The most famous cosmodrome in Russia: description, history and photos. Cosmodromes Which countries have cosmodromes
India
India is another Asian giant actively developing its rocket technology. This is primarily due to the improvement of the nuclear missile potential in the confrontation with China and Pakistan. At the same time, national space programs are being implemented along the way.

Indian launch vehicles
In the south of Andhra Pradesh, on the island of Sriharikota in the Bay of Bengal, the Indian "Satish Dhavan Space Center" was built.

It is named after the former head of the space center after his death. The cosmodrome belongs to the Indian Space Research Organization. The proximity to the equator is one of the undoubted advantages of the cosmodrome. The first launch from the cosmodrome took place on July 18, 1980.

Indian light launch vehicle ASLV
The cosmodrome has two launch sites and a third is under construction. In addition to launch complexes for missiles of various purposes, the cosmodrome has a tracking station, two assembly and test complexes, and special stands for testing rocket engines. A plant for the production of rocket fuel has been built on the territory of the cosmodrome.

Satellite image of Google Earth: launcher at the Sriharikot cosmodrome
The launch vehicles from the cosmodrome are: light type ASLV, launch weight 41,000 kg and heavy type GSLV, launch weight up to 644,750 kg.
India is one of the very few space powers that independently launches communication satellites into geostationary orbit (the first GSAT-2 - 2003), return spacecraft (SRE - 2007) and automatic interplanetary stations to the Moon (Chandrayan-1 - 2008 ) and provides international launch services.

the GSLV launch vehicle is transported to the launch position
India has its own manned space program and is expected to begin manned space flights on its own from 2016 and become the fourth space superpower. Russia is rendering great help in this.
Japan
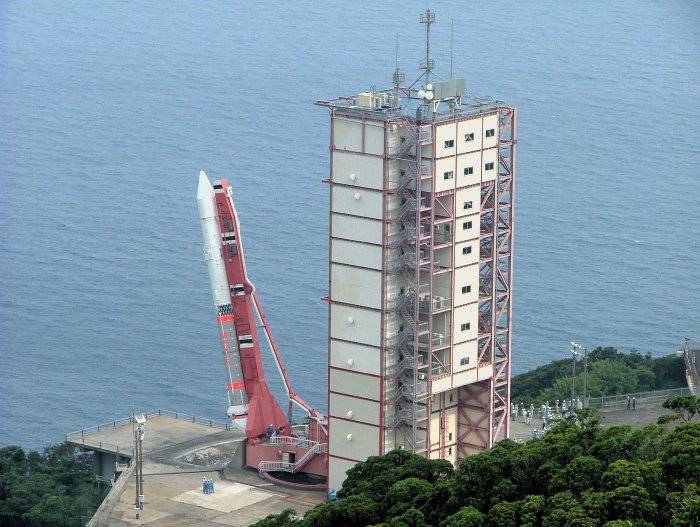
The largest Japanese cosmodrome is the Tanegashima Space Center.

The cosmodrome is located on the southeast coast of Tanegashima Island, in the south of Kagoshima Prefecture, 115 km south of Kyushu Island. It was founded in 1969 and is operated by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.

Satellite image of Google Earth: Tanegashima cosmodrome "
Here they assemble, test, launch and track satellites, as well as test rocket engines. Heavy Japanese heavy carrier rockets H-IIA and H-IIB, launch weight up to 531,000 kg, are launched from the cosmodrome.

Launch of the carrier rocket H-IIB
These are the main launch vehicles launched from the cosmodrome, besides them, light geophysical rockets intended for suborbital scientific research are also launched from here.
The launch pad for H-IIA and H-IIB missiles - includes two launch pads with service towers. RN H-IIA - transported and installed on the platform fully assembled.
The second launch site in Japan is the Uchinoura Space Center. It is located on the Pacific coast near the Japanese city of Kimotsuki (formerly Uchinoura), in Kagoshima Prefecture. Construction of the Space Center intended for experimental launches of large rockets began in 1961 and was completed in February 1962. Until the formation of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency in 2003, it was designated the Kagoshima Space Center and operated under the auspices of the Institute of Astronautics and Aeronautics.

Satellite image of Google Earth: Utinoura cosmodrome
The cosmodrome has four launchers. From the Utinoura cosmodrome, solid-propellant light launch vehicles of the Mu class, with a launch weight of up to 139,000 kg, will be launched.

They were used for all launches of Japanese scientific spacecraft, as well as geophysical and meteorological rockets.

launch of the carrier rocket Mu-5
The Epsilon rocket should replace the Mu-5, which, although it can put a slightly smaller payload into low-earth orbit than the Mu-5, should become much cheaper.
In addition to launching commercial and scientific satellites, Japan participates in a number of international programs. RN Mu-5 launched satellites for the exploration of Mars "Nozomi" and the spacecraft "Hayabusa", which explored the asteroid "Itokawa". The last launch, during which the Solar-B and HIT-SAT satellites were launched into orbit, as well as the SSSAT solar sail, are used to deliver cargo to the ISS using the H-IIB launch vehicle.
Brazil
Another South American cosmodrome after the French Kuru was the Brazilian Alcantara Launch Center, in the north of the Atlantic coast of the country. It is located even closer to the equator than the French Kuru.

Brazil's attempts to develop its own space programs, due to lack of experience, low scientific and technological base, did not lead to the desired result.

Brazilian launch vehicle VLS-1
The next tests on August 22, 2003 of the Brazilian VLS-1 light-class launch vehicle ended in tragedy. The rocket exploded on the launch pad two days before launch.

The explosion killed 21 people. This incident had an extremely negative impact on the entire Brazilian space program.

Satellite image of the launching position of the Alcantara cosmodrome after the explosion
Unable to build its own effective launch vehicles, Brazil is trying to develop the spaceport in the framework of international cooperation. In 2003, contracts were signed for the launch of Ukrainian Cyclone-4 launch vehicles and Israeli Shavit. There are plans to conclude similar contracts for Russian Protons and China's Great March 4.
Israel
A launch center has been built at the Palmachim airbase located near Kibbutz Palmachim, not far from the cities of Rishon LeZion and Yavne, to launch Shavit missiles and other missiles. The first launch took place on September 19, 1988. Rocket launches are carried out not in the east, as at the absolute majority of cosmodromes, but in the westerly direction, that is, against the rotation of the Earth. This certainly reduces the weight thrown into orbit. The reason for this is that the launch route can only be laid over the Mediterranean Sea: the land to the east of the base is densely populated, and the neighboring countries are quite close.
Israel launched a space program in connection with defense necessity: both to obtain intelligence (tracking a potential enemy using satellites) and programs to create missiles capable of delivering nuclear warheads.

night launch of the carrier rocket "Shafit"
Israeli launch vehicle "Shavit" is a three-stage solid-propellant rocket. The first two stages are identical, have a weight of 13 tons each, and are mass-produced in Israel by the IAI concern. The third stage was built by Rafael and weighs 2.6 tons. The Shavit launch vehicle was launched eight times between 1988 and 2010. This missile can be used as a carrier of a nuclear warhead. The Shavit rocket is used to launch the Israeli Ofek reconnaissance satellites. The Ofek (Horizon) satellites were developed in Israel by the IAI concern. In total, by 2010, nine Ofek satellites have been created.
The State of Israel has a developed radio-electronic industry, which makes it possible to create sufficiently advanced satellites for any purpose. But due to its small territory and geographic circumstances, there is no possibility of building a cosmodrome in this country, from which it would be possible to carry out safe launches of carrier rockets along effective trajectories. The launch of Israeli telecommunication and scientific satellites into orbit is carried out in the course of commercial launches of foreign carrier rockets from cosmodromes abroad. At the same time, Israel is demonstrating a desire to develop its own space programs and launch military satellites into orbit using its own launch vehicles. In this regard, negotiations are underway with a number of states, primarily with the United States and Brazil, on the possibility of launching Israeli missiles from spaceports located on their territory.
Iran
The Iranian Semnan cosmodrome has been operating since February 2, 2009, when the Iranian Omid satellite was launched into orbit using the Safir (Messenger) launch vehicle.

The cosmodrome is located in the Deshte-Kevir desert (north of Iran), near its administrative center - the city of Semnan.

Iranian launch vehicle "Safir"
The Safir light-class launch vehicle is based on the Shahab-3/4 medium-range combat ballistic missile.

Satellite image of Google Earth: launch pad of the Semnan cosmodrome
The Semnan Cosmodrome has disadvantages and limitations due to its location, as a result of which the Iranian Space Agency intends to begin construction of a second cosmodrome for launching spacecraft, which will be located in the south of the country.
DPRK
In the early 1980s, on the east coast of North Korea, in Hwade-gun County, Hamgyongbuk-do Province, construction began on a missile test site, which later became known as the Donghae Cosmodrome.

North Korean ballistic missiles
The choice of the location of the test site was influenced by such factors as sufficient distance from the demilitarized zone, minimization of the danger of missiles flying over the territory of neighboring countries, the general distance from large settlements, and relatively favorable meteorological factors.

During the period from the mid 80s to the early 90s were built command post, MCC, fuel storage, warehouses, test bench, modernized communications.

In the early 90s, test launches of North Korean ballistic missiles began here.

Satellite Image: Donghae Cosmodrome
American and Japanese air defense and space control systems have repeatedly recorded medium and long-range missile launches from the Donghae cosmodrome.

Test launch of the Eunha-2 launch vehicle
Some of them were regarded as attempts to launch artificial satellites into space orbit. According to the statement of the DPRK news agency, on April 5, 2009, an experimental artificial communications satellite "Gwangmyeongsong-2" was launched from the cosmodrome using the "Eunha-2" launch vehicle. Despite conflicting reports from sources different countries most likely, the launch of the satellite into orbit ended in failure.
The Republic of Korea
Construction of the South Korean Naro Cosmodrome, located near the southernmost tip of the Korean Peninsula, on Venarodo Island, began in August 2003.

On August 25, 2009, the first Korean launch vehicle, named "Naro-1", was launched from the cosmodrome. The launch ended in failure - due to a failure in the separation of the fairing, the satellite did not go into the calculated orbit. On June 10, 2010, the second launch of the launch vehicle also ended in failure.

Satellite image of Google Earth: the Naro cosmodrome
The third successful launch of the Naro-1 launch vehicle (KSLV-1) took place on January 30, 2013, making South Korea the 11th space power.

The launch was broadcast live by local TV channels, the rocket reached a predetermined altitude and launched the STSAT-2C research satellite into orbit.

Launch of "Naro-1"
The Naro-1 light-class rocket, with a launch mass of up to 140,600 kg, was produced by the Korean Aerospace Research Institute (KARI) in cooperation with Korean Air and the Khrunichev Russian Space Center. According to South Korean media reports, the KSLV-1 replicates 80% of the Angara launch vehicle being built at the Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center.
Floating spaceport "Sea Launch" ("Odyssey")
In 1995, within the framework of international space cooperation, the Sea Launch Company (SLC) consortium was created. It included: the American firm Boeing Commercial Space Company (a subsidiary of the Boeing aerospace corporation), providing general management and financing (40% of the capital), the Russian Rocket and Space Corporation Energia (25%), the Ukrainian Yuzhnoye Design Bureau ( 5%) and PO Yuzhmash (10%), as well as the Norwegian shipbuilding company Aker Kværner (20%). The consortium is headquartered in Long Beach, California. The Russian "Design Bureau of Transport Engineering" and the Central Design Bureau "Rubin" were involved as contractors.

The idea of the offshore spaceport is to deliver the launch vehicle by sea to the equator, where the best conditions for launch are available (you can make the most of the Earth's rotation speed). This method was used in 1964-1988 at the San Marco Sea Cosmodrome, which was a stationary anchored platform near the equator in Kenyan territorial waters.
The sea segment of the Sea Launch complex consists of two sea vessels: the launch platform (LP) Odyssey and the assembly and command vessel (SCS) Sea Launch Commander.

Complex "Sea Launch"
A former self-propelled oil production platform "OCEAN ODYSSEY", built in Yokosuka, Japan in 1982-1984, was used as a launch platform. The platform corresponded to the class for the unrestricted navigation area. The platform was badly damaged in a fire on September 22, 1988. After the fire, the platform was partially dismantled, and it was no longer used for its intended purpose. In 1992, the platform was repaired and re-equipped at the Vyborg shipyard. It was decided to use it in the Sea Launch project. "Odyssey" has very impressive dimensions: length 133 m, width 67 m, height 60 m, displacement 46 thousand tons.

Launch platform "Odyssey"
In 1996-1997, at the Norwegian shipyard Rosenberg in Stavanger, special launch equipment was mounted on the platform, and it became known as Odyssey. The second stage of re-equipment of the joint venture took place at the Vyborg shipyard.
The Sea Launch Commander was built specifically for the Sea Launch project by Kvaerner Govan Ltd., Glasgow, Scotland in 1997. In 1998, the SCS was retrofitted at the Kanonersky shipyard, St. Petersburg. The SCS is equipped with systems and equipment that allow carrying out complex tests of the launch vehicle and the upper stage on board, refueling the upper stage with propellant and oxidizer components, and assembly of the launch vehicle.

Assembly and command ship "Sea Launch Commander"
The SCS also performs the functions of the MCC during the preparation and launch of the launch vehicle. The SCS has a command post for controlling the flight of the upper stage and means for receiving and processing telemeasurements. SCS characteristics: length 203 m, width 32 m, height 50 m, displacement 27 thousand tons, maximum speed 21 knots.

Satellite image of Google Earth: Sea Launch complex at the Long Beach parking lot
The floating cosmodrome Sea Launch uses medium-class Zenit-2S and Zenit-3SL launch vehicles with a launch weight of up to 470,800 kg.

In "Zenith", unlike many domestic RNs, toxic hydrozine and aggressive oxidizing agents are not used. Kerosene is used as fuel, and oxygen is used as an oxidizer, which makes the rocket environmentally friendly. In total, 35 launches were carried out from the floating platform from March 27, 1999 to February 1, 2013.

The starting point is the Pacific Ocean with coordinates 0 ° 00 ′ north latitude. 154 ° 00 ′ W d., near Christmas Island. According to statistics collected over 150 years, this section of the Pacific Ocean is considered by experts to be the most calm and remote from sea routes. However, already a couple of times, difficult weather conditions forced the launch time to be postponed by several days.
Unfortunately, the Sea Launch program is currently experiencing serious financial difficulties, it has been declared bankrupt and the future has not been determined. According to the Kommersant newspaper, losses were caused by the fact that it was not possible to ensure the planned intensity of launches: initially it was planned to carry out 2-3 consecutive launches in one exit to the starting position. The low reliability of the Zenit launch vehicle also played a negative role, out of 80 launches of Zenit launch vehicles - 12 ended in an accident.
The head of the Rocket and Space Corporation (RSC) Energia, Vitaly Lopota, proposed transferring control over the Sea Launch project to the state. And to carry out launches from it as part of the Federal Space Program. However, the government of the Russian Federation does not see the need for this.
Business representatives from a number of countries - China, Australia, and the USA - are showing interest in Sea Launch. There is interest from large companies such as Loсkheed Martin. If desired, Russia could become the owner of this unique complex, making the ports of Sovetskaya Gavan, Nakhodka or Vladivostok its base.
Based on materials:
http://geimint.blogspot.ru/2007/07/fire-from-space.html
http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kosmodrom
http://georg071941.ru/kosmodromyi-ssha
http://www.walkinspace.ru/blog/2010-12-22-588
http://sea-launch.narod.ru/2013.htm
All satellite imagery courtesy of Google Earth
A cosmodrome is a territory intended to house a complex of structures from which spacecraft are launched into outer space. It got its name similar to the airfield for aircraft. The spaceport area is usually very large, it is specially selected far from dense settlements so that loose particles during launch do not harm living quarters or adjacent launch sites.
They are trying to build spaceports closer to the equator. In this place on Earth, the magnetic field is the weakest and the easiest way for a launch vehicle to overcome it. The fuel economy of the launch vehicle when launched from the equator is about 10% compared to mid-latitudes. Thus, from the equator, the carrier can launch a large payload into orbit. The construction of the International Cosmodrome at Chimborazo in Ecuador, the most distant point from the center of the Earth, is considered very promising. The launch could be carried out via an electromagnetic channel with an accelerator embedded in the rock. This would save fuel at launch and reduce the emission of harmful substances from the rocket launcher engines. Due to the fact that few countries are geographically located on the equator, sea-based cosmodromes are being built.

Cosmodromes of the world through the eyesKvant. Space
Our portal site constantly monitors space news. This section will contain a description of the launch sites, publish the latest information about the world's cosmodromes, past and upcoming launches of space rockets.

In total, there are more than two dozen cosmodromes in the world. They are similar in structure and differ only in terms of the structural component of the starter kits. The selection of a site for the construction of a cosmodrome depends on several factors.

An important component in this regard is flight ballistics. To achieve the minimum energy consumption during the launch of the spacecraft into orbit, it is necessary that its inclination corresponds to the geographic latitude of the launch pad. The latitude of the cosmodrome is considered critical when launching into orbits in the equatorial plane. First of all, commercial spacecrafts are brought into this zone: repeaters of TV programs and communication satellites. The best for such work are such cosmodromes: the new European Kourou (5 degrees latitude), the Brazilian Alcantra (2.2 degrees latitude) and the Sea Launch floating cosmodrome, capable of launching directly from the equator.

During a launch from zero latitude (equator), the booster accelerates 465 m / s and is deflected eastward by the rotation of the Earth. The geographical latitude of Baikonur makes it possible to develop an additional speed up to 315 m / s, Plesetsk - 211 m / s.

Therefore, the launch trajectory of launch vehicles is usually laid in the direction to the east. Only Israel is forced to launch missiles from its cosmodromes in the opposite direction - in the east, it neighbors unfriendly countries.

Another factor that is taken into account when choosing a suitable site for the construction of the cosmodrome is the location of the "fall fields", that is, the supposed places of the fall of spent stages, parts of rockets and other equipment. In this regard, the most successful is the close location of the launch sites to the ocean. Therefore, most of them are located on the coast.

The functioning of spaceports has a bad effect on the state of the environment. First of all, this is caused by the presence of aggressive and toxic substances in the rocket fuel. Heptyl, nitrogen tetraxide and Nitric acid can cause significant damage to plants, animal and human health.
In addition to disasters, the leakage of harmful substances into environment is carried out through the daily operation of the cosmodrome - this is the loss of fuel components during storage and during rocket refueling. An underfueling of a satellite can lead to the loss of an expensive unit, so fuel losses are inevitable.

Russian cosmodromes
The portal site invites you to get acquainted with the cosmodromes located on the territory of Russia. This section of the site will contain up-to-date information on the development of the network of launch sites in our country.

In 2014, 31 launch vehicles were launched from various spaceports by Russia, only once the launch failed. The Russian Federation has been at the top of the world list of countries for this indicator for many years. Most of the launches take place at the Baikonur cosmodrome. Also, on the territory of Russia, launch launches are made from the Kapustin Yar (Astrakhan Region), Plesetsk (Arkhangelsk Region) and Svobodny (Amur Region) cosmodromes.

Thus, at the present time, the Russians own four cosmodromes and are building one new one. In the near future, it is planned to open Eastern cosmodrome, which is being built in the Amur region in the Far East. Work on its construction started back in 2011. The first tests of launching rockets from this complex of structures are planned for 2015, and from 2018 they will launch spacecraft with astronauts from there.

The significance of cosmodromes
the site invites you to a fascinating excursion to the cosmodromes of the world. Here you will get acquainted with the history of the construction of launch sites, their characteristics, space technology, significant events and many others related to the topic of launching rockets from Earth into outer space.

Spaceports play a significant role in our life. It is thanks to their work that satellites and spacecraft are launched into Earth's orbit. They are engaged in space exploration, monitoring of the Earth's atmosphere and mineral exploration. Orbiting satellites do a lot of useful things not only for science, but also for other areas. Thanks to the information received from satellites, we can track our location using GPS technology, watch TV channels broadcasting in remote regions of the planet.

After the first successful manned flight into space, a new era began for mankind, each day of which shocks us with incredible new discoveries. In 1990, the most powerful Hubble telescope was launched into Earth's orbit, thanks to which the human eye opened up distant space.

It is hard to underestimate the importance of the space industry and its infrastructure in particular. Taking into account the rapid dynamics of the increase in the number of inhabitants on our planet, it can be assumed that soon the issue of colonizing space will not only be the plot of a science fiction film, but will also appear before people in all its relevance. In the meantime, we are slowly moving in this direction, exploring new space horizons, creating spacecraft and expanding the geography of launch facilities.
On November 30, 1993, a decision was made to build a new Russian cosmodrome in the Amur Region, named Svobodny and put into operation 3 years later. In honor of the 20th anniversary of this event site prepared an overview of the most prominent spaceports from around the world.
The largest cosmodrome
The largest cosmodrome on the planet is Baikonur, erected in 1957 on the territory of the former USSR. Now it belongs to Kazakhstan and is used by Russia on a leasehold basis. The area of the complex, including the city of the same name, is 6717 km².
but Baikonur boasts not only size. From here, the first cosmonaut and the first interplanetary station to land on the Moon were sent on a flight. According to 2012 data, the cosmodrome is still the leader in terms of the number of launches - it accounts for a third of the world's "volume" annually.

The smallest cosmodrome
The smallest area is occupied by the US-owned spaceport Wallops (Wallops). Three separate sites - the base, the launch site and the center - are compactly located only 25 km².
The most expensive cosmodrome
The Russian cosmodrome currently under construction in the Amur Region promises to become the most expensive in the history of world cosmonautics Oriental... The estimated date of "opening" is the end of 2015, the reserved area is 1035 km².
According to preliminary estimates, the creation of a "new Baikonur" designed to ensure Russia's space independence will cost Roscosmos 300 billion rubles.

The most convenient spaceport for launches
The most advantageous - as close as possible to the equator - position for placing satellites into geostationary orbit is occupied by the Brazilian cosmodrome Alcantara (Alcantara). Due to the energy of the Earth's rotation, its coordinates are 2 ° 17'S. 44 ° 23'W - provide spacecraft additional speed of 460 meters per second at the start, which can significantly reduce fuel consumption.
The most controversially located cosmodrome
The most controversial is the geographical location of the American cosmodrome ( John F. Kennedy Space Center) on Merritt Island, Florida. On the one hand, there is an economically advantageous proximity to the equator (28 ° 35´06 "N 80 ° 39´0.36" W) and a distance from settlements corresponding to safety measures. On the other hand, there is an unfavorable climate for flights. Tornadoes and tornadoes periodically pass through the territory of the center. And because of the increased thunderstorm activity, lightning "attack" the cosmodrome more often than any other place in the United States. As a result, the maintenance of the system of powerful lightning rods annually costs NASA a round sum of about $ 3-4 million.
However, in 1969 it was Kennedy Space Center sent the first man to the moon.

The most hospitable cosmodrome
Since 2009 the corporation Virgin galactic began accepting applications for flights for non-professionals. The role of the transport company is assigned to a private cosmodrome (USA, New Mexico).
The program of the space tour includes preparation and the actual journey to the conditional boundary between space and the Earth's atmosphere - the Karman Line. The flight lasts 2.5 hours, of which 60 minutes is spent on the rise, 6 - on being in zero gravity and contemplating cosmic beauties. One can accommodate up to 6 passengers. The cost of unearthly pleasure is $ 200 thousand. However, having paid in advance, you will have to wait at least 2014. The leadership Virgin galactic the date of the first flight, originally scheduled for the end of 2010, has already been postponed.

The most reliable cosmodrome
The most reliable is the cosmodrome Kuru (Kourou) located in French Guiana. Of the 192 launches carried out since the opening of the cosmodrome, 186 (about 97%) were successful. Near the equator, it is slightly inferior to the Brazilian Alcantara- 5 ° 14'21 "S 52 ° 46'15". But the development and modernization of infrastructure Kuru finances as many as 20 European member countries of the European Space Agency.
The high level of safety and quality of equipment attracts other clients to the cosmodrome, including the USA, Japan and Russia.

The most unfortunate cosmodrome
In the sad statistics of unsuccessful launches, the Australian cosmodrome is in the lead Woomera (Woomera), opened in 1947 in the area of the village of the same name. During 10 years of active operation - 1964-1971 - 10 out of 24 launch vehicles (about 41%) suffered an accident. In 1976, the unlucky spaceport was closed due to unprofitability.
"Unlucky" Australian spaceport Woomera
Now an Exhibition is organized in the center of the village military equipment, where you can see the safely landed rockets and planes.

The most "desperate" cosmodrome
Israeli air base-cosmodrome Palmachim (Palmachim) Is the only place in the world where rockets are fired outside the east. That is, "against" the rotation of the planet. The fact is that the lands to the east of the base are inhabited and there is a border with neighboring states nearby. So we had to lay a "highway" in the western direction through the Mediterranean Sea. However, 6 out of 8 produced from 1988 to 2010. launches were successful.
The most famous cosmodrome in Russia is Baikonur. The largest number of launches of carrier rockets was made from it. At the moment, Russia is building a new Vostochny cosmodrome.
How many spaceports are there in the world?
Baikonur is the oldest cosmodrome in Russia and the entire planet. Moreover, it is also the largest. It was founded in 1955 on the territory of Kazakhstan. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, the cosmodrome is rented the Russian government from the Kazakh side. At the moment, the lease is concluded until 2050.
In total, there are 14 cosmodromes in the world from which launch vehicles were launched. The territory itself is a complex of structures designed to launch special vehicles into space. As a rule, they occupy huge areas and are located at a great distance from settlements. After all, the steps that separate during the flight can cause damage to residential buildings or neighboring launch sites.
Scientists have long noticed that the most advantageous location of cosmodromes is right at the equator. Thus, a booster rocket saves about 10% of fuel compared to a rocket that is launched from mid-latitudes.
In addition to Russia, spaceports from which launch vehicles have already been launched exist in the United States, French Guiana, China, India, Japan, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea and Iran. The international launch platform "Odyssey", located in the Pacific Ocean, also operates.
No. 1 - Baikonur
The construction of the largest cosmodrome in Russia began in 1955. Initially, a special commission was created, which determined the place where this structure will appear. This area had to meet several conditions. They chose a vast, but at the same time sparsely populated area, there was to be a main railway nearby. Also, prerequisites are the availability of drinking and process water in large volumes.
Several options were considered. As a result, the choice was stopped at the Kyzylorda region on the territory of the Kazakh SSR. The cosmodrome began to be built in the desert, not far from the Aral Sea, the Syrdarya rivers and the Moscow-Tashkent railway line. Another advantage is the sunny weather, which lasts about 300 days a year in these places. In addition, the desert is relatively close to the equator.
The construction of the cosmodrome was supervised by Georgy Shubnikov, Major General of the Engineering and Technical Service. Interestingly, in order to disorient a potential enemy, in addition to the main cosmodrome, several camouflage structures were built. This is a false cosmodrome in the Karaganda region. It is located near the village of Baikonur. After the successful space flight of the first man, Yuri Gagarin, it was the name Baikonur that stuck in the minds of people. As a result, the real cosmodrome located elsewhere is now called so.

Object history
The first rocket was launched from the territory of Baikonur in 1957. True, unsuccessful. On August 21, for the first time, a rocket successfully delivered a conditional cargo from Baikonur to Kamchatka.
At 22.28 on October 4, 1957, the space age began. The Soviet Union launched the world's first artificial satellite from Baikonur. And at 09.07 the first man went on a space flight from here for the first time.
A large-scale infrastructure has been organized at Baikonur. The cosmodrome has 9 launch complexes and 15 launchers. There are two airfields at once, more than a thousand kilometers of highways, thousands of kilometers of communication lines and power transmission lines.
No. 2 - Vostochny cosmodrome
In 2007, Russian President Vladimir Putin signed a decree to start construction of a new facility. The construction of the Vostochny cosmodrome in Russia began in 2012.
It must provide the country with independent access to space. In addition, it must guarantee the fulfillment of all obligations under commercial and international space programs, and will also significantly reduce the cost of maintaining Baikonur. Ultimately, the socio-economic situation in the Amur Region, where construction is underway, will improve.
The territory on which the Vostochny cosmodrome is being built has a number of advantages. Russia will be able to send rockets into space, bypassing the densely populated regions of the country and the territories of foreign states. Railway, airfields. With the emergence of a new cosmodrome, the political risks associated with the location of Baikonur in Kazakhstan will be neutralized.
Corruption scandals
The construction of a new cosmodrome is regularly accompanied by scandals. More than 80 billion rubles were allocated for the first stage alone; in total, they plan to spend about 300 billion on construction.
At the same time, corruption scandals constantly occur. They began back in 2012, when workers who were not paid their wages began to strike at Vostochny. To solve this problem, Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Rogozin was sent there. In 2014, he became the main construction coordinator. Since then, he has visited the site of the future cosmodrome more than fifty times.
Despite this, by the spring of 2015, wage arrears amounted to about 150 million rubles. The builders went on an indefinite hunger strike, which became one of the main topics of direct communication with Russian President Vladimir Putin.
At the moment, criminal cases have been initiated into the embezzlement of 7.5 billion rubles.
The fate of Baikonur
After it became known that a cosmodrome would appear on the territory of Russia, many were worried about the fate of Baikonur. President of Kazakhstan Nursultan Nazarbayev has officially acknowledged that the state budget will not be able to maintain the cosmodrome. For this reason, Astana will not insist on its transfer by Russia.
At the same time, it is obvious that, at least for the next few years, the Kazakh cosmodrome will remain the main site for the launch of heavy rockets. Even after the commissioning of Vostochny. Although it is planned that over time it will be the main cosmodrome of Russia.
For example, the Angara super-heavy rocket at the new cosmodrome is expected to be launched no earlier than 2026. Another disadvantage of the new launch site for space rockets is that it is located about 6 degrees north of Baikonur. But the closer the launch pad is to the equator, the lower the costs and the higher the efficiency.
Therefore, for sure, Russia will not leave Baikonur in the coming years. It will decline, unless the politicization in cooperation between Moscow and Astana, which is often based on the fact that the main Russian cosmodrome is located on foreign territory.

No. 3 - Plesetsk cosmodrome
Another famous Russian cosmodrome is located in Plesetsk. This cosmodrome provides support for Russian space programs that are related to defense functions, as well as scientific and commercial tasks.
It is located in the Arkhangelsk region, almost 200 kilometers from the regional center. The Plesetskaya Northern Railway is nearby.
The administrative and residential center of the cosmodrome is located in the city of Mirny. Its population is approximately 30,000.
The first launch of the carrier rocket from Plesetsk took place in 1966. After that, he served as a test site for strategic missile systems of intercontinental range.
Since 1968, international programs have been implemented. Other cosmodromes in Russia are also doing this work. Plesetsk, for example, hosted the French spacecraft.

Tragedies in Plesetsk
Many cosmodromes in Russia, the list of which you will find in this article, fell into the sad chronicle of accidents with human casualties. Plesetsk was no exception.
In 1973, 8 people died in the explosion of the Kosmos rocket. This happened during her refueling. Another 10 people were hospitalized. One of them died as a result of his burns without regaining consciousness.
In 1980, the largest tragedy occurred, which claimed the lives of 48 people. The explosion occurred again during refueling. This time the Vostok missile and its satellite were at the epicenter of the incident.
In 1987, a fire broke out in a nearby military unit. 5 people were killed.
In 2002, a few seconds after the launch, a Soyuz rocket exploded. There was one crew member on board.
The last tragedy happened in 2013. Two were killed and three were hospitalized during routine cleaning of the rocket fuel canister.
Despite this, Plesetsk is the northernmost cosmodrome in Russia, where rocket launches continue.

No. 4 - Kapustin Yar cosmodrome
When listing the Russian cosmodromes, the list of which is present in this article, one cannot fail to mention Kapustin Yar. It is located in the northwest of the Astrakhan region. It was originally built as a ballistic missile testing ground in 1946.
Kapustin Yar is often called the "Russian Roswell". It is believed that it was here that Soviet scientists studied alien ships. In support of this legend, there are many TV programs, which, for example, describe in detail the layout of the underground complex under the landfill.

No. 5 - Svobodny cosmodrome
Those who are interested in where the cosmodromes are in Russia know about the existence of a not as popular launch site as the previous ones, Svobodny. It is located in the Amur Region, not far from the town of Tsiolkovsky, formerly Uglegorsk.
In total, five missile launches were made from here. The last one was in 2006. The cosmodrome has not been functioning for 10 years.
In the 2000s, it was planned that the Strela rocket complex would be launched from this cosmodrome. However, he did not pass the state ecological expertise. Primarily due to the highly toxic rocket fuel heptyl. By the way, many Kazakhstani public and environmental organizations are against it.
Ultimately, it was decided to eliminate it as part of a large-scale reduction of the armed forces due to low profitability and liquidity. There were very few launches from the Svobodny cosmodrome, as a result, funding was minimal.

No. 6 - floating cosmodrome "Sea Launch"
Russia also has its own floating cosmodrome - the Sea Launch platform. It is located in the Pacific Ocean. The closest land area to it is Christmas Island.
Since 1995, it has been led by an international consortium. It includes Russia and the United States. The first demonstration satellite was launched already in 1999. At the same time, the first commercial launch of the launch vehicle took place.
At the moment, 36 rockets have been sent from the Sea Launch cosmodrome. Moreover, three of them were failed, one launch was recognized as partially successful.
Historically, humanity has always looked to the sky and was interested in various celestial bodies. There are legends that the first people allegedly visited space in ancient times, but this has not been documented. But the whole world experienced surprise and joy when, in 1961, Soviet officer Yuri Gagarin went into space and then returned to Earth.
The first launch of a Soviet spacecraft took place from a secret facility called the Baikonur Cosmodrome. In this article, we will consider not only the named launch site, but also other significant places.
Discoverer
"Research test site"- that was the name of the project approved by the General Staff of the USSR Ministry of Defense in 1955. Subsequently, this place became known as the Baikonur cosmodrome.
This object is located in the Kyzylorda region on the territory of Kazakhstan, near the village of Toretam. Its area is about 6,717 sq. km. And for many years the first cosmodrome in the world has been considered one of the leaders in its industry in terms of the number of launches. For example, in 2015, 18 rockets were launched from it into Earth's orbit. The named test site for space launches is leased by Russia from Kazakhstan until 2050. About 6 billion Russian rubles a year are spent on the operation of the facility.
Secrecy level
All cosmodromes in the world are star harbors, which are protected in the most careful way, and Baikonur is no exception in this regard.
Thus, the construction of a space port was accompanied by the construction of a false cosmodrome near the village of Baikonur. This tactic was also used during World War II, when the military was building false airfields with dummy equipment.
Soldiers and officers of the construction battalion were directly involved in the construction of the cosmodrome. In short, they accomplished a real labor feat, since they were able to build a launch pad in two years.

The problems of today
Today, the legendary cosmodrome has fallen on hard times. The starting point for the emergence of problems can be considered 2009, when the military left it, and the object came under the full jurisdiction of Roscosmos. And all because, along with the military, the cosmodrome also lost a rather serious amount of money that had previously been allocated for training and testing.
Of course, launching rockets with satellites also brings in money, but these days this is not done as often as it used to be, when rockets took off almost every week. Nevertheless, the cosmodrome still remains recognized as the world leader in space launches.
Russian giant
But still, considering the cosmodromes of the world, it would be unfair not to pay attention to other similar objects, one of which is located on the territory of the Russian Federation. The technical capabilities and the money invested in its construction and development allow it to launch and launch many satellites and space stations into Earth's orbit.
The Plesetsk cosmodrome is a Russian space harbor located 180 kilometers from Arkhangelsk. The size of the object is 176,200 hectares.

The Plesetsk cosmodrome is inherently a special rather complex scientific and technical complex, which is designed both for military missions and for peaceful purposes.
The cosmodrome includes many objects:
- Complexes for launching carrier rockets.
- Technical complexes (carry out the preparation of rockets and other spacecraft).
- Multifunctional filling and neutralization station. With its help, booster rockets and booster blocks are fueled.
- Almost 1,500 buildings and structures.
- 237 objects providing energy to the entire cosmodrome.
Far Eastern site
One of the newest cosmodromes in Russia is Vostochny, which is located near the city of Tsiolkovsky in the Amur Region (Far East). The harbor is used exclusively for civilian purposes.
The construction of the facility began in 2012 and was actively accompanied by various corruption scandals and strikes by workers due to non-payment of wages.
The first launch from the Vostochny cosmodrome took place relatively recently - on April 28, 2016. The launch made it possible to put three artificial satellites into orbit. At the same time, President of the Russian Federation Vladimir Putin, as well as Deputy Prime Minister of Russia Dmitry Rogozin and the head of the Kremlin administration Sergei Ivanov, were personally present at the site at the time of launching the launch vehicles.
It should be noted that a successful launch from the Vostochny cosmodrome was carried out only on the second attempt. Initially, it was planned to launch the Soyuz 2.1A carrier rocket on April 27, but literally one and a half minutes before the launch, the automatic system canceled it. The management of Roskosmos explained this incident as an emergency failure in the operation of the control system, as a result of which the start was postponed for a day.

List of the main cosmodromes of the planet
The currently existing cosmodromes in the world are ranked by the date of their first orbital launch (or its attempt), as well as by the number of successful and failed launches. Their list currently looks like this:

This launch pad first sent a rocket into space on April 9, 1968. It is important to note that the cosmodrome is located literally five hundred kilometers from the equatorial line, which makes it possible to launch most efficiently aircrafts on our Earth. In addition, the geographic location of the space port is such that the launch angle is always 102 degrees, and this indicator significantly expands the range of launch trajectories of objects used for various tasks.
The effectiveness of the launch pad is so high that it attracted the attention of many corporate clients from many countries of the world: USA, Canada, Japan, Brazil, India, Azerbaijan.
In 2015, it invested over 1.6 billion euros in the modernization of the cosmodrome infrastructure. Also, the high level of security of the facility deserves special attention. Space Harbor is located in an area that is densely covered with equatorial forests. At the same time, the department itself is poorly populated. In addition, there is no risk of even the weakest earthquakes or hurricanes. To ensure maximum protection against external attacks, the 3rd regiment of the Foreign Legion (France) is located at the cosmodrome.
A joint project
Launch platform "Odyssey" is, in fact, a huge self-propelled, semi-submersible catamaran. The facility was built in Norway on the basis of an oil production platform. The described mobile cosmodrome includes:
- starting table;
- rocket installer;
- fuel and oxidizer refueling systems;
- thermostating system;
- nitrogen supply system;
- cable mast.

The marine space launcher is serviced by a staff of 68 people. Living quarters, a medical center and a canteen have been built for them.
The platform is based in the port of Long Beach, California (Southwest USA). The industrial giant of the space industry arrived at this place of its permanent deployment on its own, passing its way through the Strait of Gibraltar, the Suez Canal and Singapore.
Conclusion
Finally, I would like to note that all the cosmodromes of the world existing today allow mankind to actively develop and explore space. With the help of platforms for launching vehicles into Earth orbit, many different civil and military actions are carried out.
 05 01 medical biochemistry where to work
05 01 medical biochemistry where to work Biochemistry who can work
Biochemistry who can work Types of monopolies: natural, artificial, open, closed
Types of monopolies: natural, artificial, open, closed