associated with its manufacture.
- Production profitability. Production is considered profitable, where the return on investment exceeds the cost of manufacturing goods. Among the methods that affect the growth of profitability, there is a reduction in the cost of manufactured products and an improvement in quality properties.
General view of the mathematical expression of profitability:
P = P / I * 100%, where:
- R- profitability;
- NS- profit received during the implementation of the project;
- AND- investments in the project.
Determination of the threshold of profitability
It is determined by the formula:
- Profitability threshold = Fixed costs / ((Sales revenue - Variable costs) / Sales revenue).

Upon reaching the threshold of profitability, the company has neither profit nor loss.
The value of the break-even point is of great importance for investors, as it reflects the ability to repay the debt on the loan provided. The reliability of the enterprise is determined by the excess of the level of sales over the value of the threshold of profitability.
The degree of remoteness of the value of the profitability of the enterprise from the break-even point is determined by the margin of financial strength.
To obtain the value of the margin of financial strength, it is necessary to find the difference between the real amount of goods produced and the amount of goods produced at the break-even point.
Calculation formulas
By calculating the value of the break-even point, we get the marginal amount of income from product sales. Selling a product at a lower price makes the business unprofitable.
Thus, the company will make a profit only when the income exceeds the marginal value of profitability.
In monetary terms
Prd = VxZpost / (V - Zperm), where:
- Prd- break-even points in value terms;
- IN
- Zperm- variable costs;
- Zpost- fixed costs.
In kind
Prn = Zpost / (B - ZSperm), where
- Prn- the threshold of profitability, value in units of goods;
- Zpost- the value of fixed costs;
- 3C change- the average value of variable costs (per item);
- IN- the general level of income (revenue);
Examples of
An example of a calculation in monetary terms:
- The enterprise sells 200 pieces. goods at the price of 300 rubles / 1 piece.
- Variable costs in the unit cost of goods are equal to 250 rubles.
- Direct costs in the unit cost of goods - 30 rubles.
- Indirect direct costs in the unit cost of goods - 20 rubles.
It is required to determine the break-even point of the enterprise.
We calculate the threshold of profitability in value terms:
- Zpost= (30 + 20) x200 = 10,000 rubles.
- Zperm= 250 x 200 = 50,000 rubles.
- IN= 200x300 = 60,000 rubles.
- Prd= 60,000x10000 / (60,000-50000) = 60,000 rubles.
The resulting break-even point reflects that the company will make a profit after the sale of goods in the amount of more than 60,000 rubles.
An example of a calculation in kind:
Prn (Threshold of profitability in units of goods) = 10000 / (300-250) = 200.
Let's take the same input data for an example calculation.
Thus, the company will make a profit after the sale of 200 units of goods.
Main factors
 In order to analyze the financial condition of the company, the following criteria for assessing profitability are used:
In order to analyze the financial condition of the company, the following criteria for assessing profitability are used:
- Economic profitability ratio. The return on tangible assets reflects the amount of profit received from all assets that the company has. The decline in the profitability of monetary assets is characterized by a decrease in demand for the company's products.
- Financial profitability ratio. The return on equity ratio reflects the degree of return on equity of the company. In this regard, this indicator is very interesting for a certain circle of people, namely, shareholders and the owner of the enterprise.
- Operational profitability ratio. This indicator is determined by the ratio of the company's net profit to net sales proceeds. An increase in this indicator indicates an increase in the company's performance, while a decrease, on the contrary, indicates its unproductive activity.
- Economic profitability- this is one of the most important criteria for the attractiveness of a company, because the level of profitability reflects the upper threshold interest charges.
Factors affecting profitability
External
High efficiency of company management cannot reduce the level of influence external factors on the profitability of the business.
TO this kind factors include:
- territorial location of the company (remoteness from sales centers, raw material deposits, etc.);
- the competitiveness of the product and the demand for it;
- changes in the situation in the markets;
- the influence of the state on the economy (regulation of the market at the legislative level, adjustment of the refinancing rate, changes in tax laws, etc.);
Manufacturing
- means of production;
- labor resources;
The influence of these factors on the functioning of the company can be characterized from two sides:
- extensive influence (determined by changing the numerical parameters production process) includes:
- change in the time and quantity indicators of the production process;
- changes in the means of production (related to fixed assets: equipment, buildings, etc.) and their quantity (for example, an increase in the amount of stocks);
- change in the number of jobs, change in work schedules, downtime;
- an intensive influence is associated with an increase in the efficiency of the use of production factors;
It includes:
- maintenance of equipment in the best condition, and its timely replacement with a technologically more advanced one;
- application of modern materials, improvement of production technology;
- raising the level of qualifications of personnel, lowering the level of labor intensity of products, correct organization labor process.
When analyzing financial activities and economic condition any firm, one of the indicators that allows you to do this is the threshold of profitability.
The concept of the threshold of profitability
The indicator at which the proceeds received from sales with the smallest volume of sales of the enterprise cover all production costs, as well as all costs of selling products, is called the threshold of profitability. In this case, the amount of profit will be zero.
In other words, this variable determines how much of the product must be sold at a certain price in order to ensure profitability at which the firm will not incur losses.
Often, this indicator is also called the tipping point, critical production volume, or break-even point.
It is necessary to clarify that if the revenue exceeds the profitability threshold, the increase in profits will begin.
Thus, in the case set price for the product, it must be sold in quantities exceeding the value of the break-even point.
The threshold rate of profitability must be viewed from different angles:
- Its value is intended to characterize the state of the enterprise, when it is still able to function without making a profit.
- The management of the organization regarding this indicator will be able to plan the volume of production to increase profitability.
Influencing factors
Factors affecting the value of the threshold rate of return:
- revenue received from the sale of a unit of a good or service;
- fixed costs;
- variable costs;
If any of these indicators fluctuate, the profitability threshold will decrease or increase.
For a more complete understanding of the significance of these factors, it is necessary to consider in more detail the concept of variable and fixed costs.
Fixed costs (conditionally fixed) are the costs of a firm that do not depend on the volume of production for a specific period and remain relatively unchanged for a separate reporting period.
- rent for premises;
- deductions for depreciation;
- utility costs (water supply, lighting, heating);
- funds for the issuance of wages to employees of the administration of the organization;
- insurance payments;
- payment of interest on loans;
- communication costs and so on.
The peculiarity of these costs is that their organization is obliged to pay in any case, regardless of whether it is in profit or loss.
Reducing these costs is very difficult, unlike variables.
Variable costs are the costs of an enterprise that vary in direct proportion to the volume of products or services produced.
In the balance sheet of each enterprise there is such an item as "Raw materials and materials". It reflects the cost of all funds required by the organization to produce products.
- Funds intended for remuneration of employees who are directly involved in the production of products.
- Fare.
- Funds for the purchase of raw materials and supplies.
- Payment for fuel and energy required for production.
- Taxes calculated from the financial result (income tax) and others.
Formulas for calculating the threshold rate of profitability
The first formula: Vyrtb = Zpost + Zper, where:
- Vyrtb - revenue at the break-even point;
- Zpost - fixed costs;
- Zper - variable costs;
Fixed costs are also called gross margin, which is the difference between revenue and variable costs.
The profitability threshold of each organization can be calculated in two ways:
In monetary terms: PRden = Vyr * Zpost / (Vyr-Zpost), where:
- PRden - the threshold of profitability in monetary terms;
- Vyr - total revenue;
- Zpost - fixed costs;
- Zper - variable costs;
In physical terms: PRnat = Zpost / (Ts-ZSper), where:
- PRnat - the threshold rate of profitability in kind;
- Зпост - fixed costs;
- ЗСпп - average variable costs (per unit of product or service);
- C is the cost of a unit of product or service;
In order to build this graph, you need to calculate the indicator of the profitability threshold for several volumes of production and mark these points on the plane, and then draw a curve or straight line through them.
Calculating the threshold rate of return in Excel
In this program, it is incredibly convenient to carry out calculation operations.
This requires:
- In the first column, enter data on several volumes of sales or production.
- In the second column, mark the fixed costs corresponding to these volumes.
- The same should be done in the third column, only for variable costs.
- In a separate cell, you must indicate the cost per unit of product or service.
- In the last column, the formula for calculating the profitability threshold is written and stretched throughout the column.
Based on this table in Excel program you can make a schedule.
An example of calculating the threshold of profitability

Condition: the company sells goods in the amount of 110 units at a price of 510 rubles. The sum of variable costs is 365 rubles, fixed costs per unit of production - 115 rubles. It is necessary to calculate the threshold rate of return.
Calculation in monetary terms:
- Zpost = 115 * 110 = 12650 rubles
- Zper = 365 * 110 = 40150 rubles
- Exp = 510 * 110 = 56100 rubles
- PRden = (56100 * 12650) / (56100-40150) = 44493.1 rubles
Thus, the organization will remain in positive territory in the event of the sale of its products or services for a total amount that will be higher than 44,493.1 rubles.
In other words, if products for this amount are sold, the enterprise will be at the break-even point.
Calculation in kind:
- PRnat = 12650 / (510-365) = 87 pieces
Consequently, the enterprise will be able to get profit from the sale of products over 87 pieces.
Indicators of profitability of the enterprise
In order to understand how effective the company's activities are, along with the profitability threshold, it is necessary to calculate the main profitability ratios of the organization.
Profitability indicators characterize the ability of an enterprise to generate a return on invested capital.
The following variables are distinguished:
The rate of return on all assets. It talks about how many rubles of net profit the company derives for the ruble of capital invested in the business. Kra = PE / KAPSr, where: Kra is the required coefficient; PE - net profit; KAPSr - the sum of assets at the end and beginning of the year, divided in half.
Return on equity ratio. It characterizes the investment attractiveness of a business and shows how many rubles fall on the ruble of funds invested by shareholders. Krsk = PE / SKsr, where:Крск - the required coefficient; PE - net profit; SKav - the amount of equity at the end and beginning of the year, divided in half.
Profitability ratio of current assets. It indicates the efficiency of using current assets and operating activities. Krta = PE / TAcr, where: Krta is the required coefficient; PE - net profit; Tacr - the sum of current assets at the end and beginning of the year, divided in half.
Return on long-term assets ratio. It shows how efficiently non-current assets are used in general and mainly fixed assets. In addition, the indicator characterizes the investment activity of the enterprise. Krda = PE / DAav, where:Крда - the required coefficient; PE - net profit; DAav - the sum of non-current assets at the end and beginning of the year, divided in half.
Return on sales ratio. He points to efficiency marketing activities and characterizes the demand for the company's products. Krp = PP / Vyr, where:Крп - the required coefficient; PE - net profit; Vyr - revenue.
Profitability ratio of production cost. It shows how effectively the company is organized and in demand, that is, how many rubles of the net profit received is accounted for by one ruble of costs invested in production. Krps = PE / Ss, where: Krps - the required coefficient; PE - net profit; Сс - cost price.
Thus, it is necessary to conclude that it is not at all difficult to calculate the profitability threshold indicator and analyze with its help individual economic aspects of the enterprise's activities.
However, his role is extremely important. And in the case of an analysis of the economic situation with the help of the main coefficients of profitability, it is possible to fully assess the feasibility of the production of goods and services.
 The fastest boat in the world!
The fastest boat in the world! The history of the Off-White brand
The history of the Off-White brand Habakkuk: how the British tried to build an aircraft carrier from ice Why the project was curtailed
Habakkuk: how the British tried to build an aircraft carrier from ice Why the project was curtailed