Ready-made example projects in microsoft project. To help the manager: we are planning a project in MS Project. Assigning a resource to a task
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
- Introduction
- 1. Organization of the project
- 1.3 Creating a work schedule
- Conclusion
Introduction
The rapid development of computer technology, the creation of a friendly for an unskilled user software led to widespread use information technologies in all areas human activity, served as an impetus for the development of a society based on the use of various information.
Per short term information systems have evolved from computing systems used in scientific research and automated control systems large enterprises to complex automated information systems, allowing to implement the whole range of not only processing, accumulation of information, but also the management of companies and organizations at all levels.
Creation of personal computers, adapted graphical interface expanded the market of information products and services to the level of "home consumption". Information systems have turned from a technological component of business and management into a factor of production, a factor of competition. However, along with the obvious advantages of using information systems, the problem of information systems management arose.
The practice of creating and operating information systems revealed problems and contradictions that could be resolved only by introducing a comprehensive specialized information management. The cost of designing and implementing information systems usually significantly exceeded the planned amount. The quality of development turned out to be unsatisfactory: contradictions between hardware and software during operation, an increase in the cost of maintaining systems in operation, etc.
Today, the activities of any company and organization strongly depend on the unit that provides the information environment of the company, and this dependence increases over time. As a result, maintenance of information systems ceases to be only a technical task and increasingly becomes an integral part of the business, integrated into the company's business processes.
The level of development of the organization's information system, the importance of information technology for the organization's activities makes the IT departments of companies an integral part of the business. The complexity of tasks in the management of information systems and personnel leads to the need to develop strategies in the field of information technology for specialized management - information management.
The use of computer hardware, application software, network technologies is a matter of prestige and "advancement" of management for the company. Nobody demands any kind of return from the information system, let alone economic efficiency.
Information technology, information systems are applied at the level operational management enterprise, organization - accumulation, storage, classification, primary processing of information. Information systems are used to solve business problems of an enterprise or organization.
An important factor in the training of highly qualified specialists in the field of economic information systems is comprehensive training, taking into account a wide range of areas of knowledge, specialized disciplines.
A feature of the discipline "Information Management" is that this branch of knowledge originated relatively recently and is developing. Essentially, information management has neither an established terminology, nor methods and solutions that have become classical. As a result, specialists often use not only different concepts and terms, but also interpret the tasks of information management in different ways and the methodology for their solution. Research materials, practical advice, analysis of the development and implementation of IS, are the result of a discussion of specialists in the field of information technology and IT management.
1. Organization of the project
1.1 Creating a project in the program Microsoft Project
By default, Microsoft Project 2016 automatically opens the New command at startup, where you can choose how to create a new project. A project in Microsoft Project 2016 is a file of type mpp. In order to create new project in Microsoft Project 2016 forcibly, you need to open the "New" command with the "File" button.
Figure 1 - Creating a new project
Now you can choose how to create a new project:
* select "New project" and press the "Create" command: the project will be created based on the Global template. mpt;
* create a new project from an existing document - a project, Excel workbook, or a SharePoint task list;
* create from a template. You can choose a template from those available on your computer or at Office.com (if you have an internet connection).
After creating a project file, it is recommended to save it immediately. To do this, press the "File" button, select the "Save" command, select a location to save the file and give the project file a "Name" (by default, the project file is named "Project1. Mpp").
Figure 2 - Saving the project file
Microsoft Project 2016 supports export to PDF and XPS format.
Portable Document Format (PDF) is an electronic format with permanent markup that preserves document formatting and allows file sharing. The PDF format ensures that when the file is viewed online and when it is printed, the original format is preserved and the file data cannot be easily changed. PDF format is also useful for printing documents in a typography.
XML Paper Specification (XPS). XPS is an electronic file format that preserves document formatting and enables file sharing. The XPS format ensures that when the file is viewed online and when it is printed, the original format is preserved and the file data cannot be easily changed.
1.2 Creating a project calendar in Microsoft program Project
Microsoft Project uses calendars to describe working and non-working hours.
Microsoft Project uses three types of calendars:
1.the project calendar defines work time the default for the entire project (for all resources and project tasks);
2. resource calendars are used for individual resources or for groups of resources that have an individual work schedule;
3. Calendars of tasks are used for tasks that can be performed on time different from the standard calendar of the project, for example, part of the work of the project can be performed only in the first half of the working day.
The project calendar defines the work schedule for all resources and tasks that do not use a custom calendar. Changes made to the project calendar are automatically reflected in the resource calendars generated from the same project calendar.
Base calendars are used as the project and task calendars, and as the basis for resource calendars. Microsoft Project has three basic calendars:
1. Standard: business hours from Monday to Friday (9:00 am to 1:00 pm and 2:00 pm to 6:00 pm). This calendar is used by default when creating a new project;
2. 24 hours: no non-working hours;
3. Night shift: night shift from Monday night to Saturday morning (from 23:00 to 8:00 with an hour break).
Microsoft Project supports the creation of its base calendars if the existing calendars do not meet the project's requirements.
Figure 3 - Creating a calendar
You can assign the created calendar to the project through the Project Information dialog box.
Figure 4 - Purpose of the created base calendar
1.3 Creating a work schedule
Project "Development software tool"is drawn up to achieve a certain result within a certain time frame and for a certain amount of money. The project plan is drawn up in order to determine by what work the result of the project will be achieved, what people and equipment are needed to carry out these works and at what time these people and equipment will be are busy working on the project. project plan contains three main elements: tasks, resources and assignments.
Drawing up a project plan in general view is to describe the tasks of the project, the available resources and determine the interdependencies between them using assignments.
Work order:
1) Editing the initial parameters of the project.
To edit the initial parameters of the project, you need to go to the "Project" tab and click the "Project Information" button, and in the window that opens, define the start date of work (Tue 05.04.16).
Figure 5 - Start date of work
2) Create a list of project tasks and their duration
Determination of software development goals - 2 days.
Development planning - 4 days
Theme code assignment - 3d.
The choice of software development principles - 24 days.
Clarification of the basic requirements for software - 20 days.
Formation of the draft TK - 7 days.
Coordination of the draft TOR with the software customer - 5 days.
Formation of a structural model - 7 days.
Object-oriented model formation - 30 days
Determination of the principles of building the screen interface - 35 days.
Development of basic modules - 50 days.
Database development - 48 days
Integration of all modules - 35 days
Debugging - 5 days
Beta release - 2 days.
Collection of information about test results - 5 days.
Modification of modules and databases - 7 days.
Final version release - 5 days.
Formation of the documentation required for certification - 5 days.
Internal audit of the software development process - 2 days.
Conclusion of a certification agreement - 2 days.
Software certification - 2 days.
3) Create a resource list
- 1 person
Programmer - 5 people
Economist - 1 person
Software auditor - 1 person
4) Create assignments (links)
The dependence of tasks and resources is given in the table.
Table 1 - Dependence of tasks
|
Task name |
Duration |
The ending |
Predecessors |
Resource names |
||
|
Software development |
||||||
|
Organization of work |
||||||
|
Defining software development goals |
Head of Software Development Department |
|||||
|
Development planning |
Head of Software Development Department |
|||||
|
Assigning a theme code |
Economist |
|||||
|
Choosing software development principles |
Head of Software Development Department |
|||||
|
Development of technical specifications |
||||||
|
Clarification of basic software requirements |
Head of Software Development Department; Programmer 1 |
|||||
|
Formation of the draft TK |
Programmer 2 |
|||||
|
Coordination of the draft TK with the software customer |
Head of Software Development Department; Programmer 2 |
|||||
|
Software development |
||||||
|
Formation of a structural model |
Programmer 3; Programmer 4 |
|||||
|
Object-oriented model formation |
Programmer 1; Programmer 4; Programmer 5 |
|||||
|
Determination of the principles of building the screen interface |
Head of Software Development Department; Programmer 4 |
|||||
|
Development of core modules |
Programmer 1; Programmer 2; Programmer 3; Programmer 4; Programmer 5 |
|||||
|
Database development |
Programmer 1 |
|||||
|
Integration of all modules |
Programmer 2; Programmer 3; Programmer 4 |
|||||
|
Debugging and testing |
||||||
|
Debugging |
Programmer 3; Programmer 4; Programmer 5 |
|||||
|
Beta release |
Programmer 1 |
|||||
|
Collecting Test Results Information |
Programmer 2; Programmer 3 |
|||||
|
Modification of modules and databases |
Programmer 2; Programmer 4; Programmer 5 |
|||||
|
Final release |
Programmer 1 |
|||||
|
Certification |
||||||
|
Formation of documentation required for certification |
Programmer 4; Programmer 5; Programmer 1 |
|||||
|
Internal audit of the software development process |
Software auditor |
|||||
|
Conclusion of a certification agreement |
Head of Software Development Department |
|||||
|
Software certification |
Head of Software Development Department |
Using the types of links (assignments), create a Gantt chart in accordance with Table 1.
Figure 6 - Gantt chart
1.2 Formation of the structure of the work schedule
When developing large projects consisting of a large number of works, Microsoft Project allows you to combine related works into groups. The creation of a hierarchical structure of the project allows you to decompose the work of the project into smaller, visible and manageable parts, to more accurately determine the composition and characteristics of the work to be performed.
One of the basic principles of building a hierarchical project structure is the principle of completeness. All work and results of the project, including intermediate and managerial ones, must be present in the hierarchical structure of the project.
The opposite is also true - work outside the project (that is, necessary for the successful execution of another project / process) should not be included.
Let's group the work by stages and enter the names of these stages.
* To create a group (stage), right-click on the first line of the table and select "Insert task" from the context menu;
* We call it "Organization of work";
* Let's select the works: "Defining the goals of software development", "Development planning", "Assigning the theme code" and "Selecting the principles of software development" and group them by clicking on the button "Decrease the level of the problem".
In a similar way, you need to group all subsequent tasks to create the following stages: "Development of technical specifications", "Software development", "Debugging and testing", "Certification".
The final stage will be the creation of the "Software Development" group, which will group all the stages created above.
Figure 7 - Hierarchical structure of the project
Same way this task can be solved by a top-down method.
Top-down project planning first identifies milestones, which are then broken down into individual tasks.
2. Project resource assignments
An assignment refers to the relationship between a task and the resource required to complete that task. An arbitrary number of resources, both workers and material, can be assigned to one task (in other words, several assignments can be associated with one task).
To assign resources directly when describing a task, you must:
* To open the "Task Details" window, to do this, double-click on the task name or select the task and press the "Details" button on the "Task" tab;
* In the "Task details" window that opens, go to the "Resources" tab;
* In the input window, enter the name of the resource, if this name matches the name of an existing resource, it will automatically be assigned to the task, if the name does not match, a new resource of the "Labor" type will be created. To avoid duplication, select an empty line, and click on the down arrow on the right side of the line, then select the resource name from the drop-down list;
* The "Owner" field displays the name of the user of the owner of the resource, to whom the approval of the use of this resource will be sent. For all local and generic resources, this field is blank;
* In the "Units" field, enter the amount of the required resource. If the resource is labor, it is necessary to indicate the percentage of the resource's time that it will spend on the implementation of this task. If a material resource enter its quantity in the dimension specified in the "Resource Sheet" view. If you do not enter a costly resource;
* In the "Costs" field, the cost of using this resource will be displayed. For labor and material resources, this value will be calculated automatically when you click the "OK" button. For costly resources, you must indicate the amount that you plan to spend on the implementation of this task with this resource.
Figure 8 - Assigning resources when describing a task
Assigning a resource to a task:
* Go to the Gantt Chart view and go to the Resources page;
* Select the task for which you want to create a resource assignment;
* Click on the "Assign Resources" button. The corresponding dialog box will appear;
* In the "Resource name" field, select the resource that you want to assign to the task. If you need to create a new resource, go to an empty cell in the dialog box table and enter the resource name. Double-clicking on the resource name will bring up the "Resource Details" window, with which you can enter information about the resource;
* In the Units field, specify the number of resource units to be allocated in this assignment. For a work resource, the value is indicated as a percentage (the amount of working time).
The result is shown in Figure 8.
3. Tracking the progress of the project
For adoption management decisions needs an up-to-date and reliable information about the progress of the project.
When managing a project, you need to keep track of the elements of the project triangle: time, budget, and scope. Adjusting one element affects the other two. Events such as unexpected delays, cost overruns, and resource replacements can lead to scheduling issues.
If the project data is constantly updated, it is always possible to view the latest state of the project. You can track actual task progress, actual resource work, compare actual costs to planned budgets, and balance resource utilization. All this will allow you to identify potential problems in time in order to find and apply the right solution.
After you create a project and start work, you can track the actual start and finish dates, percentage of tasks completed, or actual work. The actual data shows the impact of the changes on other tasks and, ultimately, on the project finish date.
Determine one or two progress indicators to use in your project. For example, resources can quickly report on the percentage of work completed by task, giving you an overview of the progress of tasks. Or, conversely, resources can report the hours worked on each task by week. It will take longer, but will give a detailed picture of the progress of the work. The choice of indicators depends on your preferences and priorities.
To track the progress of work, you need to create a mark on the passage of the stage "Defining the goals of software development". To do this, on the Gantt chart, move the mouse pointer to the left side of the chart (the pointer will change its appearance to a percent sign with an arrow to the right). After that, you need to press the left mouse button and, without releasing it, drag the mouse pointer to the right.
Figure 9 - Mark of the passage of the stage "Defining the goals of software development"
There is a different way to mark the completion of the Development Planning stage. To do this, select the "Development planning" stage and double-click on it with the left mouse button. In the "Task Details" dialog box that appears, on the "General" tab, you need to set 100% in the "Percentage Completion" field and click the "OK" button.
Figure 10 - Mark on the passage of the "Development Planning" stage
A milestone completion mark will appear on the left of the Gantt chart table, and a dark blue bar will appear on the chart itself, which shows the percentage of completion of the work milestone. If the work is 100% complete, then the strip will be from the beginning to the end of the block of works.
Figure 11 - An example of work performed by 70%
Figure 11 shows an example of incomplete work execution, which shows that on the Gantt chart the dark blue bar is not up to the end of the work block (lower right corner). Everything that was done before would have been useless if there was no way to generate reports in Microsoft Project. "Project Overview" - a report showing the percentage of completion of the project. To generate it, go to the "Report" tab, click on the "Dashboards" button and select "Project overview".
Figure 12 - Project overview
"Cost Overview" is a more complete report showing both percentage completion of work and cash costs (both already spent and remaining costs).
Figure 13 - Overview of costs
"Critical Tasks" is a report that allows the user to see the remaining critical tasks. Critical tasks are tasks on which the entire project depends.
Figure 14 - Critical tasks
Conclusion
Microsoft Project is the most popular project management tool provided by Microsoft. The application is designed to help project managers develop plans, assign resources to complete tasks, manage budgets and analyze workload.
Microsoft Project can help you create a critical path-based plan. Graphs can also be applied to evenly distribute resource requests. The critical path is presented in the form of a Gantt chart (Gantt chart).
Resource definitions (people, equipment, and materials) can be shared across projects using a common pool of resources. Each resource can have its own calendar, which determines the days and shifts that are available to it. Resource metrics are used to calculate the cost of completing tasks, which are counted and added to the total resource level.
Each resource can be assigned multiple tasks in multiple plans, and each job can be assigned multiple resources. Microsoft Project schedules work based on resource availability as defined in its respective calendars. All resources can be defined in common base corporate resources.
Microsoft Project creates budgets based on resource metrics and assignments. Since resources are assigned to tasks and that work is evaluated, Microsoft Project calculates the cost, which is equal to the work multiplied by the metrics. This is all calculated to the overall level of the assignment, then to the total costs of the assignments and finally to the total project estimates.
project program management decision
List of sources used
Posted on Allbest.ru
1. Belyaeva S.A. The role of planning in the management process innovative projects// Production organizer. - 2010
2. Betanova I. The role of HR in project management // Handbook of personnel management. - 2011.
3. Betanova I. The role of HR in project management // Handbook of personnel management. - 2011.
4. Ganchin V.V. The role of project management in innovative development power industry in Russian Federation// Economics and Management: Ros. scientific. zhurn. - 2011.
5. Goncharenko S. Project Management // Quality Management. - 2011.
6. Emelyanov Y. Management of innovative projects in the company // Problems of management theory and practice. - 2011.
7. Ivasenko A.G. Project management: tutorial for students. - Rostov n / a .: Phoenix, 2009.
8. PMSOFT conferences on project management // Problems of management theory and practice. - 2011.
9. Kuznetsov A.A. Process management projects at the enterprise // Management today. - 2011.
10. Kuperstein V. Microsoft Project 2010 in project management. - SPb: BHV-Petersburg, 2011.
11. Lapygin Yu.N. Assessment of the effectiveness of project management // Economic analysis: theory and practice. - 2011.
12. Mazur I.I. Investment and construction project management: an international approach. - M .: Omega-L, 2011.
13. Matveeva L.G. Project management: textbook. - Rostov n / a .: Phoenix, 2009.
14. Mylnikov L.A. Microeconomic problems of management of innovative projects // Problems of management. - 2011.
Similar documents
Drawing up a project plan for the creation of a new enterprise for the production of cars. Creating a resource database in the Project Expert program. Application of the PERT methodology for project analysis. Monitoring the implementation of project tasks in terms of time and labor costs.
term paper, added 10/11/2014
Management methods complex projects... Editing project properties. Setting up the project calendar. Creating tasks in Microsoft Project and changing their properties. The choice of free resources and their use. Drawing up a project summary and budget report.
laboratory work, added 03/01/2015
Configuring Microsoft Project settings. Tables as the main means of storing data in MS Project. Prepare to draw up a plan and track the progress of work on it. Formatting Gantt charts. A set of functions for working with network graphics.
practical work, added 12/25/2010
Description of the key characteristics of the bakery project, phases, tasks and the resources required to complete them. Analysis and optimization of the project plan using Microsoft Project, data entry into the program. Automatic resource leveling.
test, added 06/02/2010
Principles of work of Microsoft Project (project management program), its basic concepts: tasks, resources, assignments. The sequence of actions for creating a new project, entering tasks and dependencies between them, entering resources. Working with calendars.
term paper, added 01/23/2011
Using MS Project to identify the critical path of a project. Tasks transport logistics... Development of a model for the formation of costs and revenues of the project. Calculation of costs associated with the implementation of the database. Creation optimal conditions operator labor.
term paper added 04/21/2013
Structure selection, overview different options creating a new project. Controlling MS Project 2007 startup behavior. Creation of a new project based on a template. List of standard templates. Setting general project parameters, planning parameters.
presentation added 03/15/2014
The concept of a hierarchical structure of work breakdown. Define, view and change the code of the project structure. Types of links between works, editing them using MS Project. Changing the form and parameters of the summary task presentation.
presentation added 03/15/2014
Purpose, creation of a modern information and analytical system. Formation working documentation in the Microsoft Project environment. Calculation of the duration of the project using the Monte Carlo method. Modeling communication types. Designing user interfaces.
term paper, added 12/16/2014
Estimation of the project cost using the Microsoft Project function on the example of creating a technical project of the complex of tasks "Quality management of products and services". Purpose and conditions of application of the program, its characteristics and user manual.
Update:
The features described in this article are now an industry supplement to MS Project for construction organizations.
We adhere to the point of view that it is not necessary to implement MS Project Server for project management in general construction contractors. But along with this bold statement, an alternative must be presented. We consider the desktop MS Project, which runs the scheduler, to be a very useful tool for construction companies, and instead of the server, we suggest using a super-desktop based on Project containing industry-specific add-ons. Now the questions to be answered are: How can you make Project more effective in the construction industry? How should you expand its capabilities?
A powerful desktop application for managing construction projects, Spider Project, has been on the market for a long time, and you need to take into account its main disadvantages when creating a competing solution. First of all, this is the complexity and inconvenience of the interface, the overload of the program with features that are rarely used in practice. The application is not intuitively understandable for novice managers. It is also worth noting the weak communication capabilities of Spider.
If you finish building MS Project with Spider functions, it is not at all necessary to implement all the bells and whistles. Better to use the popular "20/80" rule of thumb, according to which 20% of a program's functions will give us 80% of the effect of using it. In addition, an attempt to implement all the best project management methodologies on the fly can lead to the failure of the entire implementation. Control over management processes is acquired gradually.
What will we add to MS Project for construction project management
Let's briefly describe the composition of our solution for general construction contractors based on MS Project.
Interaction with contractors
To exchange project information with contractors and subcontractors, we suggest using MS Excel files. They can be exported from the project and imported into the project both using the built-in export and import wizards in MS Project, and using our PlanBridge communication add-in.
Excel exchange documents can be sent by e-mail, but it is even more convenient to use cloud storage SkyDrive documents to be shared with contractors. It allows not only storing data exchange documents, but also linking other project-related documentation to them.
Resource calculations module
The most popular addition to the resource capabilities of Project builders is planning and accounting for physical volumes. It should be possible to appoint nat. volume per task as a normal resource, after which it is detailed according to certain standards, and due to this, the scheduler receives calendar plan containing resources depending on physical. volumes. Physical standards volumes are stored in directories, from where they can be used many times.
This is partly a repetition of the functions of the estimated programs, but they have much more meager capabilities. scheduling... However, the capability is needed through the popular ARPS format. Since the Soviet Norms of expenditure of material resources and labor (SNiP 5.01.01 - SNiP 5.01.17) have long lost their relevance, estimates are the main source of data for the initial formation of reference books of standards.
Job block templates
In addition to physical. volumes, when planning construction projects, it is convenient to reuse entire blocks of work, for example, such as stages technological process... Work block templates are MS Project files previously developed by the company and assembled into a library.
A project built from blocks refers to the library and links blocks from it to upper-level tasks. The system should be able to scale the duration of the block of work used in the project, while maintaining its labor costs, costs, and physical. volumes. This achieves compliance with the target date, and thereby realizes top-down planning.
Construction projects are very diverse, and therefore there is no guarantee that the described MS Project add-ons will be used in all construction companies... First of all, they should be implemented in industries where regulation is widespread, and projects are often typical and the volume of work on them is large. For example, this is road construction and construction of infrastructure facilities. But even if the organization found a use for only one of the components of our solution, it will benefit its projects.
Digital planning tools are a perennial topic of controversy. Not all software is equally useful, but the required software can be difficult. MS Project is just that.
Meet Microsoft Project, sophisticated project management software. Helps the manager in current tasks: plan, allocate resources, analyze the complexity of the project. Automatically makes reports and calculates estimates. If you understand it, it can become irreplaceable.
The program is similar to MS Excel, but contains more functions. Visually it looks like this: on the left side there is a table with data: tasks, time and labor costs. On the right are charts, such as a Gantt chart.
How to make plans in MS Project
Create a new project
The program has different templates, for example, Simple Project Plan, New Product Launch or Agile Project Management. Choose a suitable structure or open a New Project.

New project before data entry
Define tasks
They depend on the type of project. First, write down the general steps, and then divide into specific ones. For example, we will create a simple online store. The stages can be as follows: analytics, home page, product catalog, integration with payment and delivery services, personal account.
In the top pane, select the Task block and find the Summary task button. Use it to create all the general stages. Add details later.

General steps the project
Specify tasks
Think about which ones will go into each stage. Add them to the table using the + Task button. Or double-click on the empty column where you want to insert the task. This window will open.

Task details
In this window, edit the details of the task. For example, name or duration, if already known. When there is no exact data, check the box in the Preliminary estimate. The approximate duration of the task will be displayed in the table with a question mark.

About the Requirements Aggregation Task
Add tasks to the table. Our online store will have the following.
For analytics:
- aggregation of requirements;
- prototyping;
- technical task;
- database design.
For the home page and product catalog:
- design;
- layout;
- development.
For payment and delivery:
- connecting PayPal;
- connection of CDEK.
For personal account:
- authorization;
- registration;
- password recovery;
- bonus system;
- pending orders;
- personalization;
- integration with Axapta.

Decomposition of tasks
Determine the duration of tasks
To do this, to the left of each of them there is a column in which you can select the type of planning. At automatic program determines the duration of the task, if you manually change the dates yourself. Choose the right one.

Duration of tasks
Establish dependencies between tasks
While you enter the initial data about the project in the table on the left, a Gantt chart is automatically built on the right. For it to be displayed correctly, set the dependencies between the tasks. For example, to make a prototype of an online store, you first need to collect the requirements. That is, the third task of the list depends on the second. All tasks are numbered automatically by the program as they appear.
Add dependencies in the graph Predecessors... It will turn out like this.

Dependencies between tasks
Allocate resources
Now hand out the tasks to the team and reflect this in the table. There are five different tabs in the bottom right corner. Gantt Chart (you will spend most of your time in it), Task Usage, Visual Resource Optimizer, Resource Sheet, and Report.
Select Resource Sheet. In it, enter all the employees who work on the project, their rates per hour of work and the schedule. Indicate titles or names if several employees in the team occupy the same position. This way you can avoid confusion.
Let's say that the team has one employee for each position. Here's what happens.

Resource sheet.
Return to the Gantt Chart tab. Find the Resources column and put the job titles in front of each task.
In a project to create an online store, the analyst is responsible for all analytical tasks, the designer is responsible for the design, the layout designer is responsible for the newsletter, the programmer is responsible for the development.

Tasks with assigned resources
If a resource is overloaded, the program will show it: red men will appear to the left of the task.

Overloaded resources
Eliminate the overload problem
To do this, go to the Visual Resource Optimizer. It looks like this.
Templates are meant to standardize project files internally project team or organization. There are two types of templates in MS Project: Global.mpt file and file templates. The global file stores the basic settings applied to new projects. File templates are standard projects kept for future reference for standardization purposes.
Global file
A global file cannot be opened for editing like a regular file - changes are made to it through the Organizer (we discussed the work with the Organizer in the section "Removing and moving views and their components"). Changes to general settings are made by clicking the Set as Default button on the various tabs of the Options dialog box.
The disk contains two copies of the global file Global.mpt - one in the MS Project installation folder, and the other in the user's working folder. (You can locate these files by using the Find Files command in Windows.) The installation folder contains the original template file that comes with the program, and the working folder contains a copy of it, which includes all the customizations you made while working with the program. It is this file that the program uses when working.
If you delete a global file from the user's working folder, then when MS Project starts, it will automatically place the file from the installation folder into it. Therefore, to revert the template to "initial settings, you can simply delete the work file.
Creating a file template
File templates are created by the user by saving project plans in * .mpt format. Any information can be saved in the template: data on tasks, resources and assignments, view settings, macros, etc. At the same time, when saving a template, unnecessary information from the current plan (for example, data on actual labor costs , which will definitely not be needed when creating new projects). Therefore, when saving a file in the template format, a dialog box appears (Fig. 23.16), in which it is determined which data from the current plan should not be included in the template.
Rice. 23.16. Defining the data to be stored in the template
The dialog box contains checkboxes that, when checked, you define the types of data not included in the template. The Values of all baselines checkbox will remove the project baselines from the future template. By selecting the Actual Values check box, you will remove the current actual values from the saved plan from the template. The Resource Rates checkbox determines whether resource rates are saved in the template. Fixed cost data for tasks can be removed by selecting the Fixed Costs check box, and selecting the Whether tasks have been published to Microsoft Project Server check box will exclude tasks publishing data from the template. server.
Typically, resource rates are included in the template if the same resources will be used in projects that will be scheduled using the template. In addition, it is sometimes useful to transfer data on the fixed costs of tasks, because often the fixed costs of the same tasks in similar projects are the same. In fig. 23.16 we transfer to the template only. data on resource rates.
Create a file based on a template
To create a file based on a template, use the File V New menu command, and then in the task pane on the New Project panel, in the New from template section, select a template based on which create a project plan (fig. 23.17).

Rice. 23.17. Project creation panel
In our case, the list of templates contains the BookProject.mpt file that we created to prepare the accompanying files for this book. Clicking on the name of the template will create a file based on it. In addition, in the list of templates there is an item General Templates, clicking on which will take you to a dialog box with complete list templates available for use when creating a new file (Fig. 23.18).
The template list dialog is divided into two groups: the first tab, General, contains a list of user-created templates and an empty project template. The second tab, Project Templates, presents the templates included with MS Project. By selecting any of them and double-clicking on its icon, you will create a new project based on it.
 What is KTU in the composition of wages: concept, calculation formula
What is KTU in the composition of wages: concept, calculation formula Product deficit and surplus: definition and implications
Product deficit and surplus: definition and implications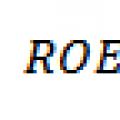 Tutorial: Financial Analysis
Tutorial: Financial Analysis